|
Least Squares Conformal Map
A Least squares conformal map (LSCM) is a 2-D representation of a 3-D shape created using the Least Squares Conformal Mapping Method. By using the map as a guide when creating a new 2-D image, the colors of the 2-D image can be applied to the original 3-D model. LSCM is used in computer graphics as a method of producing a UV map from a polygonal mesh to a texture map such that the shape of the polygons as mapped to the texture is relatively undistorted. See also * Conformal map * UV mapping UV mapping is the 3D modeling process of projecting a 3D model's surface to a 2D image for texture mapping. The letters "U" and "V" denote the axes of the 2D texture because "X", "Y", and "Z" are already used to denote the axes of the 3D object i ... External links Least Squares Conformal Maps for Automatic Texture Atlas Generation ACM SIGGRAPH conference proceedings, 2002 Computer graphics data structures {{Compu-graphics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean (flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with one of a room's walls, infinitely extended, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of two-dimensional Euclidean geometry. Sometimes the word ''plane'' is used more generally to describe a two-dimensional surface, for example the hyperbolic plane and elliptic plane. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' plane refers to the whole space. Many fundamental tasks in mathematics, geometry, trigonometry, graph theory, and graphing are performed in a two-dimensional space, often in the plane. Euclidean geometry Euclid set forth the first great landmark of mathematical thought, an axiomatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-dimensional Space
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position (geometry), position of an element (i.e., Point (mathematics), point). This is the informal meaning of the term dimension. In mathematics, a tuple of Real number, numbers can be understood as the Cartesian coordinates of a location in a -dimensional Euclidean space. The set of these -tuples is commonly denoted \R^n, and can be identified to the -dimensional Euclidean space. When , this space is called three-dimensional Euclidean space (or simply Euclidean space when the context is clear). It serves as a model of the physical universe (when relativity theory is not considered), in which all known matter exists. While this space remains the most compelling and useful way to model the world as it is experienced, it is only one example of a large variety of spaces in three dimensions called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
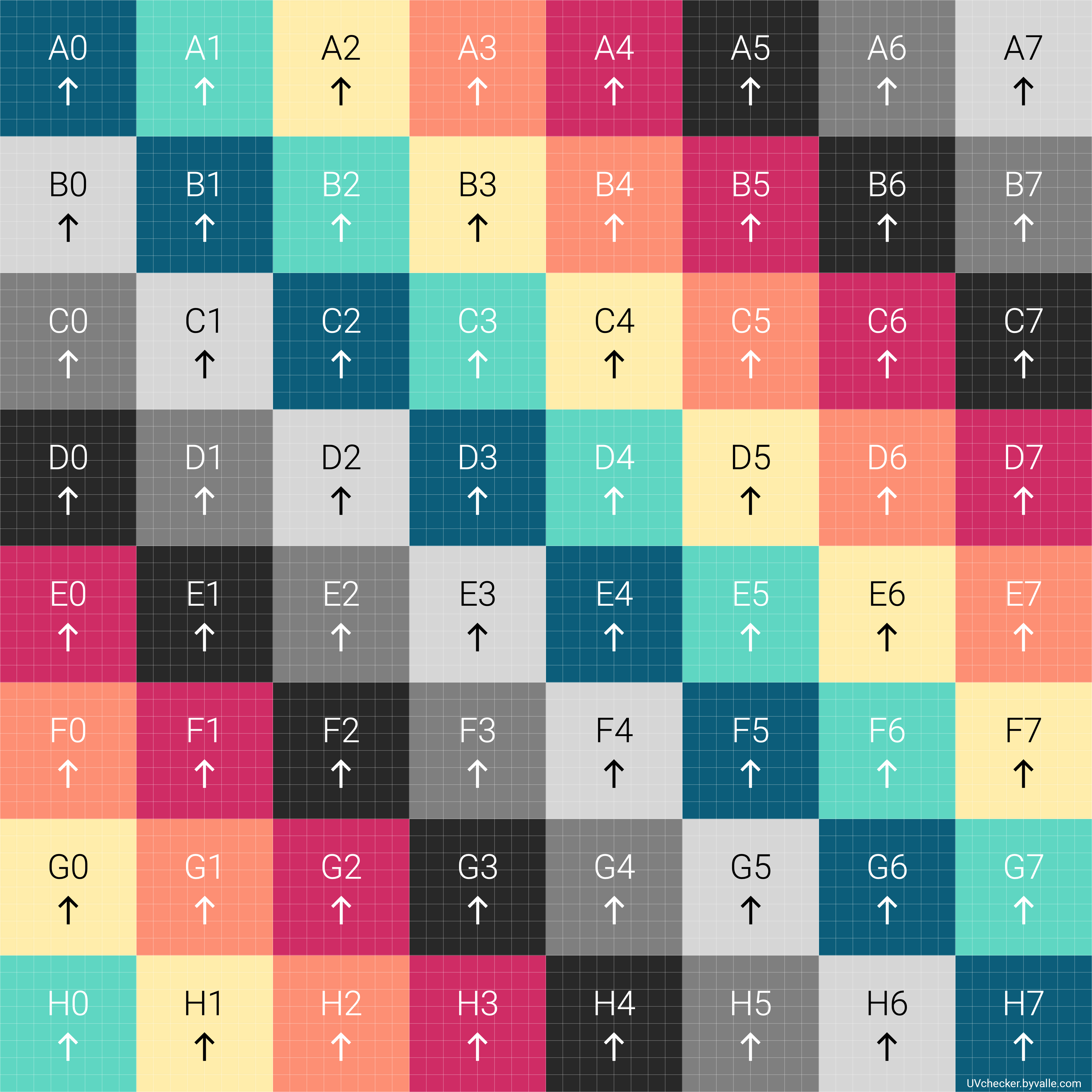
UV Mapping
UV mapping is the 3D modeling process of projecting a 3D model's surface to a 2D image for texture mapping. The letters "U" and "V" denote the axes of the 2D texture because "X", "Y", and "Z" are already used to denote the axes of the 3D object in model space, while "W" (in addition to XYZ) is used in calculating quaternion rotations, a common operation in computer graphics. Process UV texturing permits polygons that make up a 3D object to be painted with color (and other surface attributes) from an ordinary image. The image is called a UV texture map.Mullen, T (2009). Mastering Blender. 1st ed. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. The UV mapping process involves assigning pixels in the image to surface mappings on the polygon, usually done by "programmatically" copying a triangular piece of the image map and pasting it onto a triangle on the object.Murdock, K.L. (2008). 3ds Max 2009 Bible. 1st ed. Indianapolis, Indiana: Wiley Publishing, Inc. UV texturing is an alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygonal Mesh
In 3D computer graphics and solid modeling, a polygon mesh is a collection of , s and s that defines the shape of a polyhedral object. The faces usually consist of triangles (triangle mesh), quadrilaterals (quads), or other simple convex polygons (n-gons), since this simplifies rendering, but may also be more generally composed of concave polygons, or even polygons with holes. The study of polygon meshes is a large sub-field of computer graphics (specifically 3D computer graphics) and geometric modeling. Different representations of polygon meshes are used for different applications and goals. The variety of operations performed on meshes may include: Boolean logic (Constructive solid geometry), smoothing, simplification, and many others. Algorithms also exist for ray tracing, collision detection, and rigid-body dynamics with polygon meshes. If the mesh's edges are rendered instead of the faces, then the model becomes a wireframe model. Volumetric meshes are distinct from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Map
Texture mapping is a method for mapping a texture on a computer-generated graphic. Texture here can be high frequency detail, surface texture, or color. History The original technique was pioneered by Edwin Catmull in 1974. Texture mapping originally referred to diffuse mapping, a method that simply mapped pixels from a texture to a 3D surface ("wrapping" the image around the object). In recent decades, the advent of multi-pass rendering, multitexturing, mipmaps, and more complex mappings such as height mapping, bump mapping, normal mapping, displacement mapping, reflection mapping, specular mapping, occlusion mapping, and many other variations on the technique (controlled by a materials system) have made it possible to simulate near-photorealism in real time by vastly reducing the number of polygons and lighting calculations needed to construct a realistic and functional 3D scene. Texture maps A is an image applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape or polygon. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformal Map
In mathematics, a conformal map is a function that locally preserves angles, but not necessarily lengths. More formally, let U and V be open subsets of \mathbb^n. A function f:U\to V is called conformal (or angle-preserving) at a point u_0\in U if it preserves angles between directed curves through u_0, as well as preserving orientation. Conformal maps preserve both angles and the shapes of infinitesimally small figures, but not necessarily their size or curvature. The conformal property may be described in terms of the Jacobian derivative matrix of a coordinate transformation. The transformation is conformal whenever the Jacobian at each point is a positive scalar times a rotation matrix (orthogonal with determinant one). Some authors define conformality to include orientation-reversing mappings whose Jacobians can be written as any scalar times any orthogonal matrix. For mappings in two dimensions, the (orientation-preserving) conformal mappings are precisely the locally i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |