|
Lake Minto
Lake Minto ( iu, Qasigialik, "where there are spotted seals") is a lake on western Ungava Peninsula, Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. It has a total surface area of and a net area of .Natural Resources Canada, Atlas of Canada Lakes It was named by Canadian explorer and geologist Albert Peter Low in 1898 after Gilbert Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 4th Earl of Minto, who was Governor General of Canada at that time. It is only some east of Hudson Bay in a valley between several rows of hills, but Lake Minto's outlet, the Leaf River, flows north-east for about to Ungava Bay. As such, it is used by canoeists A canoe is a lightweight narrow watercraft, water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle. In British Englis ... especially when crossing Ungava from west to east.http://www.nrsweb.com/services/newsletter/2007/rtnStory_0207b.asp Crossing the Ungava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baie-d'Hudson, Quebec
Baie-d'Hudson is a very large unorganized territory (Quebec), unorganized territory in the Kativik Regional Government territory in the Nord-du-Québec region of Quebec. It is named after Hudson Bay. It consists of nearly the entire western part of northernmost Quebec. Bordering it to the east is the other large unorganized territory in Kativik, Rivière-Koksoak, Quebec, Rivière-Koksoak. Its population in the Canada 2021 Census was 5; enclaved within it, however, are various northern village (Quebec), northern villages (i.e., Inuit communities), a Cree reserved land (Quebec), Cree reserved land, and a Cree village municipality (Quebec), Cree village municipality. In the Canada 2011 Census, 2011 census it had a population of 0. References {{authority control Unorganized territories in Nord-du-Québec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians. Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most of ''Homo sapiens'' history, saw humans moving out of Africa, settling in new lands, and developing distinct cultures in relative isolation. Early explorers settled in Europe and Asia; 14,000 years ago, some crossed the Ice Age land bridge from Siberia to Alaska, and moved southbound to settle in the Americas. For the most part, these cultures were ignorant of each other's existence. The second period of exploration, occurring over the last 10,000 years, saw increased cross-cultural exchange through trade and exploration, and marked a new era of cultural intermingling, and more recently, convergence. Early writings about exploration date back to the 4th millennium B.C. in ancient Egypt. One of the earliest and most impactful thinkers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungava Bay
Ungava Bay (french: baie d'Ungava, ; iu, ᐅᖓᕙ ᑲᖏᖅᓗᒃ/) is a bay in northeastern Canada separating Nunavik (far northern Quebec) from Baffin Island. Although not geographically apparent, it is considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean for climatic reasons. The bay is roughly oval-shaped, about at its widest point and about in length; it has an area of approximately . It is generally fairly shallow, under , though at its border with the Atlantic Ocean depths of almost are reached. Geography Although it is quite close to the open Atlantic (separated only by Hudson Strait), Ungava Bay is part of the Arctic Ocean. Ungava Bay is separated from Hudson Bay by the Ungava Peninsula. Akpatok Island is largest of the many islands in Ungava Bay. Bathymetric studies suggest that Ungava Bay may be the remnant of an impact crater (age unknown) approximately in diameter. The southwestern corner of Ungava Bay vies with the Bay of Fundy for the highest tidal range in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: baie d'Hudson), sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. Although not geographically apparent, it is for climatic reasons considered to be a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It Hudson Bay drainage basin, drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The Cree language, Eastern Cree name for Hudson an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor General Of Canada
The governor general of Canada (french: gouverneure générale du Canada) is the federal viceregal representative of the . The is head of state of Canada and the 14 other Commonwealth realms, but resides in oldest and most populous realm, the United Kingdom. The , on the advice of Canadian prime minister, appoints a governor general to carry on the Government of Canada in the 's name, performing most of constitutional and ceremonial duties. The commission is for an indefinite period—known as serving ''at Majesty's pleasure''—though five years is the usual length of time. Since 1959, it has also been traditional to alternate between francophone and anglophone officeholders—although many recent governors general have been bilingual. The office began in the 17th century, when the French crown appointed governors of the colony of Canada. Following the British conquest of the colony, the British monarch appointed governors of the Province of Quebec (later the Canadas) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
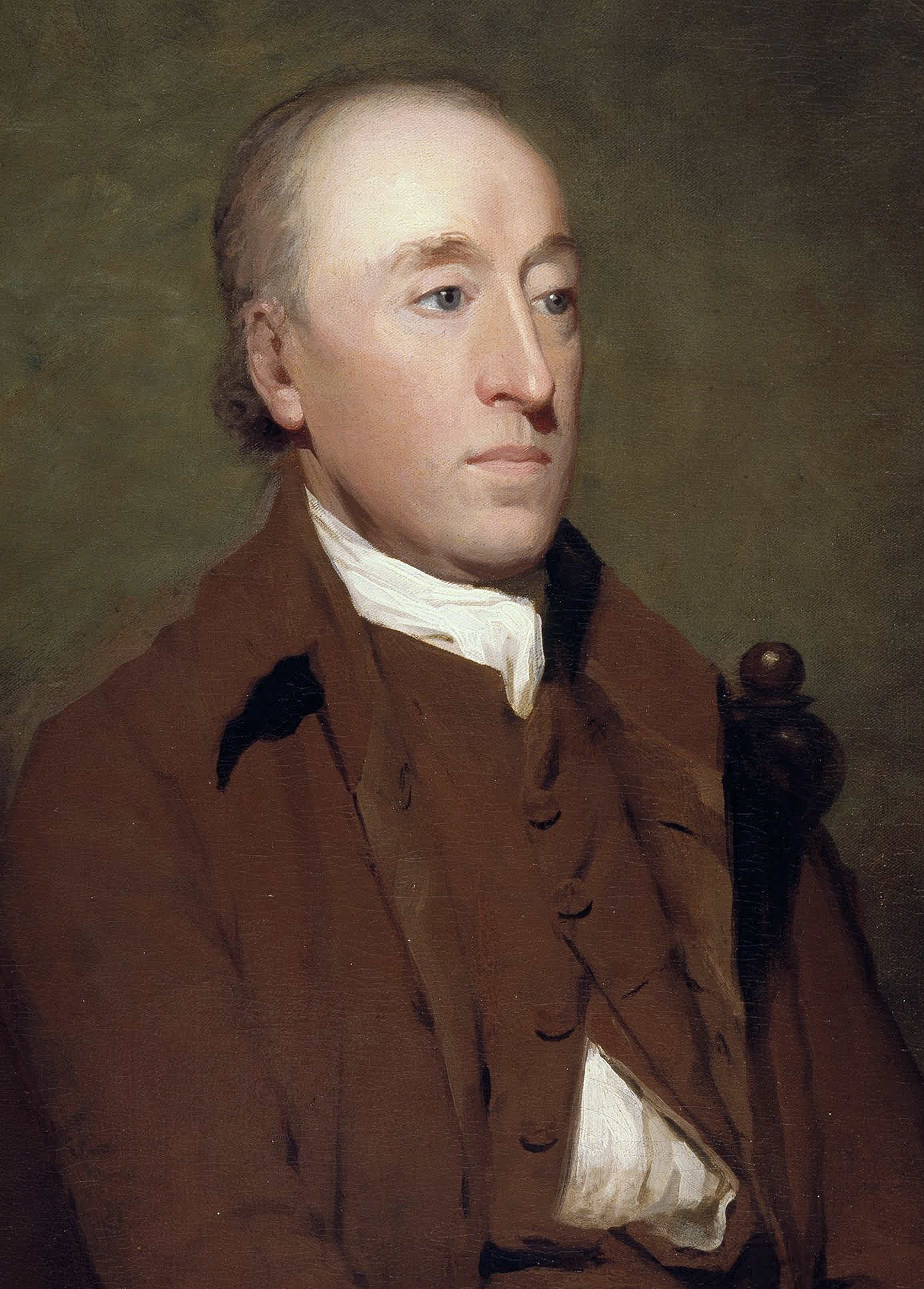
Gilbert Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 4th Earl Of Minto
Gilbert John Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 4th Earl of Minto, (; 9 July 18451 March 1914), known as Viscount Melgund by courtesy from 1859 to 1891, was a British peer and politician who served as Governor General of Canada, the eighth since Canadian Confederation, and as Viceroy and Governor-General of India, the country's 17th. Early life and career Minto was born in London, the son of William Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 3rd Earl of Minto, and Emma, daughter of General Sir Thomas Hislop, 1st Baronet. After the death of his grandfather in 1859 he became known by the courtesy title of Viscount Melgund. After completing his education at Eton College and Trinity College, Cambridge, he was commissioned a Lieutenant in the Scots Guards in 1867, but left in 1870. He joined the 1st Roxburghshire Mounted Rifle Volunteer Corps as a captain in 1872. In 1874, in the capacity of a newspaper correspondent, he witnessed the operations of the Carlists in Spain; he took service with the Turkish ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Peter Low
Albert Peter Low (May 24, 1861 – October 9, 1942) was a Canadian geologist, explorer and athlete. His explorations of 1893–1895 were important in declaring Canada's sovereignty over the Arctic, and eventually defining the border between Quebec and Labrador. Biography Albert Peter Low was born in Montreal, Quebec, and attended McGill University, graduating in 1882. He moved to Ottawa, Ontario to work as a surveyor and explorer with the Geological Survey of Canada. Low was recognized by senior officials for his excellent work and handed a series of scientific assignments in the North. Although his career is dotted with distinguished work, Low is perhaps best remembered as the commander of a 1903-04 Dominion expedition to declare Canada's authority over the Arctic, a journey that resulted in a bestselling book, ''The Cruise of the Neptune''. In 1906, he was appointed director of the Geological Survey of Canada. In 1907, he became the first deputy minister of the Natural Resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research (field work) is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors searching for natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, precious and base metals. They are also in the forefront of preventing and mitigating damage from natural hazards and disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Their studies are used to warn the general public of the occurrence of these events. Geologists are also important contributors to climate ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the largest province by area and the second-largest by population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York in the United States. Between 1534 and 1763, Quebec was called ''Canada'' and was the most developed colony in New France. Following the Seven Years' War, Quebec b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
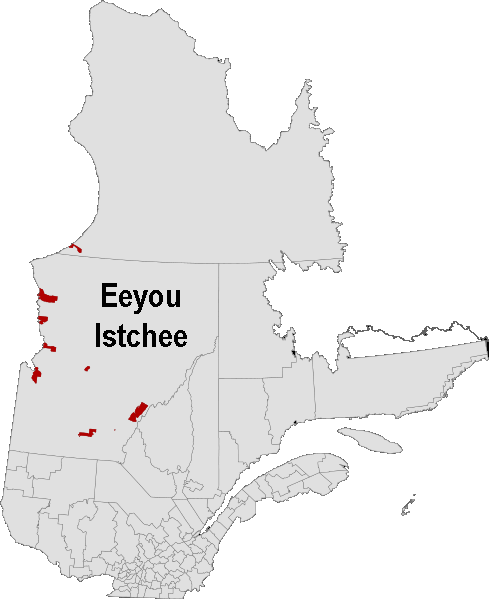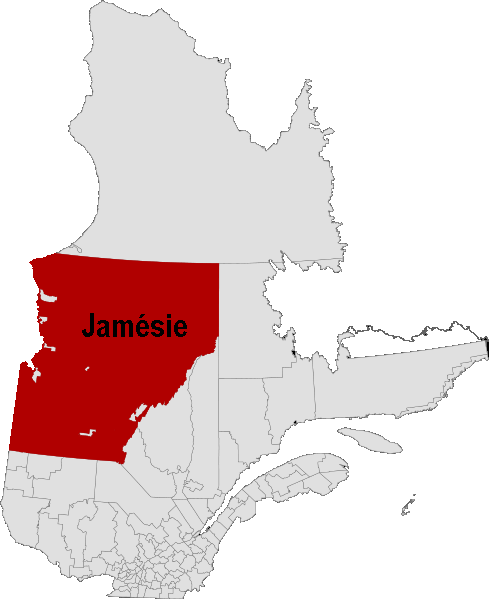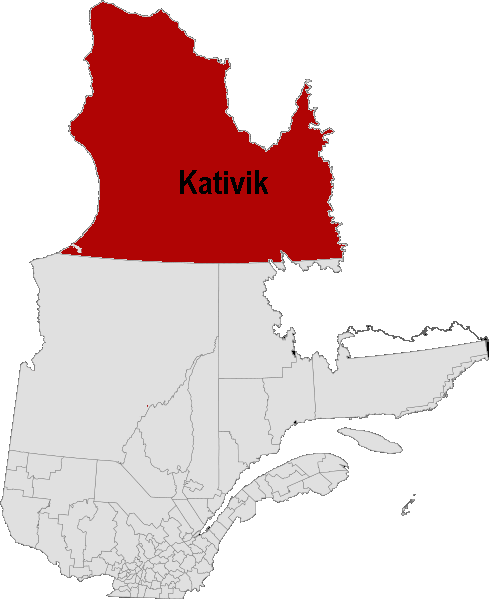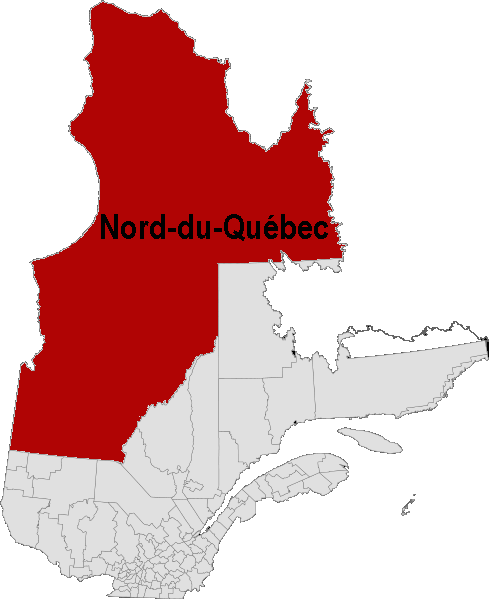
Kativik, Quebec
Kativik is a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) of Quebec, with geographical code 992. Its land area is 443,372.20 km2 (171,186.96 sq mi), and its population was 12,090 at the 2011 Census of Canada. Together with the TEs of Jamésie and Eeyou Istchee, it forms the administrative region and census division (CD) of Nord-du-Québec. The TE of Kativik is coextensive with the territory of the Kativik Regional Government. It comprises all of Nunavik except the Cree reserved land (TC) of Whapmagoostui and the Cree village municipality (VC) also called Whapmagoostui, which belong to Eeyou Istchee TE. Subdivisions The TE of Kativik consists of the following municipal units: * the unorganized territories (NO) of: :* Rivière-Koksoak :* Baie-d'Hudson * the Naskapi village (VK) of: :* Kawawachikamach (but not the Naskapi reserved land (TK) of the same name, Kawawachikamach, which lies detached, to its south, near Schefferville in the Caniapiscau Regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; iu, ᓄᓇᕕᒃ) comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homeland of the Inuit of Quebec and part of the wider Inuit Nunangat. Almost all of the 14,045 inhabitants ( 2021 census) of the region, of whom 90% are Inuit, live in fourteen northern villages on the coast of Nunavik and in the Cree reserved land (TC) of Whapmagoostui, near the northern village of Kuujjuarapik. means "great land" in the local dialect of Inuktitut and the Inuit inhabitants of the region call themselves . Until 1912, the region was part of the District of Ungava of the Northwest Territories. Negotiations for regional autonomy and resolution of outstanding land claims took place in the 2000s. The seat of government would be Kuujjuaq. Negotiations on better empowering Inuit political rights in their land are still ongoing. A flag for N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungava Peninsula
The Ungava Peninsula of Nunavik, Quebec, Canada, is bounded by Hudson Bay to the west, Hudson Strait to the north, and Ungava Bay to the east. This peninsula is part of the Labrador Peninsula, and covers about . Its northernmost point is Cape Wolstenholme, which is also the northernmost point of Quebec. The peninsula is also part of the Canadian Shield, and consists entirely of treeless tundra dissected by large numbers of rivers and glacial lakes, flowing generally east–west in a parallel fashion. The peninsula was not deglaciated until 6,500 years ago (11,500 years after the Last Glacial Maximum) and is believed to have been the prehistoric centre from which the vast Laurentide Ice Sheet spread over most of North America during the last glacial epoch. Climate The climate is extremely cold (''Dfc'' in the Köppen climate classification) because the Labrador Current keeps the region (and all of northern Québec) colder in the summer than other regions at comparable latitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |