|
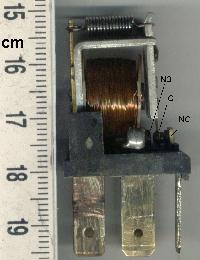
Lavet-type Stepping Motor
The Lavet-type stepping motor has widespread use as a drive in Electromechanics, electro-mechanical clocks and is a special kind of single-phase stepping motor. Both analog and stepped-movement quartz clocks use the Lavet-type stepping motor (see Quartz clock). Through miniaturization, it can be used in wristwatches and requires very little power, making a battery last for many years. The French engineer Marius Lavet invented this kind of drive and described it in 1936 in his patent application FR823395. Like other single-phase motors, the Lavet motor is only able to turn in one direction, which depends on the geometry of its stator. The rotor (electric), rotor is a permanent magnet. In a clock, a circuit generates the bipolar pulse train, which alternately delivers a positive and a negative voltage to the coil for short periods (providing a correct mechanical output to move a second hand). The motor can be built with a strong magnet and large stator to deliver high torque, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz Clock Motor
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of Silicon dioxide, SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of Jewellery, jewelry and hardstone carvings, espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromechanics
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process (generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering. Electromechanical devices are ones which have both electrical and mechanical processes. Strictly speaking, a manually operated switch is an electromechanical component due to the mechanical movement causing an electrical output. Though this is true, the term is usually understood to refer to devices which involve an electrical signal to create mechanical movement, or vice versa mechanical movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock
A clock or a timepiece is a device used to measure and indicate time. The clock is one of the oldest human inventions, meeting the need to measure intervals of time shorter than the natural units such as the day, the lunar month and the year. Devices operating on several physical processes have been used over the millennia. Some predecessors to the modern clock may be considered as "clocks" that are based on movement in nature: A sundial shows the time by displaying the position of a shadow on a flat surface. There is a range of duration timers, a well-known example being the hourglass. Water clocks, along with the sundials, are possibly the oldest time-measuring instruments. A major advance occurred with the invention of the verge escapement, which made possible the first mechanical clocks around 1300 in Europe, which kept time with oscillating timekeepers like balance wheels., pp. 103–104., p. 31. Traditionally, in horology, the term ''clock'' was used for a stri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
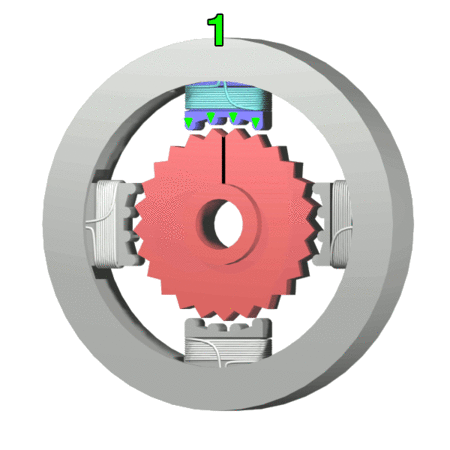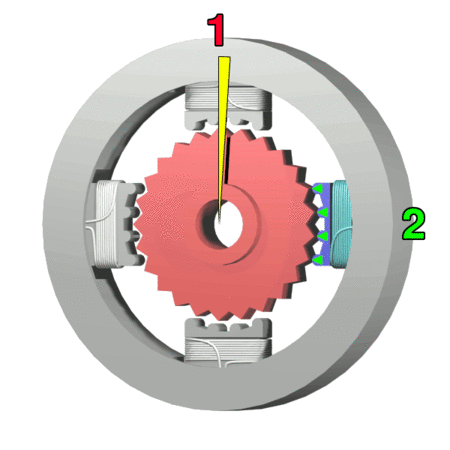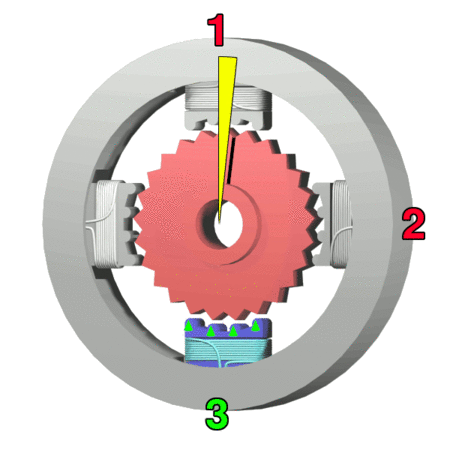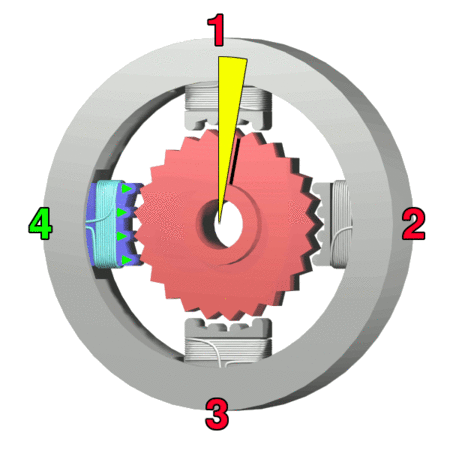
Stepping Motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any position sensor for feedback (an open-loop controller), as long as the motor is correctly sized to the application in respect to torque and speed. Switched reluctance motors are very large stepping motors with a reduced pole count, and generally are closed-loop commutated. Mechanism Brushed DC motors rotate continuously when DC voltage is applied to their terminals. The stepper motor is known for its property of converting a train of input pulses (typically square waves) into a precisely defined increment in the shaft’s rotational position. Each pulse rotates the shaft through a fixed angle. Stepper motors effectively have multiple "toothed" electromagnets arranged as a stator around a central rotor, a gear-shaped piece of iron. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
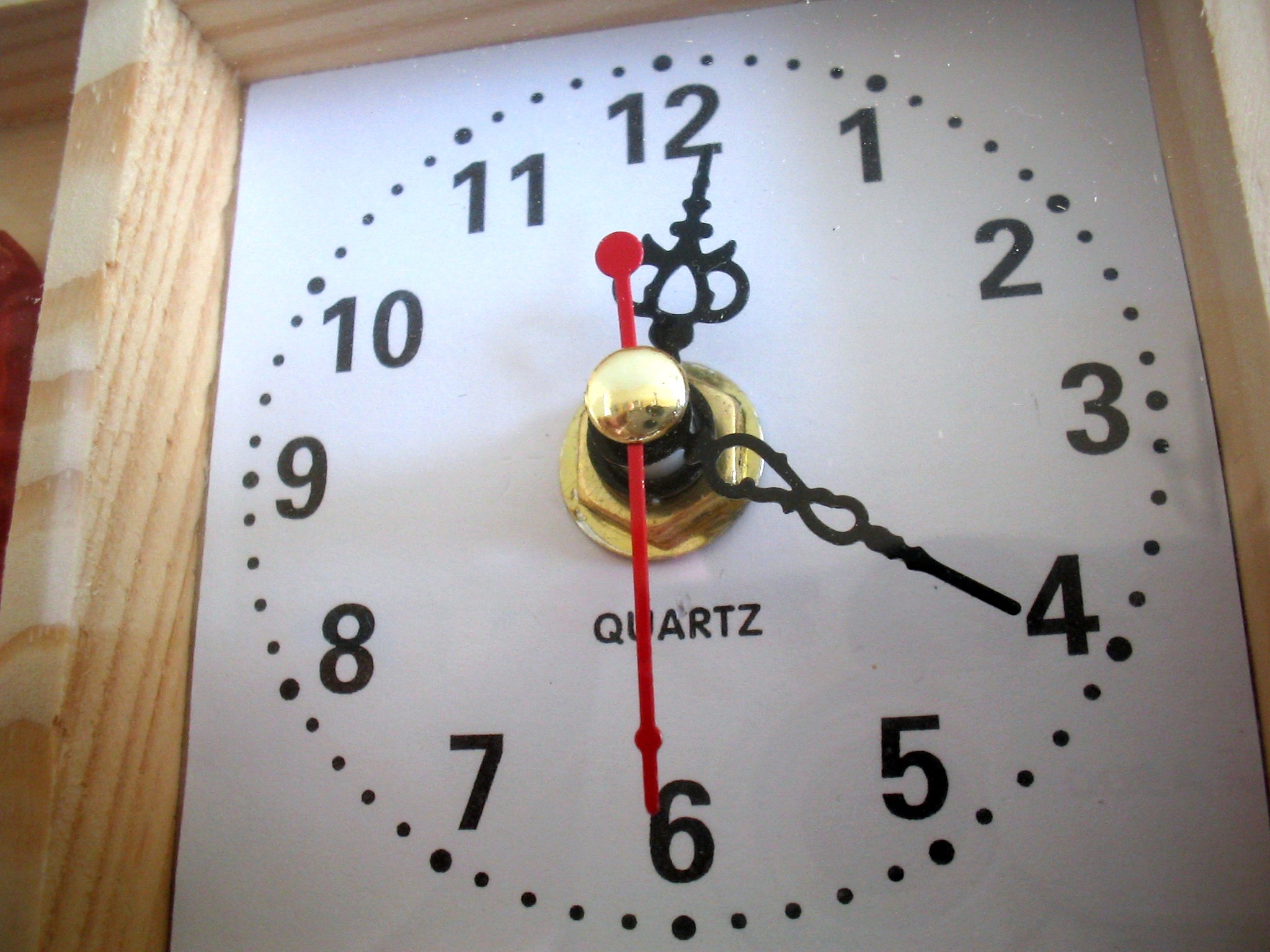
Quartz Clock
Quartz clocks and quartz watches are timepieces that use an electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. This crystal oscillator creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks and watches are at least an order of magnitude more accurate than mechanical clocks. Generally, some form of digital logic counts the cycles of this signal and provides a numerical time display, usually in units of hours, minutes, and seconds. Since the 1980s, when the advent of solid-state digital electronics allowed them to be made compact and inexpensive, quartz timekeepers have become the world's most widely used timekeeping technology, used in most clocks and watches as well as computers and other appliances that keep time. Explanation Chemically, quartz is a specific form of a compound called silicon dioxide. Many materials can be formed into plates that will resonate. However, quartz is also a piezoelectric material: that is, when a quartz crystal is su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wristwatch
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or other type of bracelet, including metal bands, leather straps or any other kind of bracelet. A pocket watch is designed for a person to carry in a pocket, often attached to a chain. Watches were developed in the 17th century from spring-powered clocks, which appeared as early as the 14th century. During most of its history the watch was a mechanical device, driven by clockwork, powered by winding a mainspring, and keeping time with an oscillating balance wheel. These are called ''mechanical watches''. In the 1960s the electronic ''quartz watch'' was invented, which was powered by a battery and kept time with a vibrating quartz crystal. By the 1980s the quartz watch had taken over most of the market from the mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marius Lavet
Marius Lavet (February 8, 1894 in Clermont-Ferrand – February 14, 1980 in Paris) was a French engineer who invented in 1936 the principle of stepper motor. He studied at Supélec, the School of Electric Power, French private engineering school. A stepper motor A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any pos ... can turn an electrical impulse in angular movement. This type of engine is very common in all devices where it is desirable to control the speed or position in open loop, usually in positioning systems. The invention of Lavet is enshrined in French Patent FR823395 and was instrumental, among other applications, for the development of watches with quartz mechanisms, using the principle known as the piezoelectric. Quartz watches dominate the world market today, due to their l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors or biological rotors. Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core, saving space and weight, and allowing a smaller air gap. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.Staff. "Understanding Alternators. What Is an Alternator and How Does It Work." N.p., n.d. Web. 24 November 2014 . Early development An early example of electromagnetic rotation was the first rotary machine built by Ányos Jedlik with electromagnets and a commutator, in 1826-27. Other pioneers in the field of electricity include Hippolyte Pixii who built an alternating current generator in 1832, and William Ritchie's construction of an electromagnetic generator with four rotor coils, a commutator and brushes, also in 1832. Development quickly included more useful applications such as Moritz Hermann Jacobi's motor that could lift 10 to 12 pounds with a speed of one foot per second, about 15 watts of mechanical power in 1834. In 1835, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaded-pole Motor
The shaded-pole motor is the original type of AC single-phase induction motor, dating back to at least as early as 1890. A shaded-pole motor is a small squirrel-cage motor in which the auxiliary winding is composed of a copper ring or bar surrounding a portion of each pole. When single phase AC supply is applied to the stator winding, due to shading provided to the poles, a rotating magnetic field is generated. This auxiliary single-turn winding is called a shading coil. Currents induced in this coil by the magnetic field create a second electrical phase by delaying the phase of magnetic flux change for that pole (a ''shaded pole'') enough to provide a 2-phase rotating magnetic field. The direction of rotation is from the unshaded side to the shaded (ring) side of the pole. Since the phase angle between the shaded and unshaded sections is small, shaded-pole motors produce only a small starting torque relative to torque at full speed. Shaded-pole motors of the asymmetrical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |