|
Liang Dynasty (other)
Liang dynasty (502–557), also known as Southern Liang, was an imperial dynasty during the Southern and Northern Dynasties period. Liang dynasty may also refer to: * Former Liang (320–376), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Later Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms) (386–403), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Southern Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms) (397–414), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Northern Liang (397–439), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Western Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms) (400–421), one of the Sixteen Kingdoms * Western Liang (555–587), a puppet state during the Northern and Southern dynasties period * Later Liang (Five Dynasties) (907–923), one of the five dynasties that ruled northern China successively during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period See also * Liang (state) (8th century BC – 641 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period * Wei (state) Wei (; ; Old Chinese: *') was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang Dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the Southern Qi dynasty and succeeded by the Chen dynasty. The rump state of Western Liang existed until it was conquered in 587 by the Sui dynasty. Rule During the Liang dynasty, in 547 a Persian embassy paid tribute to the Liang, amber was recorded as originating from Persia by the ''Book of Liang''. In 548, Hou Jing Prince of Henan started a rebellion with Xiao Zhengde the Prince of Linhe, nephew and a former heir of Emperor Wu of Liang and installed Xiao Zhengde as emperor. In 549, Hou sacked Jiankang, deposed and killed Xiao Zhengde, seized the power and put Emperor Wu effectively under house arrest. He dismissed the armies opposed to him in the name of Emperor Wu. In 550 Emperor Wu died, Hou created Emperor Wu's third son Crown Prince G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Liang
The Former Liang (; 320–376) was a dynastic state, one of the Sixteen Kingdoms, in Chinese history. It was founded by the Zhang family of the Han ethnicity. Its territories included present-day Gansu and parts of Ningxia, Shaanxi, Qinghai and Xinjiang. All rulers of the Former Liang remained largely titularly under the court of the Eastern Jin dynasty as the Duke of Xiping except Zhang Zuo who proclaimed himself ''wang'' (prince/king). However, at times the other Former Liang rulers also used the ''wang'' title when imposed on them when they were forced to submit to their powerful neighbour states - initially the Han Zhao, then the Later Zhao, and finally Former Qin. In 327, the Gaochang commandery was created by the Former Liang under Zhang Jun. After this, significant Han settlement occurred in Gaochang, a major, large part of the population becoming Han. In 376, the final ruler of Former Liang Zhang Tianxi surrendered to Former Qin, ending the state. However, in the after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms)
The Later Liang (; 386–403) was a Sovereign state, state of the Sixteen Kingdoms during the Jin Dynasty (266–420) in China. It was founded by the Lü (surname), Lü family of the Di (Wu Hu), Di ethnicity. All rulers of the Later Liang proclaimed themselves "Heavenly Prince" (''Tian Wang''). Rulers of the Later Liang Rulers family tree See also *Di (Wu Hu) *List of past Chinese ethnic groups *Five Barbarians, Wu Hu *Sixteen Kingdoms *Buddhism in China *Kumarajiva *Gansu *Dunhuang *''Memoirs of Eminent Monks'' References {{DEFAULTSORT:Liang Later Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms), Dynasties in Chinese history Former countries in Chinese history 386 establishments 4th-century establishments in China 5th-century disestablishments in China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms)
The Southern Liang (; 397–404, 408–414) was a dynastic state of China listed as one of the Sixteen Kingdoms in Chinese historiography. Members of the ruling Tufa clan were of Xianbei ethnicity and distant relatives of the Tuoba imperial house of the Northern Wei dynasty. According to the ''Book of Jin'', the surname of the ruling house was changed from Tuoba to Tufa because one of the Tufa ancestors was born on a blanket, and in the Xianbei language, "Tufa" meant "blanket." All rulers of the Southern Liang proclaimed themselves ''wang'' (king). In 414 Southern Liang was conquered by the Xianbei-led Western Qin dynasty. Rulers of the Southern Liang The family tree of Southern Liang rulers See also *Dunhuang * Wu Hu *List of past Chinese ethnic groups *Qinghai *Sixteen Kingdoms *Tuoba *Xianbei The Xianbei (; ) were a Proto-Mongolic ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Liang
The Northern Liang (; 397–439) was a dynastic state of the Sixteen Kingdoms in China. It was ruled by the Juqu family of Lushuihu origin (a branch of the Xiongnu). Although Duan Ye of Han ethnicity was initially enthroned as the Northern Liang ruler with support from the Juqu clan, Duan was subsequently overthrown in 401 and Juqu Mengxun was proclaimed monarch. All rulers of the Northern Liang proclaimed themselves "wang" (translatable as either "prince" or "king"). History Most Chinese historians view the Northern Liang as having ended in 439, when its capital Guzang (姑臧) in modern Wuwei, Gansu fell to Northern Wei forces and the Northern Liang ruler Juqu Mujian captured. However, some view his brothers Juqu Wuhui and Juqu Anzhou, who subsequently settled with Northern Liang remnants in Gaochang (高昌) in modern Turpan Prefecture, Xinjiang, as a continuation of the Northern Liang, and thus view the Northern Liang as having ended in 460 when Gaochang fell to Rouran and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms)
The Western Liang (; 400–421) was a Sovereign state, state of the Sixteen Kingdoms in China, one of the "Five Liang" (''Wu Liang'') of this era. Western Liang was founded by the Li (李), Li family of the Han Chinese. The founder of the Tang Dynasty, Li Yuan (Emperor Gaozu of Tang, Emperor Gaozu), traced his patrilineal ancestry to the Western Liang rulers, and traced the ancestry of the Western Liang rulers to Li Guang and Laozi in the paternal line. The Li family of Western Liang were known as the Longxi Li lineage (w:zh:隴西李氏, 隴西李氏).《新唐书·宗室世系表》 All rulers of the Western Liang proclaimed themselves "Chinese nobility#wang, wang". Rulers of the Western Liang Rulers family tree See also *Dunhuang *Han Chinese *Jiuquan *Gansu *Liangzhou District *List of past Chinese ethnic groups *Sixteen Kingdoms *Wuwei, Gansu *Five Barbarians, Wu Hu References {{DEFAULTSORT:Liang Western Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms), 400 establishments 421 dises ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Liang (555–587)
Liang, known in historiography as the Western Liang () or the Later Liang (), was an imperial dynasty of China during the Northern and Southern dynasties era of Chinese history. Throughout its existence, it remained a puppet state of the Western Wei, Northern Zhou and Sui dynasties. The Western Liang dynasty was ruled by members of the same imperial clan as the Liang dynasty. It was located in the middle Yangtze region in today's central Hubei province. The Western Liang's founding emperor, Xiao Cha, was a grandson of the Liang dynasty founder Emperor Wu of Liang. As a result, Western Liang is usually considered a rump state of the Liang dynasty after 557. From 555 to 557 the two states claiming the political orthodoxy of the Liang dynasty existed simultaneously: Xiao Cha ruled from Jiangling, while Xiao Yuanming and Xiao Fangzhi ruled from Jiankang. Before 555, Emperor Yuan of Liang also ruled from Jiangling before he was captured and executed by Xiao Cha and his Western Wei b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
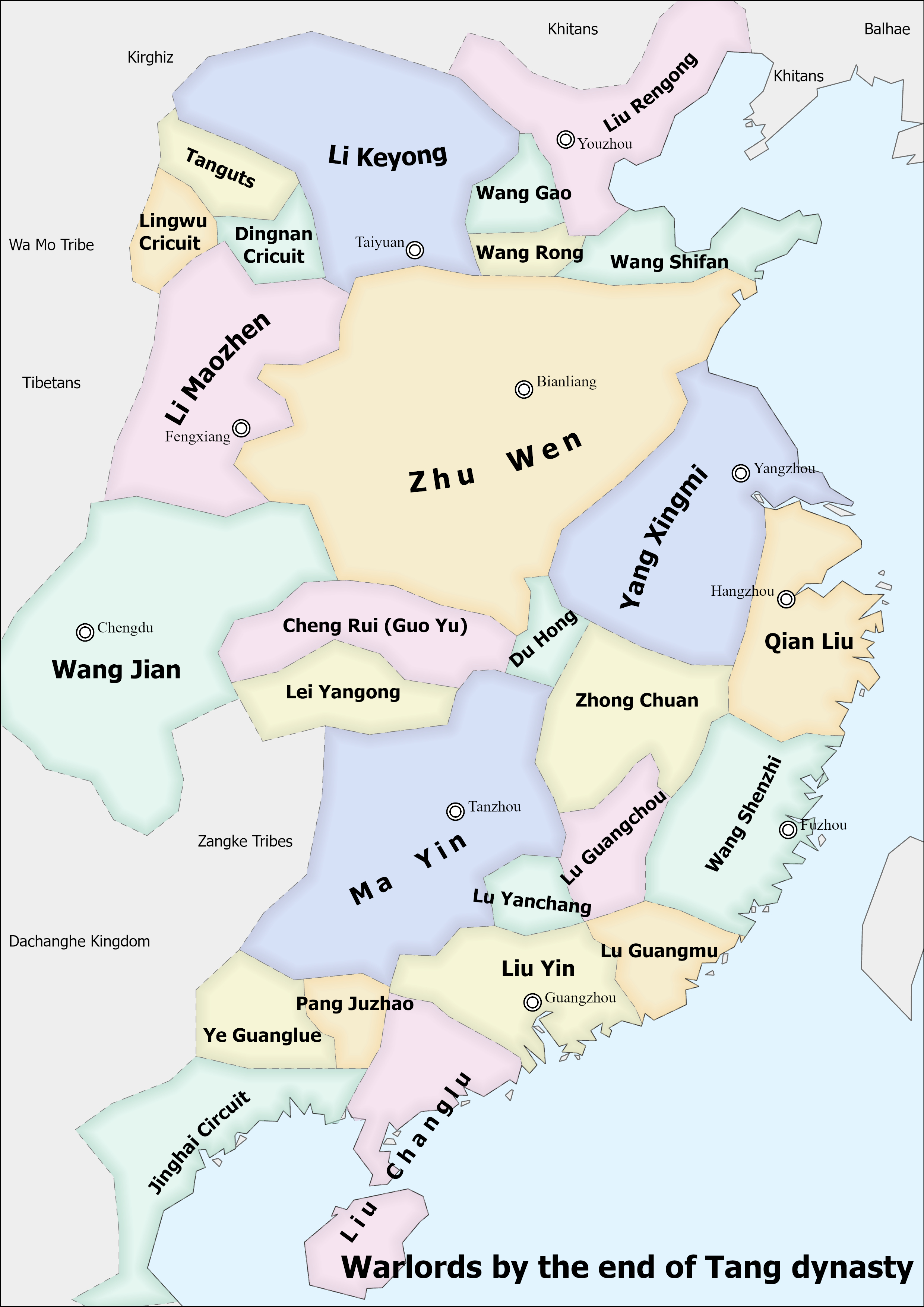
Later Liang (Five Dynasties)
Liang, known in historiography as the Later Liang () (1 June 907 – 19 November 923) or the Zhu Liang (), was an imperial dynasty of China and the first of the Five Dynasties during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Zhu Wen (Emperor Taizu), after he forced the last emperor of the Tang dynasty to abdicate in his favour (and then murdered him). The Later Liang would last until 923 when it was destroyed by the Later Tang dynasty. Formation Zhu Wen initially allied himself as Huang Chao's lieutenant. However, he took Huang's best troops and established his own power base as a warlord in Kaifeng. By 904, he had exerted control over both of the twin Tang Dynasty capitals of Chang'an and Luoyang. Tang emperor Zhaozong was ordered murdered by Zhu in 904 and the last Tang emperor, Ai Di (Emperor Ai of Tang), was deposed three years later. Emperor Ai of Tang was murdered in 908, also ordered by Zhu. Meanwhile, Zhu Wen declared himself emperor of the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Dynasties And Ten Kingdoms
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liang (state)
Liang () was one of the states during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China, bordering the State of Qin and was conquered by Duke Mu of Qin in 641 BCE. The rulers of Liang had the surname Ying (嬴).Yang Bojun, " Zuo Zhuan 17th Year of Xigong", Zhonghua Publishing 1990, p372 The capital of Liang was located south of modern City of Hancheng in Shaanxi. In 703 BC, the rulers of the five states of Western Guo, Rui, Xun (荀國) and Jia (賈國), including the State of Liang, suppressed Duke Wu of Quwo using armed force. In 654 BC, Prince Yiwu from the State of Jin escaped to Liang. The ruler of Liang (梁伯) betrothed his daughter Liang Ying (梁嬴) to Prince Yiwu. In 642 BC, the ruler of Liang wanted to build a new capital but it was seized by the State of Qin after it was completed. In 641 BC, Liang was conquered by the State of Qin. According to the '' Zuo Zhuan'', the Liang people were not able to bear the work given to them by the ruler of Liang so that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wei (state)
Wei (; ; Old Chinese: *') was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It was created from the three-way Partition of Jin, together with Han and Zhao. Its territory lay between the states of Qin and Qi and included parts of modern-day Henan, Hebei, Shanxi, and Shandong. After its capital was moved from Anyi to Daliang (present-day Kaifeng) during the reign of King Hui, Wei was also called Liang (). History Foundation Surviving sources trace the ruling house of Wei to the Zhou royalty: Gao, Duke of Bi (), was a son of King Wen of Zhou. His descendants took their surname, Bi, from his fief. After the destruction of Bi, Bi Wan () escaped to Jin, where he became a courtier of Duke Xian's, accompanying his personal carriage. After a successful military expedition, Bi Wan was granted Wei, from which his own descendants then founded the house of Wei. Spring and Autumn period Jin's political structure was drastically changed after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)