|
Lehmer Sieve
Lehmer sieves are mechanical devices that implement sieves in number theory. Lehmer sieves are named for Derrick Norman Lehmer and his son Derrick Henry Lehmer. The father was a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Berkeley at the time, and his son followed in his footsteps as a number theorist and professor at Berkeley. A sieve in general is intended to find the numbers which are remainders when a set of numbers are divided by a second set. Generally, they are used in finding solutions of Diophantine equations or to factor numbers. A Lehmer sieve will signal that such solutions are found in a variety of ways depending on the particular construction. Construction The first Lehmer sieve in 1926 was made using bicycle chains of varying length, with rods at appropriate points in the chains. As the chains turned, the rods would close electrical switches, and when all the switches were closed simultaneously, creating a complete electrical circuit, a solution had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lehmer Sieve
Lehmer sieves are mechanical devices that implement sieves in number theory. Lehmer sieves are named for Derrick Norman Lehmer and his son Derrick Henry Lehmer. The father was a professor of mathematics at the University of California, Berkeley at the time, and his son followed in his footsteps as a number theorist and professor at Berkeley. A sieve in general is intended to find the numbers which are remainders when a set of numbers are divided by a second set. Generally, they are used in finding solutions of Diophantine equations or to factor numbers. A Lehmer sieve will signal that such solutions are found in a variety of ways depending on the particular construction. Construction The first Lehmer sieve in 1926 was made using bicycle chains of varying length, with rods at appropriate points in the chains. As the chains turned, the rods would close electrical switches, and when all the switches were closed simultaneously, creating a complete electrical circuit, a solution had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century Of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), celebrated the city's centennial. The theme of the fair was technological innovation, and its motto was "Science Finds, Industry Applies, Man Adapts", trumpeting the message that science and American life were wedded. Its architectural symbol was the Sky Ride, a transporter bridge perpendicular to the shore on which one could ride from one side of the fair to the other. One description of the fair noted that the world, "then still mired in the malaise of the Great Depression, could glimpse a happier not-too-distant future, all driven by innovation in science and technology." Fair visitors saw the latest wonders in rail travel, automobiles, architecture and even cigarette-smoking robots. The exposition "emphasized technology an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Computing Hardware
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans. The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a voltage). Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor technology and then the integrated circuit chip led to a series of breakthroughs, starting with transistor computers and then integrated circuit computers, causing digital computers to largely replace analog computers. Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Monthly
''The American Mathematical Monthly'' is a mathematical journal founded by Benjamin Finkel in 1894. It is published ten times each year by Taylor & Francis for the Mathematical Association of America. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is an expository journal intended for a wide audience of mathematicians, from undergraduate students to research professionals. Articles are chosen on the basis of their broad interest and reviewed and edited for quality of exposition as well as content. In this the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' fulfills a different role from that of typical mathematical research journals. The ''American Mathematical Monthly'' is the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to records on JSTOR. Tables of contents with article abstracts from 1997–2010 are availablonline The MAA gives the Lester R. Ford Awards annually to "authors of articles of expository excellence" published in the ''American Mathematical Monthly''. Editors *2022– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scripta Mathematica
''Scripta Mathematica'' was a quarterly journal published by Yeshiva University devoted to the philosophy, history, and expository treatment of mathematics. It was said to be, at its time, "the only mathematical magazine in the world edited by specialists for laymen.". The journal was established in 1932 under the editorship of Jekuthiel Ginsburg, a professor of mathematics at Yeshiva University, and its first issue appeared in 1933 at a subscription price of three dollars per year. It ceased publication in 1973. Notable papers published in ''Scripta Mathematica'' included work by Nobelist Percy Williams Bridgman concerning the implications for physics of set-theoretic paradoxes, and Hermann Weyl's obituary of Emmy Noether Amalie Emmy NoetherEmmy is the ''Rufname'', the second of two official given names, intended for daily use. Cf. for example the résumé submitted by Noether to Erlangen University in 1907 (Erlangen University archive, ''Promotionsakt Emmy Noethe .... Some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
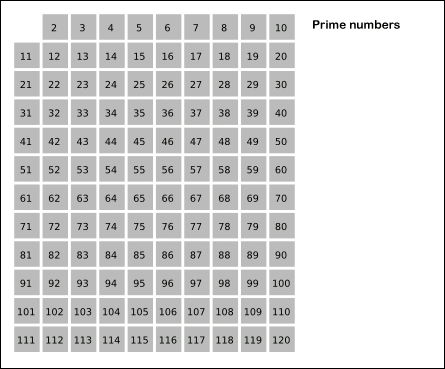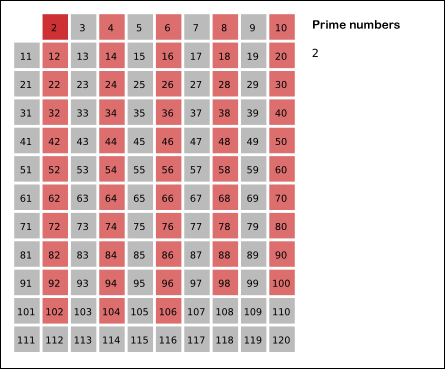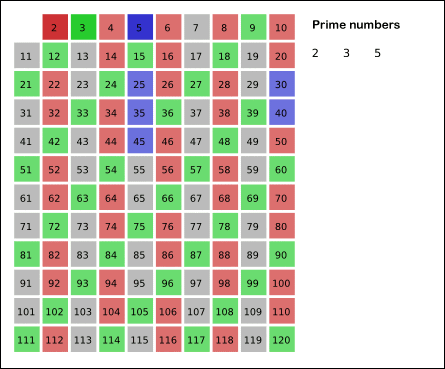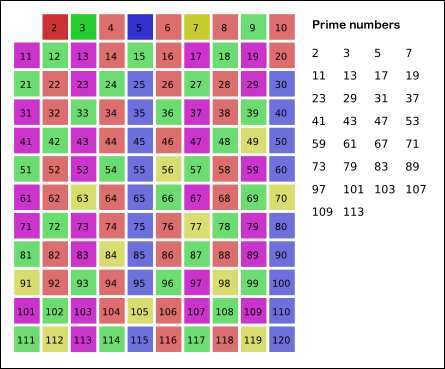
Sieve Of Eratosthenes
In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It does so by iteratively marking as composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime, starting with the first prime number, 2. The multiples of a given prime are generated as a sequence of numbers starting from that prime, with constant difference between them that is equal to that prime.Horsley, Rev. Samuel, F. R. S., "' or, The Sieve of Eratosthenes. Being an account of his method of finding all the Prime Numbers,''Philosophical Transactions'' (1683–1775), Vol. 62. (1772), pp. 327–347 This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime. Once all the multiples of each discovered prime have been marked as composites, the remaining unmarked numbers are primes. The earliest known reference to the sieve ( grc, κόσκινον Ἐρατοσθένους, ''kóskinon Erat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work. At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer History Museum
The Computer History Museum (CHM) is a museum of computer history, located in Mountain View, California. The museum presents stories and artifacts of Silicon Valley and the information age, and explores the computing revolution and its impact on society. History The museum's origins date to 1968 when Gordon Bell began a quest for a historical collection and, at that same time, others were looking to preserve the Whirlwind computer. The resulting ''Museum Project'' had its first exhibit in 1975, located in a converted coat closet in a DEC lobby. In 1978, the museum, now ''The Digital Computer Museum'' (TDCM), moved to a larger DEC lobby in Marlborough, Massachusetts. Maurice Wilkes presented the first lecture at TDCM in 1979 – the presentation of such lectures has continued to the present time. TDCM incorporated as '' The Computer Museum'' (TCM) in 1982. In 1984, TCM moved to Boston, locating on Museum Wharf. In 1996/1997, the TCM History Center (TCMHC) was established; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16 Mm Film
16 mm film is a historically popular and economical gauge of film. 16 mm refers to the width of the film (about inch); other common film gauges include 8 and 35 mm. It is generally used for non-theatrical (e.g., industrial, educational, televisual) film-making, or for low-budget motion pictures. It also existed as a popular amateur or home movie-making format for several decades, alongside 8 mm film and later Super 8 film. Eastman Kodak released the first 16 mm "outfit" in 1923, consisting of a camera, projector, tripod, screen and splicer, for US$335 (). RCA-Victor introduced a 16 mm sound movie projector in 1932, and developed an optical sound-on-film 16 mm camera, released in 1935. History Eastman Kodak introduced 16 mm film in 1923, as a less expensive alternative to 35 mm film for amateurs. The same year the Victor Animatograph Corporation started producing their own 16 mm cameras and projectors. During the 1920s, the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will , image_map = , map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = United States , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = Counties , subdivision_name1 = Illinois , subdivision_name2 = Cook and DuPage , established_title = Settled , established_date = , established_title2 = Incorporated (city) , established_date2 = , founder = Jean Baptiste Point du Sable , government_type = Mayor–council , governing_body = Chicago City Council , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Lori Lightfoot ( D) , leader_title1 = City Clerk , leader_name1 = Anna Valencia ( D) , unit_pref = Imperial , area_footnotes = , area_tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response. A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

