|
Latimer Diagram
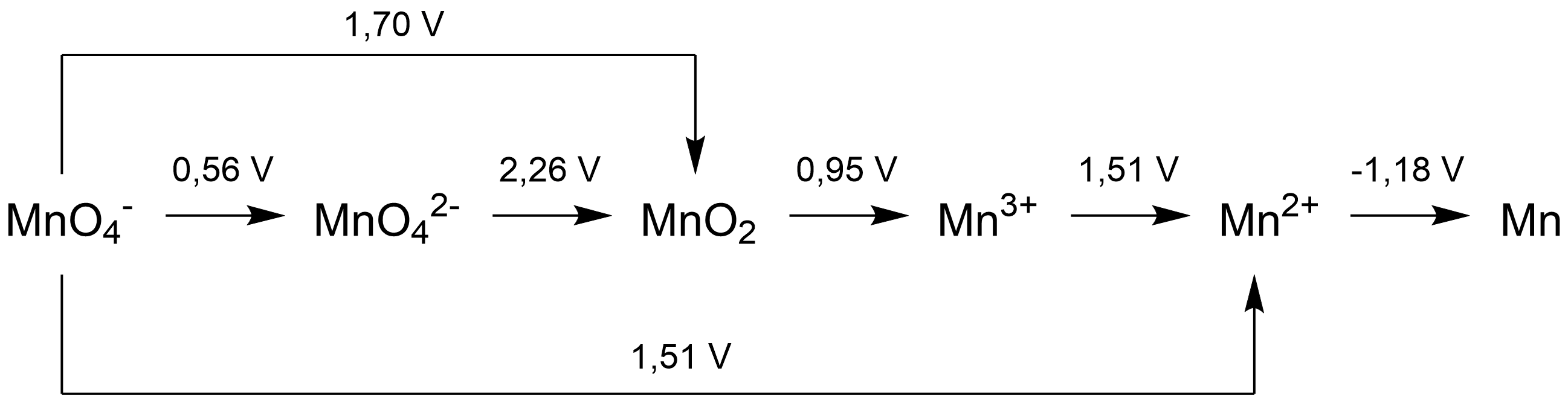
A Latimer diagram of a chemical element is a summary of the standard electrode potential data of that element. This type of diagram is named after Wendell Mitchell Latimer, an American chemist. Construction In a Latimer diagram, the most highly oxidized form of the element is on the left, with successively lower oxidation states to the right. The species are connected by arrows, and the numerical value of the standard potential (in volts) for the reduction is written at each arrow. For example, for oxygen, the species would be in the order O2 (0), H2O2 (–1), H2O (-2): : The arrow between O2 and H2O2 has a value +0.68 V over it, it indicates that the standard electrode potential for the reaction: :O2(''g'') + 2H+ + 2''e''− ⇄ H2O2(''aq'') is 0.68 volts. Application Latimer diagrams can be used in the construction of Frost diagrams, as a concise summary of the standard electrode potentials relative to the element. Since ΔrGo = -n FEo, the electrode potential is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latimer - Manganese
Latimer may refer to: Places England * Latimer, Buckinghamshire, a village ** Latimer and Ley Hill, a civil parish that until 2013 was just called "Latimer" * Latimer, Leicester, an electoral ward and administrative division of the city of Leicester * Burton Latimer, a small town in Northamptonshire United States * Latimer, Iowa, a city * Latimer, Kansas, a city * Latimer, Mississippi, a census-designated place * Latimer County, Oklahoma * Latimer Lake, Minnesota People and fictional characters * Latimer (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Latimer Whipple Ballou (1812–1900), U.S. Representative from Rhode Island * Latimer Fuller (1870–1950), Anglican bishop, the second Bishop of Lebombo, South Africa * Lewis Howard Latimer (1848–1928), Inventor Other uses * Baron Latimer, a title in the peerage of England and Britain, including a list of people who have held the title * Latimer Arts College, a foundation secondary school in Barton Seagrave, Northampton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frost Diagram
A Frost diagram or Frost–Ebsworth diagram is a type of graph used by inorganic chemists in electrochemistry to illustrate the relative stability of a number of different oxidation states of a particular substance. The graph illustrates the free energy vs oxidation state of a chemical species. This effect is dependent on pH, so this parameter also must be included. The free energy is determined by the oxidation–reduction half-reactions. The Frost diagram allows easier comprehension of these reduction potentials than the earlier-designed Latimer diagram, because the “lack of additivity of potentials” was confusing. The free energy Δ''G''° is related to reduction potential ''E'' in the graph by given formula: Δ''G''° = −''nFE''° or ''nE''° = −Δ''G''°/''F'', where ''n'' is the number of transferred electrons, and ''F'' is Faraday constant (''F'' = 96,485 J/(V·mol)). The Frost diagram is named after , who originally created it as a way to "show both free energy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellingham Diagram
An Ellingham diagram is a graph showing the temperature dependence of the stability of compounds. This analysis is usually used to evaluate the ease of reduction of metal oxides and sulfides. These diagrams were first constructed by Harold Ellingham in 1944.. In metallurgy, the Ellingham diagram is used to predict the equilibrium temperature between a metal, its oxide, and oxygen — and by extension, reactions of a metal with sulfur, nitrogen, and other non-metals. The diagrams are useful in predicting the conditions under which an ore will be reduced to its metal. The analysis is thermodynamic in nature and ignores reaction kinetics. Thus, processes that are predicted to be favourable by the Ellingham diagram can still be slow. Thermodynamics Ellingham diagrams are a particular graphical form of the principle that the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction depends on the sign of Δ''G'', the Gibbs free energy change, which is equal to Δ''H − T''Δ''S'', where Δ''H'' is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pourbaix Diagram
In electrochemistry, and more generally in solution chemistry, a Pourbaix diagram, also known as a potential/pH diagram, EH–pH diagram or a pE/pH diagram, is a plot of possible thermodynamically stable phases (''i.e.'', at chemical equilibrium) of an aqueous electrochemical system. Boundaries (50 %/50 %) between the predominant chemical species (aqueous ions in solution, or solid phases) are represented by lines. As such a Pourbaix diagram can be read much like a standard phase diagram with a different set of axes. Similarly to phase diagrams, they do not allow for reaction rate or kinetic effects. Beside potential and pH, the equilibrium concentrations are also dependent upon, e.g., temperature, pressure, and concentration. Pourbaix diagrams are commonly given at room temperature, atmospheric pressure, and molar concentrations of 10−6 and changing any of these parameters will yield a different diagram. The diagrams are named after Marcel Pourbaix (1904–1998), the Russian-bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disproportionation
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. More generally, the term can be applied to any desymmetrizing reaction of the following type, regardless of whether it is a redox or some other type of process: :2A -> A' + A'' Examples *Mercury(I) chloride disproportionates upon UV-irradiation: :Hg2Cl2 → Hg + HgCl2 *Phosphorous acid disproportionates upon heating to give phosphoric acid and phosphine: :4 → 3 H3PO4 + PH3 *Desymmetrizing reactions are sometimes referred to as disproportionation, as illustrated by the thermal degradation of bicarbonate: :2 → + H2CO3 :The oxidation numbers remain constant in this acid-base reaction. This process is also called autoionization. *Another variant on disproportionation is radical disproportionation, in which two radicals form an alkene and an alkane. : Reverse r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Constant
In physical chemistry, the Faraday constant, denoted by the symbol and sometimes stylized as ℱ, is the electric charge per mole of elementary charges. It is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday. Since the 2019 redefinition of SI base units, which took effect on 20 May 2019, the Faraday constant has the exactly defined value given by the product of the elementary charge ''e'' and Avogadro constant ''N''A: : : :. Derivation The Faraday constant can be thought of as the conversion factor between the mole (used in chemistry) and the coulomb (used in physics and in practical electrical measurements), and is therefore of particular use in electrochemistry. Because 1 mole contains exactly entities, and 1 coulomb contains exactly elementary charges, the Faraday constant is given by the quotient of these two quantities: :. One common use of the Faraday constant is in electrolysis calculations. One can divide the amount of charge (the current integrated over time) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring elements occur in the Earth as compounds or mixtures. Air is primarily a mixture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
%2C_black_and_white.png)