|
Leeson's Equation
Leeson's equation is an empirical expression that describes an oscillator's phase noise spectrum. Leeson's expression for single-sideband (SSB) phase noise in dBc/Hz (decibels relative to output level per hertz) and augmented for flicker noise: :L(f_m) = 10 \log \bigg \frac \bigg( \bigg(\frac\bigg)^2 + 1\bigg)\bigg(\frac + 1\bigg)\bigg(\frac\bigg) \bigg/math> where is the output frequency, is the loaded quality factor, is the offset from the output frequency (Hz), is the corner frequency, is the noise factor of the amplifier, is Boltzmann's constant in joules/kelvin, is absolute temperature in kelvins, and is the available power at the sustaining amplifier input.https://www.ieee.li/pdf/essay/phase_noise_basics.pdf There is often misunderstanding around Leeson's equation, even in text books. In the 1966 paper, Leeson stated correctly that " is the signal level at the oscillator active element input" (often referred to as the power through the resonator now, strictly spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or Periodic function, periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
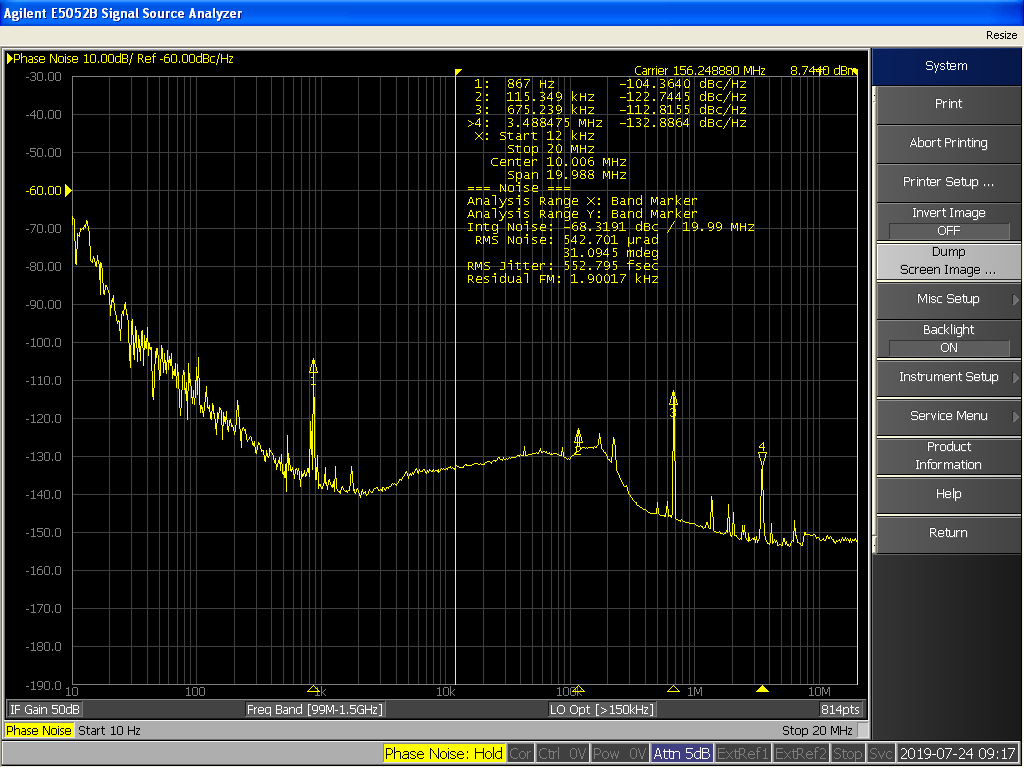
Phase Noise
In signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity (jitter). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock. Definitions Historically there have been two conflicting yet widely used definitions for phase noise. Some authors define phase noise to be the spectral density of a signal's phase only, while the other definition refers to the phase spectrum (which pairs up with the amplitude spectrum) resulting from the spectral estimation of the signal itself. Both definitions yield the same result at offset frequencies well removed from the carrier. At close-in offsets however, the two definitions differ. The IEEE defines phase noise as where the "phase instability" is the one-sided spectral density of a signal's phase deviation. Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flicker Noise
Flicker noise is a type of electronic noise with a 1/''f'' power spectral density. It is therefore often referred to as 1/''f'' noise or pink noise, though these terms have wider definitions. It occurs in almost all electronic devices and can show up with a variety of other effects, such as impurities in a conductive channel, generation and recombination noise in a transistor due to base current, and so on. Properties 1/''f'' noise in current or voltage is usually related to a direct current, as resistance fluctuations are transformed to voltage or current fluctuations by Ohm's law. There is also a 1/''f'' component in resistors with no direct current through them, likely due to temperature fluctuations modulating the resistance. This effect is not present in manganin, as it has negligible temperature coefficient of resistance. In electronic devices, it shows up as a low-frequency phenomenon, as the higher frequencies are overshadowed by white noise from other sources. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Factor
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or ''Q'' factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in one radian of the cycle of oscillation. Q factor is alternatively defined as the ratio of a resonator's centre frequency to its bandwidth when subject to an oscillating driving force. These two definitions give numerically similar, but not identical, results. Higher ''Q'' indicates a lower rate of energy loss and the oscillations die out more slowly. A pendulum suspended from a high-quality bearing, oscillating in air, has a high ''Q'', while a pendulum immersed in oil has a low one. Resonators with high quality factors have low damping, so that they ring or vibrate longer. Explanation The Q factor is a parameter that describes the resonance behavior of an underdamped harmonic oscillator (resonator). Sinusoidally driven resonato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutoff Frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced ( attenuated or reflected) rather than passing through. Typically in electronic systems such as filters and communication channels, cutoff frequency applies to an edge in a lowpass, highpass, bandpass, or band-stop characteristic – a frequency characterizing a boundary between a passband and a stopband. It is sometimes taken to be the point in the filter response where a transition band and passband meet, for example, as defined by a half-power point (a frequency for which the output of the circuit is −3 dB of the nominal passband value). Alternatively, a stopband corner frequency may be specified as a point where a transition band and a stopband meet: a frequency for which the attenuation is larger than the required stopband attenuation, which for example may be 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Factor
Noise figure (NF) and noise factor (''F'') are figures of merit that indicate degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is caused by components in a signal chain. These figures of merit are used to evaluate the performance of an amplifier or a radio receiver, with lower values indicating better performance. The noise factor is defined as the ratio of the output noise power of a device to the portion thereof attributable to thermal noise in the input termination at standard noise temperature ''T''0 (usually 290 K). The noise factor is thus the ratio of actual output noise to that which would remain if the device itself did not introduce noise, or the ratio of input SNR to output SNR. The noise ''factor'' and noise ''figure'' are related, with the former being a unitless ratio and the latter being the same ratio but expressed in units of decibels (dB). General The noise figure is the difference in decibels (dB) between the noise output of the actual receiver to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boltzmann's Constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, and in Planck's law of black-body radiation and Boltzmann's entropy formula, and is used in calculating thermal noise in resistors. The Boltzmann constant has dimensions of energy divided by temperature, the same as entropy. It is named after the Austrian scientist Ludwig Boltzmann. As part of the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, the Boltzmann constant is one of the seven " defining constants" that have been given exact definitions. They are used in various combinations to define the seven SI base units. The Boltzmann constant is defined to be exactly . Roles of the Boltzmann constant Macroscopically, the ideal gas law states that, for an ideal gas, the product of pressure and volume is proportional to the product of amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by other disturbances. Whereas positive feedback tends to lead to instability via exponential growth, oscillation or chaotic behavior, negative feedback generally promotes stability. Negative feedback tends to promote a settling to equilibrium, and reduces the effects of perturbations. Negative feedback loops in which just the right amount of correction is applied with optimum timing can be very stable, accurate, and responsive. Negative feedback is widely used in mechanical and electronic engineering, and also within living organisms, and can be seen in many other fields from chemistry and economics to physical systems such as the climate. General negative feedback systems are studied in control systems engineering. Negative feedback l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |