|
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is thick leathery skin with exaggerated skin markings caused by sudden itching and excessive rubbing and scratching. It generally results in small bumps, patches, scratch marks and scale. It typically affects the neck, scalp, upper eyelids, ears, palms, soles, ankles, wrists, genital areas and bottom. It often develops gradually and the scratching becomes a habit. Signs and symptoms People burdened with LSC report pruritus, followed by uncontrollable scratching of the same body region, excessively. Most common sites of LSC are the sides of the neck, the scalp, ankles, vulva, pubis, scrotum, and extensor sides of the forearms. However, due to the stigma associated with chronic scratching, some patients will not admit to chronic rubbing or abrasion. The skin may become thickened and hyperpigmented (lichenified) as a direct result of chronic excoriation. Typically this period of increased scratching is associated with stressors. Causes This is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
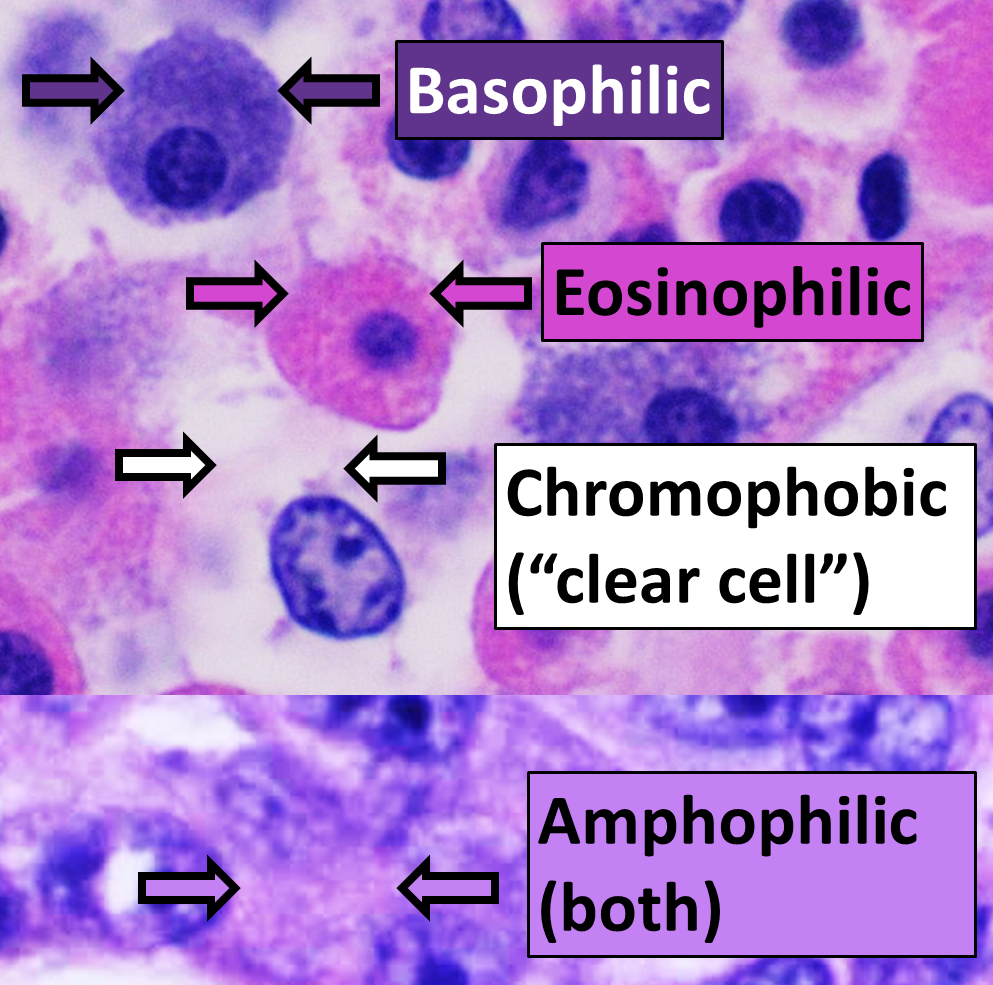
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Depression
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introduced by a group of US clinicians in the mid-1970s, the term was adopted by the American Psychiatric Association for this symptom cluster under mood disorders in the 1980 version of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-III), and has become widely used since. The diagnosis of major depressive disorder is based on the person's reported experiences, behavior reported by relatives or friends, and a mental status examination. There is no laboratory test for the disorder, but testing may be done to rule out physical conditions that can cause similar symptoms. The most common time of onset is in a person's 20s, with females affected about twice as often as males. The course of the disorder varies widely, from one epis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychosomatic
A somatic symptom disorder, formerly known as a somatoform disorder,(2013) Somatic Symptom Disorder Fact Sheet " dsm5.org. Retrieved April 8, 2014. is any mental disorder that manifests as physical symptoms that suggest Physical illness, illness or injury, but cannot be explained fully by a general medical condition or by the direct effect of a substance, and are not attributable to another mental disorder (e.g., panic disorder). Somatic symptom disorders, as a group, are included in a number of diagnostic schemes of mental illness, including the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders''. (Before DSM-5 this disorder was split into ''somatization disorder'' and ''undifferentiated somatoform disorder''.) In people who have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxepin
Doxepin is a medication falling in the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) class used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and insomnia. For label updates seFDA index page for NDA 022036/ref> For hives it is a less preferred alternative to antihistamines. It has a mild to moderate benefit for sleeping problems. It is used as a cream (pharmaceutical), cream for itchiness due to atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus. For label updates seFDA index page for NDA 020126/ref> Common side effects include sleepiness, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, and blurry vision. Serious side effects may include increased risk of suicide in those under the age of 25, mania, and urinary retention. A antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, withdrawal syndrome may occur if the dose is rapidly decreased. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not generally recommended. Doxepin is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). Although how it works for treating depression remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betamethasone
Betamethasone is a steroid medication. It is used for a number of diseases including rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, skin diseases such as dermatitis and psoriasis, allergic conditions such as asthma and angioedema, preterm labor to speed the development of the baby's lungs, Crohn's disease, cancers such as leukemia, and along with fludrocortisone for adrenocortical insufficiency, among others. It can be taken by mouth, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin, typically in cream, lotion, or liquid forms. Serious side effects include an increased risk of infection, muscle weakness, severe allergic reactions, and psychosis. Long-term use may cause adrenal insufficiency. Stopping the medication suddenly following long-term use may be dangerous. The cream commonly results in increased hair growth and skin irritation. Betamethasone belongs to the glucocorticoid class of medication. It is a stereoisomer of dexamethasone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin (dermatitis). It results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thickens over time. While the condition may occur at any age, it typically starts in childhood, with changing severity over the years. In children under one year of age, much of the body may be affected. As children get older, the areas on the insides of the knees and elbows are most commonly affected. In adults, the hands and feet are most commonly affected. Scratching the affected areas worsens the symptoms, and those affected have an increased risk of skin infections. Many people with atopic dermatitis develop hay fever or asthma. The cause is unknown but believed to involve genetics, immune system dysfunction, environmental exposures, and difficulties with the Semipermeable membrane, permeability of the skin. If one identical twin is affected, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopy
Atopy is the tendency to produce an exaggerated immunoglobulin E (IgE) immune response to otherwise harmless substances in the environment. Allergic diseases are clinical manifestations of such inappropriate, atopic responses. Atopy may have a hereditary component, although contact with the allergen or irritant must occur before the hypersensitivity reaction can develop (characteristically after re-exposure). Maternal psychological trauma ''in utero'' may also be a strong indicator for development of atopy. The term ''atopy'' was coined by Arthur F. Coca and Robert Cooke in 1923. Many physicians and scientists use the term "atopy" for any IgE-mediated reaction (even those that are appropriate and proportional to the antigen), but many pediatricians reserve the word "atopy" for a genetically mediated predisposition to an excessive IgE reaction. The term is from Greek ἀτοπία meaning "the state of being out of place", "absurdity". Signs and symptoms Atopic sensitization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat whereas the latter is defined as the emotional response to a real threat. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, somatic complaints, and rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight or flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of future threat including dread. People facing anxiety may withdraw fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Stigma
Social stigma is the disapproval of, or discrimination against, an individual or group based on perceived characteristics that serve to distinguish them from other members of a society. Social stigmas are commonly related to culture, gender, race, socioeconomic class, age, sexual orientation, body image, physical disability, intelligence or lack thereof, and health. Some stigma may be obvious, while others are known as concealable stigmas that must be revealed through disclosure. Stigma can also be against oneself, stemming from negatively viewed personal attributes in a way that can result in a "spoiled identity" (i.e., self-stigma). Description Stigma (plural stigmas or ''stigmata'') is a Greek word that in its origins referred to a type of marking or the tattoo that was cut or burned into the skin of people with criminal records, slaves, or those seen as traitors in order to visibly identify them as supposedly blemished or morally polluted persons. These individuals were to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |