|
Lenses For SLR And DSLR Cameras
This article is about photographic lenses for single-lens reflex film cameras (SLRs) and digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs). Emphasis is on modern lenses for 35 mm film SLRs and for DSLRs with sensor sizes less than or equal to 35 mm (" full-frame"). Interchangeable lenses Most SLR and DSLR cameras provide the option of changing the lens. This enables the use of lens that are best suited for the current photographic need, and allows the attachment of specialized lenses. Film SLR cameras have existed since the late 1950s, and over the years a very large number of different lenses have been produced, both by camera manufacturers (who typically only make lenses intended for their own camera bodies) and by third-party optics companies who may make lenses for several different camera lines. DSLRs became affordable around the mid-1990s, and have become extremely popular in recent years. Some manufacturers, for example Minolta, Canon and Nikon, chose to make thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (optics)
In optics, a diaphragm is a thin opaque structure with an opening (aperture) at its center. The role of the diaphragm is to ''stop'' the passage of light, except for the light passing through the ''aperture''. Thus it is also called a stop (an aperture stop, if it limits the brightness of light reaching the focal plane, or a field stop or flare stop for other uses of diaphragms in lenses). The diaphragm is placed in the light path of a lens or objective, and the size of the aperture regulates the amount of light that passes through the lens. The centre of the diaphragm's aperture coincides with the optical axis of the lens system. Most modern cameras use a type of adjustable diaphragm known as an iris diaphragm, and often referred to simply as an iris. See the articles on aperture and f-number for the photographic effect and system of quantification of varying the opening in the diaphragm. Iris diaphragms versus other types A natural optical system that has a diaphragm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon EOS 400D
The EOS 400D, called Digital Rebel XTi in North America and EOS Kiss Digital X in Japan, is an entry-level digital single-lens reflex camera introduced by Canon on 24 August 2006. Details It is the successor of the Canon EOS 350D, and upgrades to a 10.1 megapixel CMOS sensor, a larger continuous shooting buffer, an integrated image sensor vibrating cleaning system (first used in a Canon EOS DSLR), a more precise nine-point autofocus system from the EOS 30D, improved grip, and a bigger LCD with 230,000 pixels and a larger viewing angle which replaces the top status screen. The 400D uses the DIGIC II image processor, as is used in the 350D. The 400D file numbering system holds 9,999 pictures, as opposed to 100 photos in one folder with the 350D. Support for the Media Transfer Protocol (MTP) USB protocol is available since version 1.1.0. The latest firmware available is version 1.1.1. It was succeeded by the Canon EOS 450D (Rebel XSi in North America) which was announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon EOS 5D
The Canon EOS 5D is a 12.8 megapixel digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) camera body produced by Canon. The EOS 5D was announced by Canon on 22 August 2005, and at the time was priced above the EOS 20D but below the EOS-1D Mark II and EOS-1Ds Mark II in Canon's EOS digital SLR series. The camera accepts EF lens mount lenses. The EOS 5D is notable for being the first full-frame DSLR camera with a standard body size (as opposed to the taller, double-grip "professional" camera body style). It is also notable for its price, suggested at US$3299 without lens, which set a significant new low price point for full-frame DSLRs; its only full-frame competition at the time was the Canon 1Ds Mark II, which cost more than twice as much. On 17 September 2008, Canon announced the camera's successor, the Canon EOS 5D Mark II. Features Sensor and image processing The 5D has a DIGIC II processor and a 35.8 x 23.9 mm full-frame CMOS sensor with 13.3 million pixels (12.7 megapixel ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APS-C
Advanced Photo System type-C (APS-C) is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System film negative in its C ("Classic") format, of 25.1×16.7 mm, an aspect ratio of 3:2 and Ø 31.15 mm field diameter. It is therefore also equivalent in size to the Super 35 motion picture film format, which has the dimensions of 24.89 mm × 18.66 mm (0.980 in × 0.735 in) and Ø 31.11 mm field diameter. Sensors approximating these dimensions are used in many digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and a few large-sensor live-preview digital cameras. APS-C size sensors are also used in a few digital rangefinders. Such sensors exist in many different variants depending on the manufacturer and camera model. All APS-C variants are considerably smaller than 35 mm standard film which measures 36×24 mm. Because of this, devices with APS-C sensors are known as "cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sony α100
Sony α100 (DSLR-A100) is the first digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) marketed by Sony in 2006. It is the successor to the previous Konica Minolta DSLR models (primarily the Maxxum/Dynax 5D and 7D) through Sony's purchase of the Konica Minolta camera division. The α100 retains a similar body design and claimed improvements on Konica Minolta's Anti-Shake sensor-shifting image stabilization feature, renamed Super SteadyShot. It uses a 10.2 megapixel APS-C sized CCD sensor. Another notable feature inherited from Konica Minolta is Eyestart, which provides for automatic autofocus activation by detecting the presence of the photographer's eye on the viewfinder, thus quickening the camera's response. Another notable feature is an automatically vibrating CCD to remove dust each time the camera is shut off. The α100 shipped from Sony and resellers by the end of July 2006 with MSRP prices of US$1000 with the 18–70 mm 3.5–f/5.6 kit lens and US$900 for the body only. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikon D3
The Nikon D3 is a 12.0-megapixel professional-grade full frame (35 mm) digital single lens reflex camera (DSLR) announced by the Nikon Corporation on 23 August 2007 along with the Nikon D300 DX format camera. It was Nikon's first full-frame DSLR. The D3, along with the Nikon D3X, was a flagship model in Nikon's line of DSLRs, superseding the D2Hs and D2Xs. It was replaced by the D3S as Nikon's flagship DSLR. The D3, D3X, D3S, D4, D4s, D5, D6, D700, D800, D800Е and Df are the only Nikon FX format DSLRs manufactured in Japan. The D3S was replaced by the D4 in 2012. Technology The D3 features a full-frame 35 mm equivalent CMOS image sensor measuring 23.9 mm × 36.0 mm. This sensor is larger than the DX format sensors of all previous Nikon DSLRs, and Nikon has coined the term " FX format" to describe it. While the D3's sensor has larger pixels than some previous DX sensors, some previous DX sensors have larger pixels. The design of the D3's CMOS sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephoto Lens
A telephoto lens, in photography and cinematography, is a specific type of a long-focus lens in which the physical length of the lens is shorter than the focal length. This is achieved by incorporating a special lens group known as a ''telephoto group'' that extends the light path to create a long-focus lens in a much shorter overall design. The angle of view and other effects of long-focus lenses are the same for telephoto lenses of the same specified focal length. Long-focal-length lenses are often informally referred to as ''telephoto lenses'', although this is technically incorrect: a telephoto lens specifically incorporates the telephoto group. Telephoto lenses are sometimes broken into the further sub-types of short telephoto (85–135 mm in 35 mm film format), medium telephoto: (135–300 mm in 35 mm film format) and super telephoto (over 300 mm in 35 mm film format) . Construction In contrast to a telephoto lens, for any given focal lengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide-angle Lens
In photography and cinematography, a wide-angle lens refers to a lens whose focal length is substantially smaller than the focal length of a normal lens for a given film plane. This type of lens allows more of the scene to be included in the photograph, which is useful in architectural, interior and landscape photography where the photographer may not be able to move farther from the scene to photograph it. Another use is where the photographer wishes to emphasise the difference in size or distance between objects in the foreground and the background; nearby objects appear very large and objects at a moderate distance appear small and far away. This exaggeration of relative size can be used to make foreground objects more prominent and striking, while capturing expansive backgrounds. A wide angle lens is also one that projects a substantially larger image circle than would be typical for a standard design lens of the same focal length. This large image circle enables either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor Format
In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor. The image sensor format of a digital camera determines the angle of view of a particular lens when used with a particular sensor. Because the image sensors in many digital cameras are smaller than the 24 mm × 36 mm image area of full-frame 35 mm cameras, a lens of a given focal length gives a narrower field of view in such cameras. Sensor size is often expressed as optical format in inches. Other measures are also used; see table of sensor formats and sizes below. Lenses produced for 35 mm film cameras may mount well on the digital bodies, but the larger image circle of the 35 mm system lens allows unwanted light into the camera body, and the smaller size of the image sensor compared to 35 mm film format results in cropping of the image. This latter effect is known as field-of-view crop. The format size ratio (relative to the 35 mm film format) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Format
A film format is a technical definition of a set of standard characteristics regarding image capture on photographic film for still images or film stock for filmmaking. It can also apply to projected film, either slides or movies. The primary characteristic of a film format is its size and shape. In the case of motion picture A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ... film, the format sometimes includes audio parameters. Other characteristics usually include the film gauge, pulldown method, lens anamorphosis (or lack thereof), and film gate or projector aperture dimensions, all of which need to be defined for photography as well as projection, as they may differ. Motion picture film formats Digital camera formats Photographic film formats See also * Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
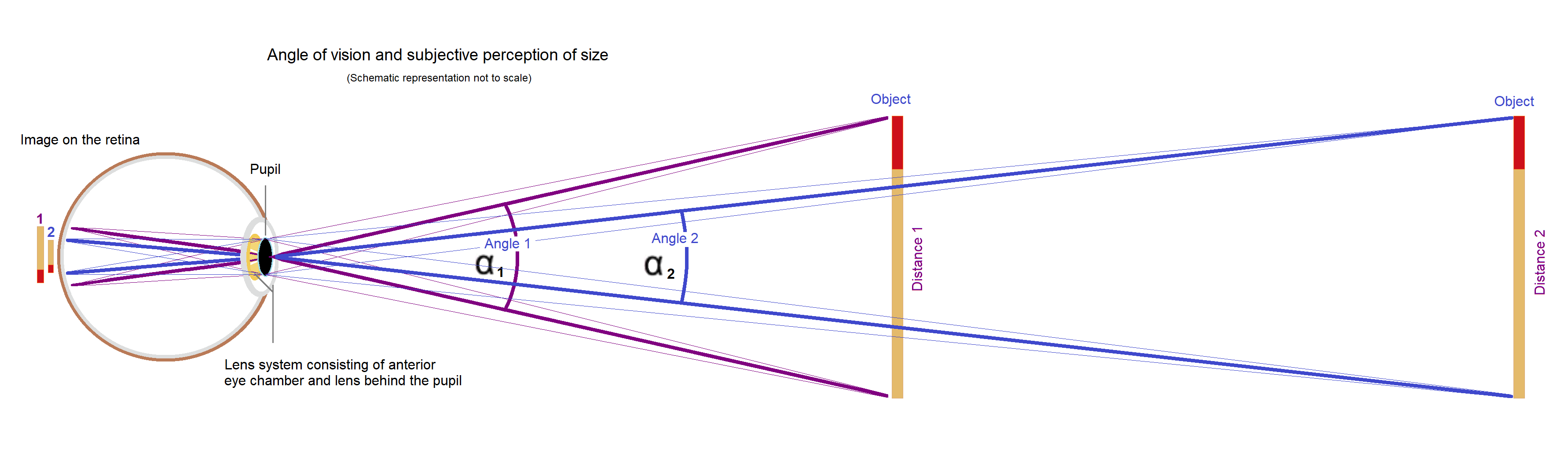
Angle Of View
The angle of view is the decisive variable for the visual perception of the size or projection of the size of an object. Angle of view and perception of size The perceived size of an object depends on the size of the image projected onto the retina. The size of the image depends on the angle of vision. A near and a far object can appear the same size if their edges produce the same angle of vision. With an optical device such as glasses or binoculars, microscope and telescope the angle of vision can be widened so that the object appears larger, which is favourable for the resolving power of the eye (see visual angle). Angle of view in photography In photography, angle of view (AOV) describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view. It is important to distinguish the angle of view from the angle of coverage, which describes the angle range that a lens can image. Typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |