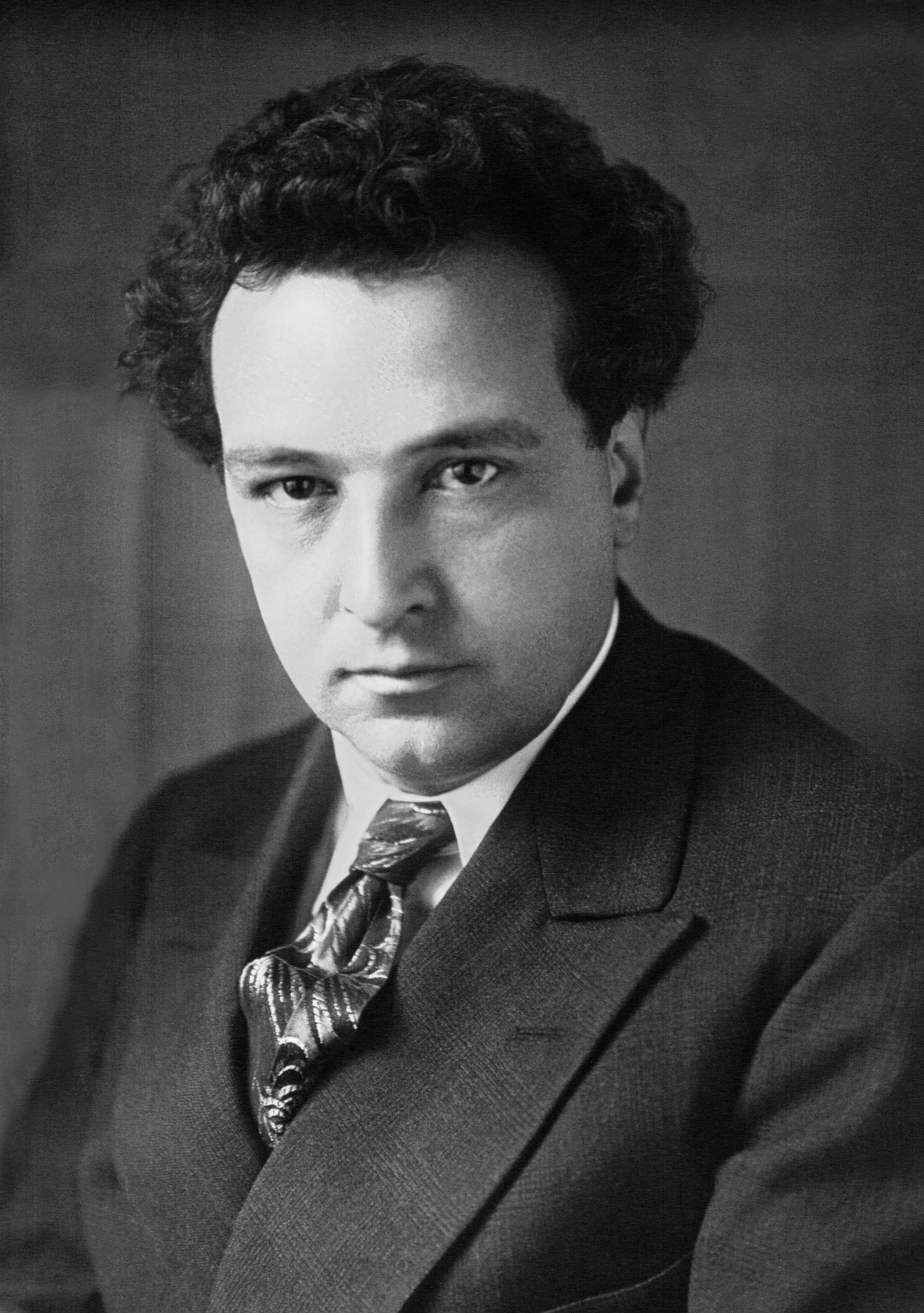|
Lieutenant Kijé (Prokofiev)
Sergei Prokofiev's ''Lieutenant Kijé'' (russian: Поручик Киже, links=no, '' Poruchik Kizhe'') music was originally written to accompany the film of the same name, produced by the Belgoskino film studios in Leningrad in 1933–34 and released in March 1934. It was Prokofiev's first attempt at film music, and his first commission. In the early days of sound cinema, among the various distinguished composers ready to try their hand at film music, Prokofiev was not an obvious choice for the commission. Based in Paris for almost a decade, he had a reputation for experimentation and dissonance, characteristics at odds with the cultural norms of the Soviet Union. By early 1933, however, Prokofiev was anxious to return to his homeland, and saw the film commission as an opportunity to write music in a more popular and accessible style. After the film's successful release, the five-movement ''Kijé'' suite was first performed in December 1934, and quickly became part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor who later worked in the Soviet Union. As the creator of acknowledged masterpieces across numerous music genres, he is regarded as one of the major composers of the 20th century. His works include such widely heard pieces as the March from ''The Love for Three Oranges,'' the suite ''Lieutenant Kijé'', the ballet ''Romeo and Juliet''—from which "Dance of the Knights" is taken—and ''Peter and the Wolf.'' Of the established forms and genres in which he worked, he created—excluding juvenilia—seven completed operas, seven symphonies, eight ballets, five piano concertos, two violin concertos, a cello concerto, a symphony-concerto for cello and orchestra, and nine completed piano sonatas. A graduate of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East through the 1920s and 1930s.{{cite book, last=Mawdsley, first=Evan, title=The Russian Civil War, location=New York, publisher=Pegasus Books, year=2007, isbn=9781681770093, url=https://archive.org/details/russiancivilwar00evan, url-access=registration{{rp, 3,230(5 years, 7 months and 9 days) {{Collapsible list , bullets = yes , title = Peace treaties , Treaty of Brest-LitovskSigned 3 March 1918({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=3, day2=3, year2=1918) , Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)Signed 2 February 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=2, day2=2, year2=1920) , Soviet–Lithuanian Peace TreatySigned 12 July 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Honegger
Arthur Honegger (; 10 March 1892 – 27 November 1955) was a Swiss composer who was born in France and lived a large part of his life in Paris. A member of Les Six, his best known work is probably ''Antigone'', composed between 1924 and 1927 to the French libretto by Jean Cocteau based on the tragedy ''Antigone'' by Sophocles. It premiered on 28 December 1927 at the Théâtre Royal de la Monnaie with sets designed by Pablo Picasso and costumes by Coco Chanel. However, his most frequently performed work is probably the orchestral work ''Pacific 231'', which was inspired by the sound of a steam locomotive. Biography Born Oscar-Arthur Honegger (the first name was never used) to Swiss parents in Le Havre, France, he initially studied harmony with Robert-Charles Martin (to whom he dedicated his first published work and violin in Le Havre. After studying for two years at the Zurich Conservatory, he enrolled in the Paris Conservatoire from 1911 to 1918, studying with both Charl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius Milhaud
Darius Milhaud (; 4 September 1892 – 22 June 1974) was a French composer, conductor, and teacher. He was a member of Les Six—also known as ''The Group of Six''—and one of the most prolific composers of the 20th century. His compositions are influenced by jazz and Brazilian music and make extensive use of polytonality. Milhaud is considered one of the key modernist composers.Reinhold Brinkmann & Christoph Wolff, ''Driven into Paradise: The Musical Migr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortimer Wilson
Mortimer Wilson (August 6, 1876 – January 27, 1932) was an American composer of classical music. He also scored several musical and dramatic films in the 1920s. Wilson was born in Chariton, Iowa in Lucas County, Iowa, Lucas County, a rural area in the south-central portion of the state. He studied organ, violin and composition with Frederick Grant Gleason at the Chicago Music College. He then studied in Leipzig, Germany with Max Reger. Upon return to the USA in 1911 he taught composition at the Atlanta Conservatory and conducted the Atlanta Philharmonic Orchestra. In 1916, he moved to Brenau College in Gainesville, Georgia. In 1918, Wilson took a job as consulting editor for the National Academy of Music in New York City, where he remained until his death at the age of 55. As a composer, Mortimer's style was similar to his contemporaries Henry Kimball Hadley and Frederick Converse, Frederick Shepherd Converse. Today his works are mostly in manuscript. They include five symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Herbert
Victor August Herbert (February 1, 1859 – May 26, 1924) was an American composer, cellist and conductor of English and Irish ancestry and German training. Although Herbert enjoyed important careers as a cello soloist and conductor, he is best known for composing many successful operettas that premiered on Broadway from the 1890s to World War I. He was also prominent among the Tin Pan Alley composers and was later a founder of the American Society of Composers, Authors, and Publishers (ASCAP). A prolific composer, Herbert produced two operas, a cantata, 43 operettas, incidental music to 10 plays, 31 compositions for orchestra, nine band compositions, nine cello compositions, five violin compositions with piano or orchestra, 22 piano compositions and numerous songs, choral compositions and orchestrations of works by other composers, among other music. In the early 1880s, Herbert began a career as a cellist in Vienna and Stuttgart, during which he began to compose orchestral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Carl Breil
Joseph Carl Breil (29 June 1870 – 23 January 1926) was an American lyric tenor, stage director, composer and conductor. He was one of the earliest American composers to compose specific music for motion pictures. His first film was ''Les amours de la reine Élisabeth'' (1912) starring Sarah Bernhardt. He later composed and arranged scores for several other early motion pictures, including such epics as D. W. Griffith's ''The Birth of a Nation'' (1915) and ''Intolerance'' (1916), as well as scoring the preview version of ''The Phantom of the Opera'' (1925), a score that is now lost. His love theme for "Birth of a Nation", titled "The Perfect Song", was published by Chappell & Co. in an arrangement for voice and keyboard. It was later used as the theme for the radio show "Amos and Andy".M. Marks: ''Music and the Silent Film'' (New York, 1997) Life Joseph was the first of four children born to Joseph and Margaret Breil of Pittsburgh. (Joseph Sr., a lawyer, was an immigrant fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Birth Of A Nation
''The Birth of a Nation'', originally called ''The Clansman'', is a 1915 American silent epic drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Lillian Gish. The screenplay is adapted from Thomas Dixon Jr.'s 1905 novel and play ''The Clansman''. Griffith co-wrote the screenplay with Frank E. Woods and produced the film with Harry Aitken. ''The Birth of a Nation'' is a landmark of film history, lauded for its technical virtuosity. It was the first non-serial American 12-reel film ever made. Its plot, part fiction and part history, chronicles the assassination of Abraham Lincoln by John Wilkes Booth and the relationship of two families in the Civil War and Reconstruction eras over the course of several years—the pro-Union ( Northern) Stonemans and the pro- Confederacy ( Southern) Camerons. It was originally shown in two parts separated by an intermission, and it was the first American-made film to have a musical score for an orchestra. It pioneered closeups and fadeout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pump Organ
The pump organ is a type of free-reed organ that generates sound as air flows past a vibrating piece of thin metal in a frame. The piece of metal is called a reed. Specific types of pump organ include the reed organ, harmonium, and melodeon. The idea for the free reed was imported from China through Russia after 1750, and the first Western free-reed instrument was made in 1780 in Denmark. More portable than pipe organs, free-reed organs were widely used in smaller churches and in private homes in the 19th century, but their volume and tonal range were limited. They generally had one or sometimes two manuals, with pedal-boards being rare. The finer pump organs had a wider range of tones, and the cabinets of those intended for churches and affluent homes were often excellent pieces of furniture. Several million free-reed organs and melodeons were made in the US and Canada between the 1850s and the 1920s, some of which were exported. The Cable Company, Estey Organ, and Mason & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silent Film
A silent film is a film with no synchronized recorded sound (or more generally, no audible dialogue). Though silent films convey narrative and emotion visually, various plot elements (such as a setting or era) or key lines of dialogue may, when necessary, be conveyed by the use of title cards. The term "silent film" is something of a misnomer, as these films were almost always accompanied by live sounds. During the silent era that existed from the mid-1890s to the late 1920s, a pianist, theater organist—or even, in large cities, a small orchestra—would often play music to accompany the films. Pianists and organists would play either from sheet music, or improvisation. Sometimes a person would even narrate the inter-title cards for the audience. Though at the time the technology to synchronize sound with the film did not exist, music was seen as an essential part of the viewing experience. "Silent film" is typically used as a historical term to describe an era of cinema pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Art
Soviet art is a form of visual art produced after the October Socialist Revolution of 1917 in Soviet Russia (1917—1922) and the Soviet Union (1922—1991), when the short-lived Russian Republic was overthrown and replaced. This led to an artistic and cultural shift within Russia and the Soviet Union as a whole, including a new focus on Socialist Realism in officially approved art. Soviet art of the post-revolutionary period The consolidation of Soviet art was preceded throughout the 1920s by an era of intense ideological competition between different artistic groupings, with members each striving to ensure their own views would have priority in determining the forms and directions in which Soviet art would develop; seeking to occupy key posts in cultural institutions and to win the favor and support of the authorities. This struggle was made even more bitter by the growing crisis of radical ''leftist'' art. At the turn of the 1930s, many ''avant-garde'' tendencies that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Important Person
A very important person or personage (VIP or V.I.P.) is a person who is accorded special privileges due to their high social status, influence or importance. The term was not common until sometime after World War 2 by RAF pilots. Examples include celebrities, heads of state or heads of government, other politicians, major employers, high rollers, high-level corporate officers, bankers, economists, physicians, clergy, military personnel, Crime bosses, wealthy individuals, or any other socially notable person who receives special treatment for any reason. The special treatment usually involves separation from common people, and a higher level of comfort or service. In some cases, such as with ticket Ticket or tickets may refer to: Slips of paper * Lottery ticket * Parking ticket, a ticket confirming that the parking fee was paid (and the time of the parking start) * Toll ticket, a slip of paper used to indicate where vehicles entered a tol ...s, VIP may be used as a title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |