|
Lateral Shoot
A lateral shoot, commonly known as a branch, is a part of a plant's shoot system that develops from axillary buds on the stem's surface, extending laterally from the plant's stem. Importance to photosynthesis As a plant grows it requires more energy, it also is required to out-compete nearby plants for this energy. One of the ways a plant can compete for this energy is to increase its height, another is to increase its overall surface area. That is to say, the more lateral shoots a plant develops, the more foliage the plant can support increases how much photosynthesis the plant can perform as it allows for more area for the plant to uptake carbon dioxide as well as sunlight. Genes, transcription factors, and growth Through testing with Arabidopsis thaliana (A plant considered a model organism for plant genetic studies) genes including MAX1 and MAX2 have been found to affect growth of lateral shoots. Gene knockouts of these genes cause abnormal proliferation of the plants affect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lace Of Tree Branch (Pavlovsk Park)
Lace is a delicate fabric made of yarn or thread in an open weblike pattern, made by machine or by hand. Generally, lace is divided into two main categories, needlelace and bobbin lace, although there are other types of lace, such as knitted or crocheted lace. Other laces such as these are considered as a category of their specific craft. Knitted lace, therefore, is an example of knitting. This article considers both needle lace and bobbin lace. While some experts say both needle lace and bobbin lace began in Italy in the late 1500s, there are some questions regarding its origins. Originally linen, silk, gold, or silver threads were used. Now lace is often made with cotton thread, although linen and silk threads are still available. Manufactured lace may be made of synthetic fiber. A few modern artists make lace with a fine copper or silver wire instead of thread. Etymology The word lace is from Middle English, from Old French ''las'', noose, string, from Vulgar Latin *''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Hormone
Plant hormone (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, from embryogenesis, the regulation of organ size, pathogen defense, stress tolerance and through to reproductive development. Unlike in animals (in which hormone production is restricted to specialized glands) each plant cell is capable of producing hormones. Went and Thimann coined the term "phytohormone" and used it in the title of their 1937 book. Phytohormones occur across the plant kingdom, and even in algae, where they have similar functions to those seen in higher plants. Some phytohormones also occur in microorganisms, such as unicellular fungi and bacteria, however in these cases they do not play a hormonal role and can better be regarded as secondary metabolites. Characteristics The word hormone is derived from Greek, meaning ''set in motion''. Plant hormones affect gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
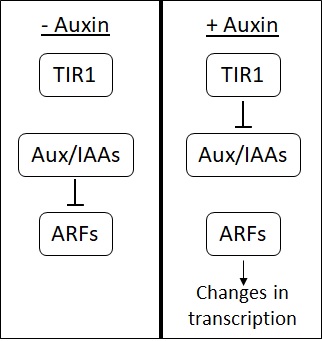
Auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essential for plant body development. The Dutch biologist Frits Warmolt Went first described auxins and their role in plant growth in the 1920s. Kenneth V. Thimann became the first to isolate one of these phytohormones and to determine its chemical structure as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA). Went and Thimann co-authored a book on plant hormones, ''Phytohormones'', in 1937. Overview Auxins were the first of the major plant hormones to be discovered. They derive their name from the Greek word αυξειν (''auxein'' – "to grow/increase"). Auxin is present in all parts of a plant, although in very different concentrations. The concentration in each position is crucial developmental information, so it is subject to tight regulation through both meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoot Apical Meristem
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide. Differentiated plant cells generally cannot divide or produce cells of a different type. Meristematic cells are undifferentiated or incompletely differentiated. They are totipotent and capable of continued cell division. Division of meristematic cells provides new cells for expansion and differentiation of tissues and the initiation of new organs, providing the basic structure of the plant body. The cells are small, with no or small vacuoles and protoplasm fills the cell completely. The plastids (chloroplasts or chromoplasts), are undifferentiated, but are present in rudimentary form (proplastids). Meristematic cells are packed closely together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone–releasing Hormone
Growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), also known as somatocrinin or by several other names in its endogenous forms and as somatorelin (INN) in its pharmaceutical form, is a releasing hormone of growth hormone (GH). It is a 44-amino acid peptide hormone produced in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. GHRH first appears in the human hypothalamus between 18 and 29 weeks of gestation, which corresponds to the start of production of growth hormone and other somatotropes in fetuses. Nomenclature * Endogenous: ** somatocrinin ** somatoliberin ** growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH or GH-RH; HGNC symbol is GHRH) ** growth hormone–releasing factor (GHRF or GRF) ** somatotropin-releasing hormone (SRH) ** somatotropin-releasing factor (SRF) * Pharmaceutical: ** somatorelin (INN) Origin GHRH is released from neurosecretory nerve terminals of these arcuate neurons, and is carried by the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system to the anterior pituitary gland, where it st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutant
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It is a characteristic that would not be observed naturally in a specimen. The term mutant is also applied to a virus with an alteration in its nucleotide sequence whose genome is in the nuclear genome. The natural occurrence of genetic mutations is integral to the process of evolution. The study of mutants is an integral part of biology; by understanding the effect that a mutation in a gene has, it is possible to establish the normal function of that gene. Mutants arise by mutation Mutants arise by mutations occurring in pre-existing genomes as a result of errors of DNA replication or errors of DNA repair. Errors of replication often involve translesion synthesis by a DNA polymerase when it encounters and bypasses a damaged base in the temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florigen
Florigen (or flowering hormone) is the hypothesized hormone-like molecule responsible for controlling and/or triggering flowering in plants. Florigen is produced in the leaves, and acts in the shoot apical meristem of buds and growing tips. It is known to be graft-transmissible, and even functions between species. However, despite having been sought since the 1930s, the exact nature of florigen is still disputed. Mechanism Essentially, to understand florigen, you must first understand how flowering works. For a plant to begin flowering, it must make its changes to the shoot apical meristem (SAM). However, there are factors the plant must first consider before it begins this process such as the environment but even more specifically, light. It is through "the evolution of both internal and external control systems that enables plants to precisely regulate flowering so that it occurs at the optimal time for reproductive success." The way the plant determines this optimal time is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Type
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, "mutant" allele. "Mutant" alleles can vary to a great extent, and even become the wild type if a genetic shift occurs within the population. Continued advancements in genetic mapping technologies have created a better understanding of how mutations occur and interact with other genes to alter phenotype. It is now appreciated that most or all gene loci exist in a variety of allelic forms, which vary in frequency throughout the geographic range of a species, and that a uniform wild type does not exist. In general, however, the most prevalent allele – i.e., the one with the highest gene frequency – is the one deemed wild type. The concept of wild type is useful in some experimental organisms such as fruit flies ''Drosophila melanogaster'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch
A branch, sometimes called a ramus in botany, is a woody structural member connected to the central trunk (botany), trunk of a tree (or sometimes a shrub). Large branches are known as boughs and small branches are known as twigs. The term ''twig'' usually refers to a wikt:terminus, terminus, while ''bough'' refers only to branches coming directly from the trunk. Due to a broad range of species of trees, branches and twigs can be found in many different shapes and sizes. While branches can be nearly vertical and horizontal, horizontal, vertical, or diagonal, the majority of trees have upwardly diagonal branches. A number of mathematical properties are associated with tree branchings; they are natural examples of fractal patterns in nature, and, as observed by Leonardo da Vinci, their cross section (geometry), cross-sectional areas closely follow the da Vinci branching rule. Terminology Because of the enormous quantity of branches in the world, there are numerous names in Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)