|
Leptomyxa Ambigua
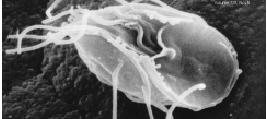
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * '' Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * '' Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * '' Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Australiensis
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * '' Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * '' Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa Genera
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Variabilis
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * ''Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Valladaresi
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * ''Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Neglecta
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * '' Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelomyxa
''Pelomyxa'' is a genus of giant flagellar amoebae, usually 500-800 μm but occasionally up to 5 mm in length, found in anaerobic or microaerobic bottom sediments of stagnant freshwater ponds or slow-moving streams.Chistyakova, L. V., and A. O. Frolov. "Light and electron microscopic study of Pelomyxa stagnalis sp. n.(Archamoebae, pelobiontida)." Cell and Tissue Biology 5.1 (2011): 90-97. The genus was created by R. Greeff, in 1874, with ''Pelomyxa palustris'' as its type species. In the decades following the erection of ''Pelomyxa'', researchers assigned numerous new species to it. However, in the last quarter of the 20th century, investigators reduced the genus to a single species, ''Pelomyxa palustris'', which was understood to be a highly changeable organism with a complex life cycle, whose various phases had been mistaken for separate species. All described species were relegated to the status of synonyms, or moved to the unrelated genus ''Chaos''. Since 2004, four new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Fragilis
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * ''Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Flabellata
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * ''Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * '' Leptomyxa flabellata'' * ''L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Arborea
''Leptomyxa'' is a free-living genus of lobose naked multinucleate amoebae in the order Leptomyxida that inhabits freshwater, soil and mosses. It is very closely related to the genus ''Rhizamoeba'', and some species have been moved between the two genera due to molecular data. Description Members of this genus have loboreticulopodia: wide and smooth cytoplasmic projections (like lobopodia) that can also connect to each other to form a net-like structure (like reticulopodia). They differ from ''Rhizamoeba'' not only on a molecular level but also in their morphology: each ''Leptomyxa'' cell has usually up to hundreds of nuclei, while ''Rhizamoeba'' cells contain between one and up to dozens of nuclei, and the organization of the cell is plasmodial among ''Leptomyxa'' while monopodial among ''Rhizamoeba''. Classification As of 2017, nine species belong to this genus. * ''Leptomyxa ambigua'' * '' Leptomyxa arborea'' * ''Leptomyxa australiensis'' * ''Leptomyxa flabellata'' * ''Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptomyxa Reticulata
''Leptomyxa reticulata'' is a species of Amoebozoa. A relationship to ''Rhizamoeba'' has been suggested. See also * Leptomyxida Leptomyxida is an order of Amoebozoa. It includes species such as '' Flabellula citata'', '' Paraflabellula hoguae'', '' Paraflabellula reniformis'', '' Rhizamoeba saxonica'' and '' Leptomyxa reticulata''. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Leptomyxida ... References Tubulinea {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(2).jpg)