|
Lamellibrachia Donwalshi
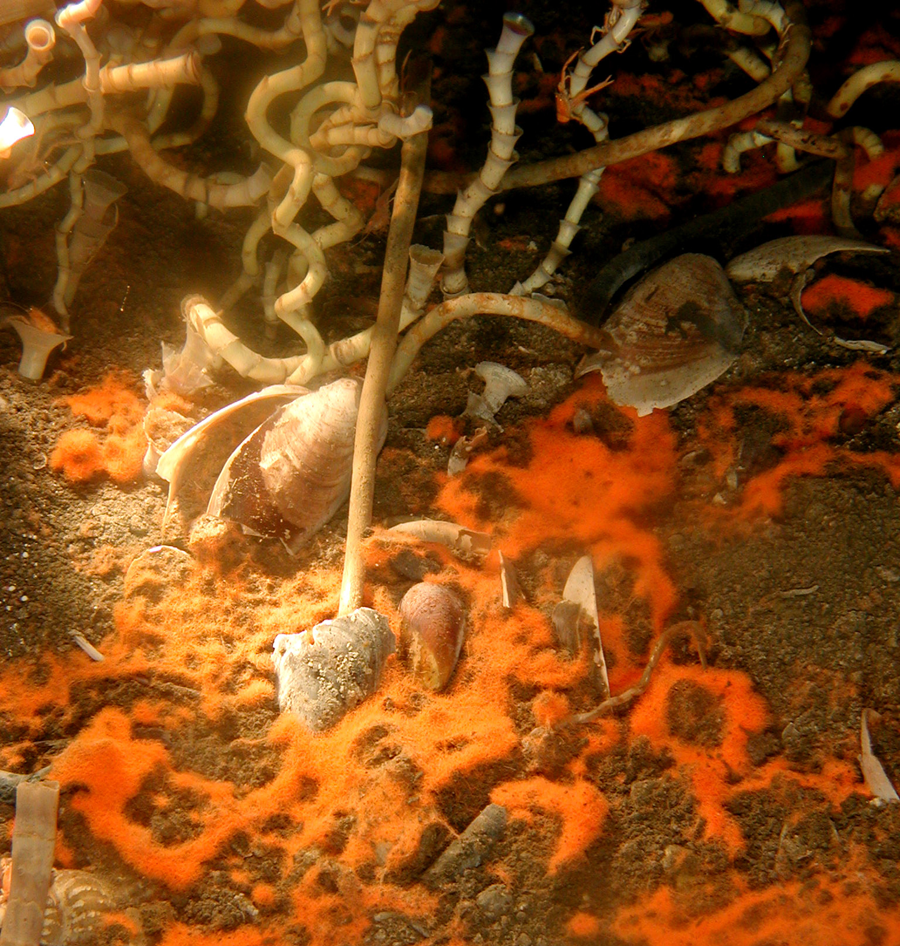
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, ''Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for their nutrition. The symbionts, gammaproteobacteria, require sulfide and inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide). The tube worms extract dissolved oxygen and hydrogen sulfide from the sea water with the crown of plumes. Species living near seeps can also obtain sulfide through their "roots", posterior extensions of their body and tube. Several sorts of hemoglobin are present in the blood and coelomic fluid to bind to the different components and transport them to the symbionts. ''L. luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Luymesi
''Lamellibrachia luymesi'' is a species of tube worms in the family Siboglinidae. It lives at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) are leaking out of the seafloor. It is entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for its nutrition. These are located in a centrally located "trophosome". ''Lamellibrachia luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms ''Riftia pachyptila'' that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses a posterior extension of its body called the root to take up hydrogen sulfide from the seep sediments. ''L. luymesi'' may also help fuel the generation of sulfide by excreting sulfate through their roots into the sediments below the aggregations. To support the carbon fixation they need for maintenance and growth, ''L. luymesi'' needs to extract sulfide, oxygen, and inorganic carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
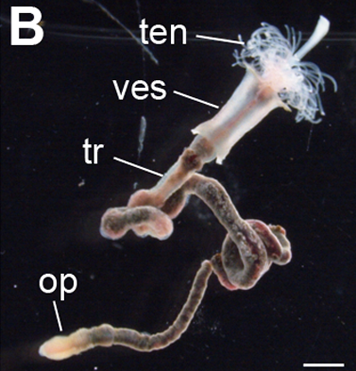
Vestimentiferan
Siboglinidae is a family of polychaete annelid worms whose members made up the former phyla Pogonophora and Vestimentifera (the giant tube worms). The family is composed of about 100 species of vermiform creatures which live in thin tubes buried in sediments (Pogonophora) or in tubes attached to hard substratum (Vestimentifera) at ocean depths ranging from . They can also be found in association with hydrothermal vents, methane seeps, sunken plant material, and whale carcasses. The first specimen was dredged from the waters of what is now Indonesia in 1900. These specimens were given to French zoologist Maurice Caullery, who studied them for nearly 50 years. Anatomy Most siboglinids are less than in diameter, but in length. They inhabit tubular structures composed of chitin and fixed to rocks or substrate. The tubes are often clustered together in large colonies. Their bodies are divided into four regions. The anterior end is called the cephalic lobe, which bears from one to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Juni
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, ''Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for their nutrition. The symbionts, gammaproteobacteria, require sulfide and inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide). The tube worms extract dissolved oxygen and hydrogen sulfide from the sea water with the crown of plumes. Species living near seeps can also obtain sulfide through their "roots", posterior extensions of their body and tube. Several sorts of hemoglobin are present in the blood and coelomic fluid to bind to the different components and transport them to the symbionts. ''L. luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greg W
Greg is a masculine given name, and often a shortened form of the given name Gregory. Greg (more commonly spelled " Gregg") is also a surname. People with the name *Greg Abbott (other), multiple people *Greg Abel (born 1961/1962), Canadian businessman *Greg Adams (other), multiple people *Greg Allen (other), multiple people *Greg Anderson (other), multiple people *Greg Austin (other), multiple people *Greg Ball (other), multiple people *Greg Bell (other), multiple people *Greg Bennett (other), multiple people *Greg Berlanti (born 1972), American writer and producer *Greg Biffle (born 1969), American NASCAR driver * Greg Blankenship (born 1954), American football player *Greg Boyd (other), multiple people *Greg Boyer (other), multiple people * Greg Brady (broadcaster) (born 1971), Canadian sports radio host *Greg Brock (baseball) (born 1957), American baseball player *Greg Brooker (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marina F
A marina (from Spanish , Portuguese and Italian : ''marina'', "coast" or "shore") is a dock or basin with moorings and supplies for yachts and small boats. A marina differs from a port in that a marina does not handle large passenger ships or cargo from freighters. The word ''marina'' may also refer to an inland wharf on a river or canal that is used exclusively by non-industrial pleasure craft such as canal narrowboats. Emplacement Marinas may be located along the banks of rivers connecting to lakes or seas and may be inland. They are also located on coastal harbors (natural or man made) or coastal lagoons, either as stand alone facilities or within a port complex. History In the 19th century, the few existing pleasure craft shared the same facilities as trading and fishing vessels. The marina appeared in the 20th century with the popularization of yachting. Facilities and services A marina may have refuelling, washing and repair facilities, marine and boat chandle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Donwalshi
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, ''Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for their nutrition. The symbionts, gammaproteobacteria, require sulfide and inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide). The tube worms extract dissolved oxygen and hydrogen sulfide from the sea water with the crown of plumes. Species living near seeps can also obtain sulfide through their "roots", posterior extensions of their body and tube. Several sorts of hemoglobin are present in the blood and coelomic fluid to bind to the different components and transport them to the symbionts. ''L. luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Columna
''Lamellibrachia columna'' is a vestimentiferan tube worm from the South Pacific Ocean that has been shown to be very closely related genetically to ''Lamellibrachia satsuma ''Lamellibrachia satsuma'' (also known as Satsuma tubeworm or Satsumahaorimushi or ) was discovered near a hydrothermal vent in Kagoshima Bay, Kagoshima at the depth of only the shallowest depth record for a vestimentiferan. Its symbiotic s ...'' found in Japanese waters. References Sabellida Animals described in 1991 Fauna of the Pacific Ocean {{Annelid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Barhami
''Lamellibrachia barhami'' is a large pogonophore. Description Its tentacular crown is formed of several, fused, horseshoe-shaped tentacle lamellae. The second segment has two body folds, near which open the genital ducts. The trunk, which comprises 89% of its total body length, is undifferentiated. The true metasoma is without setae. The heart is a simple muscular elaboration of the anterior end of the ventral blood vessel. The brain is large, and from it arises a pair of intraepidermal The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water relea ... nerve cords, which extend the full length of the vestimental region; thereafter, they join and form the a nerve cord of the trunk. Associated with the brain and the nerve cords are the dorsal tubes. References Further reading *Kiel, Steffen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephane Hourdez , a town of ancient Paphlagonia, now in Turkey
{{dab ...
Stephane may refer to: * Stéphane, a French given name * Stephane (Ancient Greece), a vestment in ancient Greece * Stephane (Paphlagonia) Stephane ( grc, Στεφάνη) was a small port town on the coast of ancient Paphlagonia, according to Arrian 180 stadion (unit), stadia east of Cimolis, but according to Marcian of Heraclea only 150. The place was mentioned as early as the time o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne C
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie. Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the Netherlands, particularly in the Frisian speaking part (for example, author Anne de Vries). In this incarnation, it is related to Germanic arn-names and means 'eagle'.See entry on "Anne" in th''Behind the Name'' databaseand th"Anne"an"Ane"entries (in Dutch) in the Nederlandse Voornamenbank (Dutch First Names Database) of the Meertens Instituut (23 October 2018). It has also been used for males in France ( Anne de Montmorency) and Scotland (Lord Anne Hamilton). Anne is a common name and the following lists represent a small selection. For a comprehensive list, see instead: . As a feminine name Anne * Saint Anne, Mother of the Virgin Mary * Anne, Queen of Great Britain (1665–1714), Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland (1702–07) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eve C
Eve (; ; ar, حَوَّاء, Ḥawwāʾ; el, Εὕα, Heúa; la, Eva, Heva; Syriac: romanized: ) is a figure in the Book of Genesis in the Hebrew Bible. According to the origin story, "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Creation myths develop through oral traditions and therefore typically have multiple versions." of the Abrahamic religions, she was the first woman, yet some debate within Judaism has also given that position to Lilith. Eve is known also as Adam's wife. According to the second chapter of Genesis, Eve was created by God (Yahweh) by taking her from the rib of Adam, to be Adam's companion. Adam is charged with guarding and keeping the garden before her creation; she is not present when God commands Adam not to eat the forbidden fruit – although it is clear that she was aware of the command. She decides to eat the forbidden fruit from the tree of the knowledge of good and evil after she hears t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellibrachia Anaximandri
''Lamellibrachia'' is a genus of tube worms related to the giant tube worm, ''Riftia pachyptila''. They live at deep-sea cold seeps where hydrocarbons (oil and methane) leak out of the seafloor, and are entirely reliant on internal, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial symbionts for their nutrition. The symbionts, gammaproteobacteria, require sulfide and inorganic carbon (carbon dioxide). The tube worms extract dissolved oxygen and hydrogen sulfide from the sea water with the crown of plumes. Species living near seeps can also obtain sulfide through their "roots", posterior extensions of their body and tube. Several sorts of hemoglobin are present in the blood and coelomic fluid to bind to the different components and transport them to the symbionts. ''L. luymesi'' provides the bacteria with hydrogen sulfide and oxygen by taking them up from the environment and binding them to a specialized hemoglobin molecule. Unlike the tube worms that live at hydrothermal vents, ''L. luymesi'' uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |