|
Ladakhi–Balti Languages
The Ladakhi–Balti languages (ལ་དྭགས་དང་སྦལ་ཏི་སྐད)or Western Archaic Tibetan languages are a subgroup of the Tibetic languages spoken in the Ladakh region of India and in the Gilgit-Baltistan territory of Pakistan. The Ladakhi, Zangskari, Changthang skat is easily mutually intelligible to each other. The Purgi language is intermediate between Balti language and the Ladakhi language and the Purgi language is intelligible to both Ladakhi and Balti speakers. The Purgi language and the Shamskat are very close to each other among these language groups. However, the Ladakhi and Balti languages are slightly lesser intelligible to each other because of the accent, however the vocabulary is the same among these two languages. The group includes: * Ladakhi or Bauti/Bhoti (Ladakh) * Zangskari (Ladakh) * Purgi (Ladakh, Baltistan) * Balti (Baltistan, Ladakh) * Chorbat Skad (Baltistan) * Changthang (Tibet, Ladakh, Baltistan) * Skardu Skad (Baltist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir, state of India, located in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the vicinity of the Karakoram and westernmost Himalayan mountain ranges. From 1947 to 2019, Ladakh was part of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since the partition of the subcontinent in 1947." Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China." Ladakh is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, both the Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and the Pakistan-administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skardu
, nickname = , motto = , image_skyline = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Gilgit Baltistan#Pakistan , pushpin_label_position = left , pushpin_relief = , area_total_km2 = 77 , elevation_m = 2228 , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Pakistan , subdivision_type1 = Adm. Unit , subdivision_name1 = Gilgit−Baltistan , subdivision_type2 = District , subdivision_name2 = Skardu District , population_total = 26,023 , population_as_of = 1998 , timezone = PKT , utc_offset = +5:00 , coordinates = , website = , footnotes = Skardu ( ur, , translit=Skardū, ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Pakistan
Pakistan is a multilingual country with dozens of languages spoken as first languages. The majority of Pakistan's languages belong to the Indo-Iranian group of the Indo-European language family. Urdu is the national language and the lingua franca of Pakistan, and while sharing official status with English, it is the preferred and dominant language used for inter-communication between different ethnic groups. Numerous regional languages are spoken as first languages by Pakistan's various ethnolinguistic groups. Languages with more than a million speakers each include Punjabi, Pashto, Sindhi, Saraiki, Urdu, Balochi, Hindko, Pahari-Pothwari and Brahui. There are approximately 60 local languages with less than a million speakers. List of languages The 2022 edition of ''Ethnologue'' lists 77 established languages in Pakistan. Of these, 68 are indigenous and 9 are non-indigenous. In terms of their vitality, 4 are classified as 'institutional', 24 are 'developing', 30 are 'vig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Gilgit-Baltistan
Gilgit-Baltistan (; ), formerly known as the Northern Areas, is a region administered by Pakistan as an administrative territory, and constituting the northern portion of the larger Kashmir region which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947, and between India and China from somewhat later.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the tertiary sources (a) through (d), reflecting due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (e) through (g) below, "held" is also considered politicized usage, as is the term "occupied," (see (h) below): (a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Ladakh
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamskat
The Shamskat dialect ( lbj, ) of the Ladakhi language is spoken in the Sham region of Ladakh, a region administered by India as a union territory. Along the Indus, there is a clear geographical boundary between two dialects of Shamskat and Kenskat. Nimo, the first village of Shamskat speakers, lies in the sharply cut basin near the narrow gorge of Indus river. It is the predominant language in the west of the Buddhist-dominated district of Leh. Shamskat pronunciation resembles classical Tibetan language. Shamskat retains its classical Tibetan vocabulary while the Balti language and Purgi language have little influence from its neighbour Shina vocabulary. The native speakers of these languages are called shamma. Pronunciation Shamskat is usually written using Tibetan script, with the pronunciation being much closer to written Classical Tibetan than most other Tibetic languages. Shamskat pronounces many of the prefix, suffix and head letters that are silent in many othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
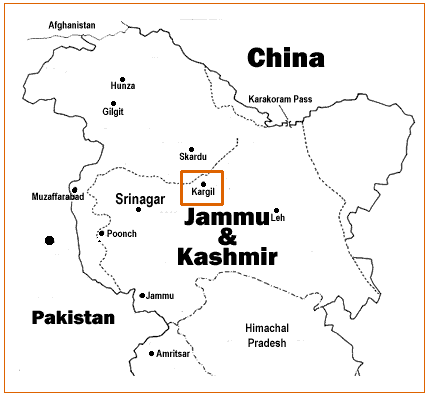
Kargil
Kargil ( lbj, ) is a city and a joint capital of the union territory of Ladakh, India. It is also the headquarters of the Kargil district. It is the second-largest city in Ladakh after Leh. Kargil is located to the east of Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir, and to the west of Leh. It is the centre point of the Suru River. Etymology The name ''Kargil'' is said to derive from the words ''Khar'', meaning castle, and ''rKil'' meaning "centre". "Kargil denotes a place between many forts, a central place where people could stay". It appears to be a fitting description for a place that is equidistant from Srinagar, Leh and Skardu Historically, the region around Kargil was called Purig. A major study of the history of Purig is included in the 1987 book ''Qadeem Ladakh'' by Kacho Sikander Khan, which includes genealogies of various dynasties that ruled the region. History Kargil is the main town in the historical region of Purig, which consists of the Suru river basin. It was n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharmang
The Kharmang Valley (), also known as Kartaksho, is one of the five main valleys situated in Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan. The area became an individual district in 2015, with its temporary headquarters set at the town of Tolti. The valley is located approximately from the city of Skardu. Tourist destinations in the area include Manthokha Waterfall, Khamosh Waterfall Mehdiabad Valley and Kharmang khas valley. Kharmang is where the Indus River enters Pakistani-controlled territory from the Leh district in Indian-controlled territory. Etymology ''Kahrmang'' is a Balti word that consists of two parts (''khar'' means "fort" and ''mang'' means "abundant"). The name ''Kharmang'' was given to the valley in the era of Ali Sher Khan Anchan, who built many forts in this region because of its strategic importance. Geography According to the ''Gazetteer of Kashmir and Ladak'' (1890), Kharmang is an old ''ilaqa'' of Baltistan that consists of the right bank of Indus from the borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaplu
Khaplu (Urdu: ) and ( Balti: ཁཔ་ལུ།), also spelt Khapalu, is a city that serves as the administrative capital of the Ghanche District of Gilgit-Baltistan, in northern Pakistan. Lying east of the city of Skardu, it was the second-largest kingdom in old Baltistan of the Yabgo dynasty. It guarded the trade route to Ladakh along the Shyok River east of its confluence with the Indus. Khaplu is a base for trekking into the Hushe valley which leads to the high peaks of Masherbrum, K6, K7, and Chogolisa. Khaplu has a 700-year-old mosque, Chaqchan, founded by Ameer Kabeer Syed Ali Hamadani (RA). Other tourist sites include Ehlie broq, Hanjor, ThoqsiKhar, Kaldaq, and Shyok River views. History According to tradition, Syed Ali Hamdani arrived to Khaplu in the late 14th century and converted the locals to Islam. To this day, mosques and khanqahs attributed to him exist in the region. The first mention of the former small kingdom called Khápula is in Mirza Haidar's (149 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundu District
The Rondu District ( ur, ), also spelled Roundu District, is one of the 14 districts of Pakistan-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan. The district encompasses the entire Roundu Valley, which is the fourth-largest valley in Gilgit-Baltistan, after the Skardu Valley, the Khaplu Valley, and the Shigar Valley The valley is situated in the western part of the Baltistan Division and forms the main trade and travel route between the Baltistan Division and the Gilgit Division. The Rondu District was created out of the Skardu District in 2019. Demographics The people of the Rondu Valley are predominantly Balti people, who speak the Balti language, but there are a significant number of Shina speaking people, as well. People of the Roundu valley belong to Shia sect of Islam. The district headquarters is the town of Dambudas, which is about 65–70 km from Skardu. Although the population of Dambudas is less than that of the Stak, Thorchay, and Tormik valleys, Dambudas D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shigar
Shigar () is the headquarter of its namesake district and tehsil in the Baltistan division of Gilgit–Baltistan in northern Pakistan. It is located at the bank of Shigar River in the most remote and dramatic part of the region. It is a popular site for tourists and trekkers and contains many historical buildings of architectural significance associated with several different communities. The town is inhabited almost exclusively by the Balti people of Tibetan descent. Almost 65% of the population belongs to the Shia sect of Islam, 26% belongs to the Norbakhshi sect and the remaining belong to the Sunni sect. It is the gateway to the great mountain range of Karakoram including where 5 Eight-thousanders of the world falls, including the K2. The town serves as a gateway to the Karakoram mountains including K2, via the Shigar Valley. History According to tradition, Syed Ali Hamdani arrived to Shigar in the late 14th century and converted the locals to Islam. To this day, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |