|
Levant Mine
Levant Mine and Beam Engine is a National Trust property at Trewellard, Pendeen, near St Just, Cornwall, England, UK. Its main attraction is that it has the world's only Cornish beam engine still operated by steam on its original site. There is also a visitor centre, a short underground tour, and the South West Coast Path leads to Botallack Mine, via a cliff-top footpath. In 1919 the engine used to transport men between the different levels of the mine failed, leading to the deaths of thirty-one men. Since 2006, the area has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site, Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape. Site The property is on the site of the former Levant Mine, established in 1820 and closed in 1930, where tin and copper ores were raised. The mine reached a depth of about 600 metres. It got the nickname "mine under the sea", because tunnels were driven up to 2.5 km from the cliffs under the sea. The surviving beam engine was built by Harvey's of Hayle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winding Engine
A winding engine is a stationary engine used to control a cable, for example to power a mining hoist at a pit head. Electric hoist controllers have replaced proper winding engines in modern mining, but use electric motors that are also traditionally referred to as ''winding engines''. Early winding engines were hand, or more usually horse powered. The first powered winding engines were stationary steam engines. The demand for winding engines was one factor that drove James Watt to develop his rotative beam engine, with its ability continuously to turn a winding drum, rather than the early reciprocating beam engines that were only useful for working pumps. They differ from most other stationary steam engines in that, like a steam locomotive, they need to be able to stop frequently and also reverse. This requires more complex valve gear and other controls than are needed on engines used in mills or to drive pump A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lelant Engine
Lelant ( kw, Lannanta) is a village in west Cornwall, England, UK. It is on the west side of the Hayle Estuary, about southeast of St Ives and one mile (1.6 km) west of Hayle.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 203 ''Land's End'' The village is part of St Ives civil parish (meaning that it falls within the parish area of St Ives Town Council), the Lelant and Carbis Bay ward on Cornwall Council, and also the St Ives Parliamentary constituency. The birth, marriage, and death registration district is Penzance. Its population at the 2011 census was 3,892 The South West Coast Path, which follows the coast of south west England from Somerset to Dorset passes through Lelant, along the estuary and above Porth Kidney Sands. History The name is derived from the Cornish ''lann'' and ''Anta'', meaning ''church-site of Anta''. The earliest attested spelling is Lananta in about 1170. Nothing is known about Anta, and Lelant parish church is dedicated to St Uny. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II Listed Buildings In Cornwall
Grade most commonly refers to: * Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance * Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage * Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope Grade or grading may also refer to: Music * Grade (music), a formally assessed level of profiency in a musical instrument * Grade (band), punk rock band * Grades (producer), British electronic dance music producer and DJ Science and technology Biology and medicine * Grading (tumors), a measure of the aggressiveness of a tumor in medicine * The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach * Evolutionary grade, a paraphyletic group of organisms Geology * Graded bedding, a description of the variation in grain size through a bed in a sedimentary rock * Metamorphic grade, an indicatation of the degree of metamorphism of rocks * Ore grade, a measure that describes the concentration of a valuable natural material in the surroundin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Mines In Cornwall
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 350 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geevor Tin Mine
Geevor Tin Mine (from kw, Whel an Gever, meaning "mine of the goats"), formerly North Levant Mine is a tin mine in the far west of Cornwall, United Kingdom, between the villages of Pendeen and Trewellard. It was operational between 1911 and 1990 during which time it produced about 50,000 tons of black tin. It is now a museum and heritage centre left as a living history of a working tin mine. The museum is an Anchor Point of ERIH, The European Route of Industrial Heritage. Since 2006, the mine has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site Cornwall and West Devon Mining Landscape. History Tin and copper have been mined from the general area of Geevor since the late 18th century. It was originally a small enterprise known as ''Wheal an Giver'', "a piece of ground occupied by goats". The area was worked under the name of East Levant Mine until 1840 and then as North Levant from 1851 to 1891 when it closed.Stanier, 1998 p.53 During the 1880s as many as 176 workers were employed at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
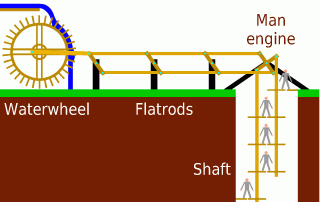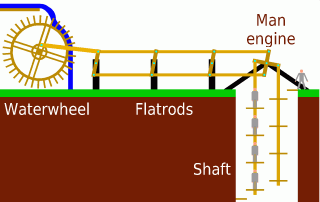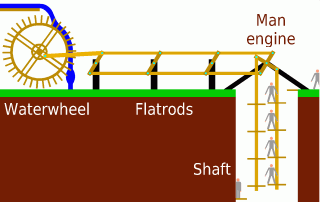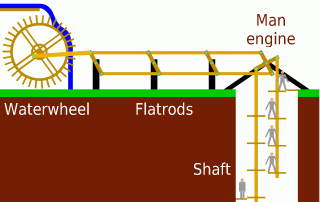
Man Engine
A man engine is a mechanism of reciprocating ladders and stationary platforms installed in Mining, mines to assist the miners' journeys to and from the working levels. It was invented in Germany in the 19th century and was a prominent feature of tin and copper mines in Cornwall until the beginning of the twentieth century. Operation In the Cornish examples the motive power was provided by waterwheels, or one of the mine's steam engines. The steam engine or water wheel would be linked to a series of beams – known as "rods" – fastened together and reaching to the bottom of the mineshaft. These were arranged to offer a reciprocating motion of, typically, twelve to fifteen feet (three to five metres). Small foot platforms were attached to the rods at the same distance apart as the engine stroke and fixed platforms ("sollars") were built onto the shaft walls, spaced to coincide with the top and bottom positions of each of the moving platforms. The moving platforms were often sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcocite
Chalcocite (), copper(I) sulfide (Cu2S), is an important copper ore mineral. It is opaque and dark gray to black, with a metallic luster. It has a hardness of 2.5–3 on the Mohs scale. It is a sulfide with a monoclinic crystal system. The term ''chalcocite'' comes from the alteration of the obsolete name ''chalcosine'', from the Greek ''khalkos'', meaning "copper". It is also known as redruthite, vitreous copper, or copper-glance. Occurrence Chalcocite is sometimes found as a primary vein mineral in hydrothermal veins. However, most chalcocite occurs in the supergene enriched environment below the oxidation zone of copper deposits as a result of the leaching of copper from the oxidized minerals. It is also often found in sedimentary rocks. It has been mined for centuries and is one of the most profitable copper ores. The reasons for this is its high copper content (66.7% atomic ratio and nearly 80% by weight) and the ease at which copper can be separated from sulfur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments. The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called ''flos-ferri'' ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines. Occurrence The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of arago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and stone trade pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Passivation (chemistry), Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly Iridescence, iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most Diamagnetism, diamagnetic element and one of the least Thermal conductivity, thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man Engine
A man engine is a mechanism of reciprocating ladders and stationary platforms installed in Mining, mines to assist the miners' journeys to and from the working levels. It was invented in Germany in the 19th century and was a prominent feature of tin and copper mines in Cornwall until the beginning of the twentieth century. Operation In the Cornish examples the motive power was provided by waterwheels, or one of the mine's steam engines. The steam engine or water wheel would be linked to a series of beams – known as "rods" – fastened together and reaching to the bottom of the mineshaft. These were arranged to offer a reciprocating motion of, typically, twelve to fifteen feet (three to five metres). Small foot platforms were attached to the rods at the same distance apart as the engine stroke and fixed platforms ("sollars") were built onto the shaft walls, spaced to coincide with the top and bottom positions of each of the moving platforms. The moving platforms were often sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |