|
Laporte Selection Rule
The Laporte rule is a rule that explains the intensities of absorption spectra for chemical species. It is a selection rule that rigorously applies to chromophores that are centrosymmetric, i.e. with an inversion centre. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity are forbidden. Thus transitions between states that are symmetric with respect to an inversion centre will not be observed. Transitions between states that are unsymmetric with respect to inversion are forbidden as well. In the language of symmetry, ''g'' (gerade = even (German)) → ''g'' and ''u'' (ungerade = odd) → ''u'' transitions are forbidden. Allowed transitions in such molecules must involve a change in parity, either ''g'' → ''u'' or ''u'' → ''g''. The Laporte rule stipulates that s to s, p to p, d to d, etc. transitions should not be observed in centrosymmetric compounds. Practically speaking, only d-d transitions occur in the visible region of the spectrum. Thus, the Laporte rule is mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selection Rule
In physics and chemistry, a selection rule, or transition rule, formally constrains the possible transitions of a system from one quantum state to another. Selection rules have been derived for electromagnetic transitions in molecules, in atoms, in atomic nuclei, and so on. The selection rules may differ according to the technique used to observe the transition. The selection rule also plays a role in chemical reactions, where some are formally spin-forbidden reactions, that is, reactions where the spin state changes at least once from reactants to products. In the following, mainly atomic and molecular transitions are considered. Overview In quantum mechanics the basis for a spectroscopic selection rule is the value of the ''transition moment integral'' :\int \psi_1^* \, \mu \, \psi_2 \, \mathrm\tau\,, where \psi_1 and \psi_2 are the wave functions of the two states, "state 1" and "state 2", involved in the transition, and is the transition moment operator. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
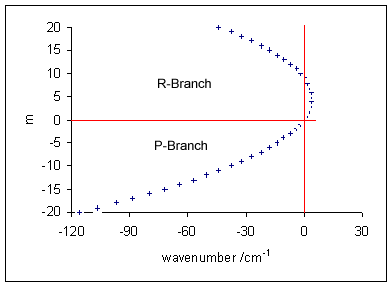
Vibronic Transition
Vibronic spectroscopy is a branch of molecular spectroscopy concerned with vibronic transitions: the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. In the gas phase, vibronic transitions are accompanied by changes in rotational energy also. Vibronic spectra of diatomic molecules have been analysed in detail; emission spectra are more complicated than absorption spectra. The intensity of allowed vibronic transitions is governed by the Franck–Condon principle. Vibronic spectroscopy may provide information, such as bond length, on electronic excited states of stable molecules. It has also been applied to the study of unstable molecules such as dicarbon, C2, in discharges, flames and astronomical objects.Hollas, p. 211. Principles Electronic transitions are typically observed in the visible and ultraviolet regions, in the wavelength range approximately 200–700 nm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanabe–Sugano Diagram
In coordination chemistry, Tanabe–Sugano diagrams are used to predict absorptions in the ultraviolet (UV), visible and infrared (IR) electromagnetic spectrum of coordination compounds. The results from a Tanabe–Sugano diagram analysis of a metal complex can also be compared to experimental spectroscopic data. They are qualitatively useful and can be used to approximate the value of 10Dq, the ligand field splitting energy. Tanabe–Sugano diagrams can be used for both high spin and low spin complexes, unlike Orgel diagrams, which apply only to high spin complexes. Tanabe–Sugano diagrams can also be used to predict the size of the ligand field necessary to cause high-spin to low-spin transitions. In a Tanabe–Sugano diagram, the ground state is used as a constant reference, in contrast to Orgel diagrams. The energy of the ground state is taken to be zero for all field strengths, and the energies of all other terms and their components are plotted with respect to the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Field Theory
Ligand field theory (LFT) describes the bonding, orbital arrangement, and other characteristics of coordination complexes. It represents an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metal complexes. A transition metal ion has nine valence atomic orbitals - consisting of five ''n''d, one (''n''+1)s, and three (''n''+1)p orbitals. These orbitals are of appropriate energy to form bonding interaction with ligands. The LFT analysis is highly dependent on the geometry of the complex, but most explanations begin by describing octahedral complexes, where six ligands coordinate to the metal. Other complexes can be described by reference to crystal field theory.G. L. Miessler and D. A. Tarr "Inorganic Chemistry" 3rd Ed, Pearson/Prentice Hall publisher, . History Ligand field theory resulted from combining the principles laid out in molecular orbital theory and crystal field theory, which describes the loss of degeneracy of metal d orbitals in transition metal complexes. John Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Optical Society Of America
The ''Journal of the Optical Society of America'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of optics, published by Optica. It was established in 1917 and in 1984 was split into two parts, A and B. ''Journal of the Optical Society of America A'' Part A covers various topics in optics, vision, and image science. The editor-in-chief is Olga Korotkova (University of Miami, USA). ''Journal of the Optical Society of America B'' Part B covers various topics in the field of optical physics, such as guided waves, laser spectroscopy, nonlinear optics, quantum optics, lasers, organic and polymer materials for optics, and ultrafast phenomena In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by .... The editor-in-chief is Kurt Busch ( Humboldt University of Berlin, Germany). References {{reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Laporte
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', ''Odo'', ''Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded from the 7th century ( Odo, son of Uro, courtier of Sigebert III). It was the name of three 10th-century German kings, the first of whom was Otto I the Great, the first Holy Roman Emperor, founder of the Ottonian dynasty. The Gothic form of the prefix was ''auda-'' (as in e.g. '' Audaþius''), the Anglo-Saxon form was ''ead-'' (as in e.g. ''Eadmund''), and the Old Norse form was '' auð-''. The given name Otis arose from an English surname, which was in turn derived from ''Ode'', a variant form of ''Odo, Otto''. Due to Otto von Bismarck, the given name ''Otto'' was strongly associated with the German Empire in the later 19th century. It was comparatively frequently given in the United States (presumably in German American families) during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral Molecular Geometry
In a tetrahedral molecular geometry, a central atom is located at the center with four substituents that are located at the corners of a tetrahedron. The bond angles are cos−1(−) = 109.4712206...° ≈ 109.5° when all four substituents are the same, as in methane () as well as its heavier analogues. Methane and other perfectly symmetrical tetrahedral molecules belong to point group Td, but most tetrahedral molecules have lower symmetry. Tetrahedral molecules can be chiral. Tetrahedral bond angle The bond angle for a symmetric tetrahedral molecule such as CH4 may be calculated using the dot product of two vectors. As shown in the diagram, the molecule can be inscribed in a cube with the tetravalent atom (e.g. carbon) at the cube centre which is the origin of coordinates, O. The four monovalent atoms (e.g. hydrogens) are at four corners of the cube (A, B, C, D) chosen so that no two atoms are at adjacent corners linked by only one cube edge. If the edge length of the cube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibronic Coupling
Vibronic coupling (also called nonadiabatic coupling or derivative coupling) in a molecule involves the interaction between electronic and nuclear vibrational motion. The term "vibronic" originates from the combination of the terms "vibrational" and "electronic", denoting the idea that in a molecule, vibrational and electronic interactions are interrelated and influence each other. The magnitude of vibronic coupling reflects the degree of such interrelation. In theoretical chemistry, the vibronic coupling is neglected within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. Vibronic couplings are crucial to the understanding of nonadiabatic processes, especially near points of conical intersections. The direct calculation of vibronic couplings is not common due to difficulties associated with its evaluation. Definition Vibronic coupling describes the mixing of different electronic states as a result of small vibrations. : \mathbf_\equiv\langle\,\chi_(\mathbf;\mathbf)\,, \, \hat_\ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahn–Teller Effect
The Jahn–Teller effect (JT effect or JTE) is an important mechanism of spontaneous symmetry breaking in molecular and solid-state systems which has far-reaching consequences in different fields, and is responsible for a variety of phenomena in spectroscopy, stereochemistry, crystal chemistry, molecular and solid-state physics, and materials science. The effect is named for Hermann Arthur Jahn and Edward Teller, who first reported studies about it in 1937.Bunker, Philip R.; Jensen, Per (1998) ''Molecular Symmetry and Spectroscopy'' (2nd ed.). NRC Research Press, Ottaw/ref> Simplified overview The Jahn–Teller effect, sometimes also referred to as Jahn–Teller distortion, describes the geometrical distortion of molecules and ions that result from certain electron configurations. The Jahn–Teller theorem essentially states that any non-linear molecule with a spatially degenerate energy level, degenerate electronic ground state will undergo a geometrical distortion that removes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrosymmetric
In crystallography, a centrosymmetric point group contains an inversion center as one of its symmetry elements. In such a point group, for every point (x, y, z) in the unit cell there is an indistinguishable point (-x, -y, -z). Such point groups are also said to have ''inversion'' symmetry. Point reflection is a similar term used in geometry. Crystals with an inversion center cannot display certain properties, such as the piezoelectric effect. The following space groups have inversion symmetry: the triclinic space group 2, the monoclinic 10-15, the orthorhombic 47-74, the tetragonal 83-88 and 123-142, the trigonal 147, 148 and 162-167, the hexagonal 175, 176 and 191-194, the cubic 200-206 and 221-230. Point groups lacking an inversion center (non-centrosymmetric) can be ''polar'', ''chiral'', both, or neither. A ''polar'' point group is one whose symmetry operations leave more than one common point unmoved. A polar point group has no unique origin because each of those unmoved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of The West Indies, Mona
The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 17 English-speaking countries and territories in the Caribbean: Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, and Turks and Caicos Islands. Each country is either a member of the Commonwealth of Nations or a British Overseas Territory. The aim of the university is to help "unlock the potential for economic and cultural growth" in the West Indies, thus allowing improved regional autonomy. The university was originally instituted as an independent external college of the University of London. The university has produced students who have excelled in a number of disciplines such as the arts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
-3D-balls.png)