|
Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the standard service rifle of the British Armed Forces from its official adoption in 1895 until 1957. A redesign of the Lee–Metford (adopted by the British Army in 1888), the Lee–Enfield superseded it and the earlier Martini–Henry and Martini–Enfield rifles. It featured a ten-round box magazine which was loaded with the .303 British cartridge manually from the top, either one round at a time or by means of five-round chargers. The Lee–Enfield was the standard-issue weapon to rifle companies of the British Army, colonial armies (such as India and parts of Africa), and other Commonwealth nations in both the First and Second World Wars (such as Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and Canada). Although officially replaced in the United Kingdom with the L1A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bolt Action
Bolt action is a type of manual firearm action that is operated by ''directly'' manipulating the turn-bolt via a bolt handle, most commonly placed on the right-hand side of the firearm (as most users are right-handed). The majority of bolt-action firearms are rifles, but there are also some variants of shotguns and handguns that are bolt-action. Bolt action firearms are generally repeating firearms, but many single-shot designs are available particularly in shooting sports where single-shot firearms are mandated, such as most Olympic and ISSF rifle disciplines. From the late 19th century all the way through both World Wars, bolt action rifles were the standard infantry service weapons for most of the world's military forces, with the exception of the United States Armed Forces, who used the M1 Garand Semi-automatic rifle. In modern military and law enforcement after the Second World War, bolt-action firearms have been largely replaced by semi-automatic and selec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rifle
A rifle is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a gun barrel, barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles are used in warfare, law enforcement, hunting and shooting sports, target shooting sports. The invention of rifling separated such firearms from the earlier smoothbore weapons (e.g., arquebuses, muskets, and other long guns), greatly elevating their accuracy and general effectiveness. The raised areas of a barrel's rifling are called ''lands''; they make contact with and exert torque on the projectile as it moves down the bore, imparting a spin. When the projectile leaves the barrel, this spin persists and lends gyroscopic stability to the projectile due to conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, also known as the First Arab–Israeli War, followed the 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war in Mandatory Palestine as the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. The civil war became a war of separate states with the Israeli Declaration of Independence on 14 May 1948, the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight, and the entry of a Arab League, military coalition of Arab states into the territory of Mandatory Palestine the following morning. The war formally ended with the 1949 Armistice Agreements which established the Green Line (Israel), Green Line. Since the 1917 Balfour Declaration and the 1920 creation of the British Mandate of Palestine, and in the context of Zionism and the Aliyah, mass migration of European Jews to Palestine, there had been Intercommunal conflict in Mandatory Palestine, tension and conflict between Arabs, Jews, and the British in Palestine. The conflict escalated into a civil war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Mengo Hill
The Buganda Crisis, also called the 1966 Mengo Crisis, the Kabaka Crisis, or the 1966 Crisis, domestically, was a period of political turmoil that occurred in Buganda. It was driven by conflict between Prime Minister Milton Obote and the Kabaka of Buganda, Mutesa II, culminating in a military assault upon the latter's residence that drove him into exile. Background UPC-KY coalition In 1960, Milton Obote helped to establish a political party in Uganda, known as the Uganda People's Congress (UPC). The UPC aimed to erode the power and influence of the "Mengo Establishment", a group of traditionalist Baganda that led the sub-national kingdom of Buganda. The Mengo establishment was plagued by rivalries and infighting, but most of its members, as Protestant Christians, were united by their dislike of the Democratic Party (DP), which was dominated by Catholics. The DP won a majority in Uganda's first free national elections in 1961, and formed a government. The UPC and tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre
The Jallianwala Bagh massacre (), also known as the Amritsar massacre, took place on 13 April 1919. A large crowd had gathered at the Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar, Punjab, British India, during the annual Vaisakhi, Baisakhi fair to protest against the Rowlatt Act and the arrest of pro-Indian independence activists Saifuddin Kitchlew and Satyapal. In response to the public gathering, the temporary Brigadier (India), brigadier general R. E. H. Dyer surrounded the people with his Gurkha and Sikh infantry regiments of the British Indian Army. The Jallianwala Bagh could only be exited on one side, as its other three sides were enclosed by buildings. After blocking the exit with his troops, Dyer ordered them to shoot at the crowd, continuing to fire even as the protestors tried to flee. The troops kept on firing until their ammunition was low and they were ordered to stop. Estimates of those killed vary from 379 to 1,500 or more people; over 1,200 others were injured, of whom 192 sust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and Orange Free State) over Britain's influence in Southern Africa. The Witwatersrand Gold Rush caused a large influx of "Uitlander, foreigners" (''Uitlanders'') to the South African Republic (SAR), mostly British from the Cape Colony. As they, for fear of a hostile takeover of the SAR, were permitted to vote only after 14 years of residence, they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed at the botched Bloemfontein Conference in June 1899. The conflict broke out in October after the British government decided to send 10,000 troops to South Africa. With a delay, this provoked a Boer and British ultimatum, and subsequent Boer Irregular military, irregulars and militia attacks on British colonial settlements in Natal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mau Mau Uprising
The Mau Mau rebellion (1952–1960), also known as the Mau Mau uprising, Mau Mau revolt, or Kenya Emergency, was a war in the British Kenya Colony (1920–1963) between the Kenya Land and Freedom Army (KLFA), also known as the Mau Mau, and the British authorities. Dominated by Kikuyu people, Kikuyu, Meru people, Meru and Embu people, Embu fighters, the KLFA also comprised units of Kamba people, Kamba and Maasai people, Maasai who fought against the European colonists in Kenya — the British Army, and the local Kenya Regiment (British colonists, local auxiliary militia, and pro-British Kikuyu). The capture of Field Marshal Dedan Kimathi on 21 October 1956 signalled the defeat of the Mau Mau, and essentially ended the British military campaign. However, the rebellion survived until after Kenya's independence from Britain, driven mainly by the Meru people, Meru units led by Field Marshal Musa Mwariama. General Baimungi, one of the last Mau Mau leaders, was killed shortly after Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was supported by China and the Soviet Union, while South Korea was supported by the United Nations Command (UNC) led by the United States. The conflict was one of the first major proxy wars of the Cold War. Fighting ended in 1953 with an armistice but no peace treaty, leading to the ongoing Korean conflict. After the end of World War II in 1945, Korea, which had been a Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese colony for 35 years, was Division of Korea, divided by the Soviet Union and the United States into two occupation zones at the 38th parallel north, 38th parallel, with plans for a future independent state. Due to political disagreements and influence from their backers, the zones formed their governments in 1948. North Korea was led by Kim Il S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
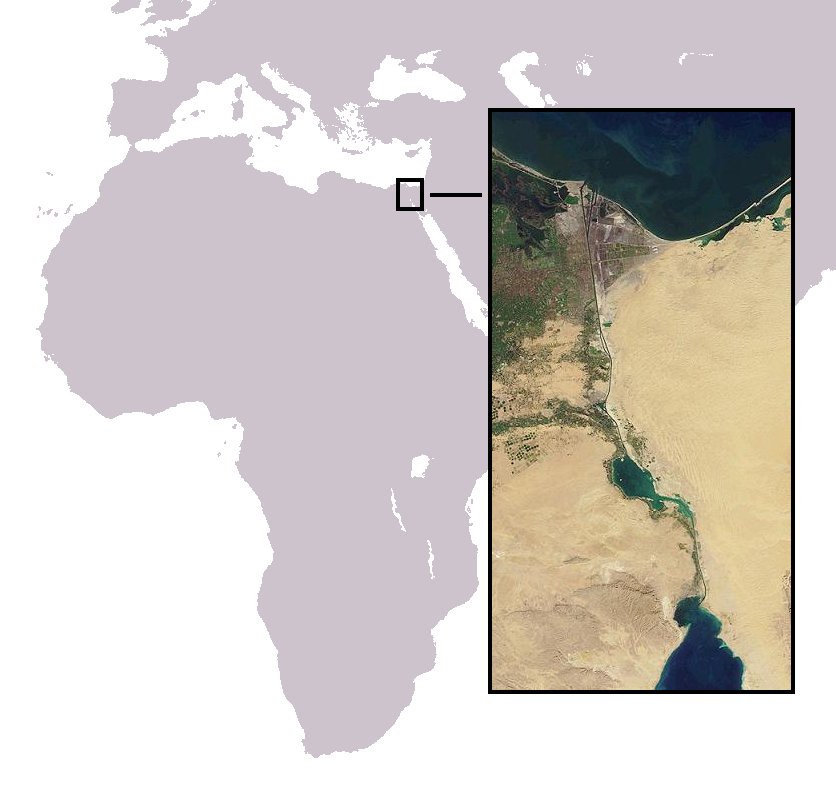
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, also known as the Second Arab–Israeli War, the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was a British–French–Israeli invasion of Egypt in 1956. Israel invaded on 29 October, having done so with the primary objective of re-opening the Straits of Tiran and the Gulf of Aqaba as the recent tightening of the eight-year-long Egyptian blockade further prevented Israeli passage. After issuing a joint ultimatum for a ceasefire, the United Kingdom and France joined the Israelis on 5 November, seeking to depose Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser and regain control of the Suez Canal, which Nasser had earlier nationalised by transferring administrative control from the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company to Egypt's new government-owned Suez Canal Authority. Shortly after the invasion began, the three countries came under heavy political pressure from both the United States and the Soviet Union, as well as from the United Nations, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1958 Lebanon Crisis
The 1958 Lebanon crisis was a political crisis in Lebanon caused by political and religious tensions in the country that included an American military intervention, which lasted for around three months until President Camille Chamoun, who had requested the assistance, completed his term as president of Lebanon. American and Lebanese government forces occupied the Port of Beirut and Beirut International Airport. With the crisis over, the United States withdrew. Background Arab Cold War After the end of World War II in 1945, the United States and Soviet Union were the two major world powers. Two years later, the Truman Doctrine was issued, aimed at containing the spread of communism and the Soviet Union. The Cold War is generally considered to have begun around this time. As the world divided into the Eastern (communist) and Western (capitalist) Blocs, a struggle for ideological geopolitical supremacy between the US and USSR emerged. One of the ways it manifested was throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algerian War
The Algerian War (also known as the Algerian Revolution or the Algerian War of Independence) ''; '' (and sometimes in Algeria as the ''War of 1 November'') was an armed conflict between France and the Algerian National Liberation Front (Algeria), National Liberation Front (FLN) from 1954 to 1962, which led to Algeria winning its independence from France. * * * * * * An important decolonization war, it was a complex conflict characterized by guerrilla warfare and war crimes. The conflict also became a civil war between the different communities and within the communities. The war took place mainly on the territory of Algeria, with repercussions in metropolitan France. Effectively started by members of the FLN on 1 November 1954, during the ("Red All Saints' Day"), the conflict led to serious political crises in France, causing the fall of the Fourth French Republic, Fourth Republic (1946–58), to be replaced by the Fifth French Republic, Fifth Republic with a strengthened pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |