|
LacI
The ''lac'' repressor (LacI) is a DNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of genes coding for proteins involved in the metabolism of lactose in bacteria. These genes are repressed when lactose is not available to the cell, ensuring that the bacterium only invests energy in the production of machinery necessary for uptake and utilization of lactose when lactose is present. When lactose becomes available, it is firstly converted into allolactose by β-Galactosidase (lacZ) in bacteria. The DNA binding ability of lac repressor bound with allolactose is inhibited due to allosteric regulation, thereby genes coding for proteins involved in lactose uptake and utilization can be expressed. Function The ''lac'' repressor (LacI) operates by a helix-turn-helix motif in its DNA-binding domain, binding base-specifically to the major groove of the operator region of the ''lac'' operon, with base contacts also made by residues of symmetry-related alpha helices, the "hinge" he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
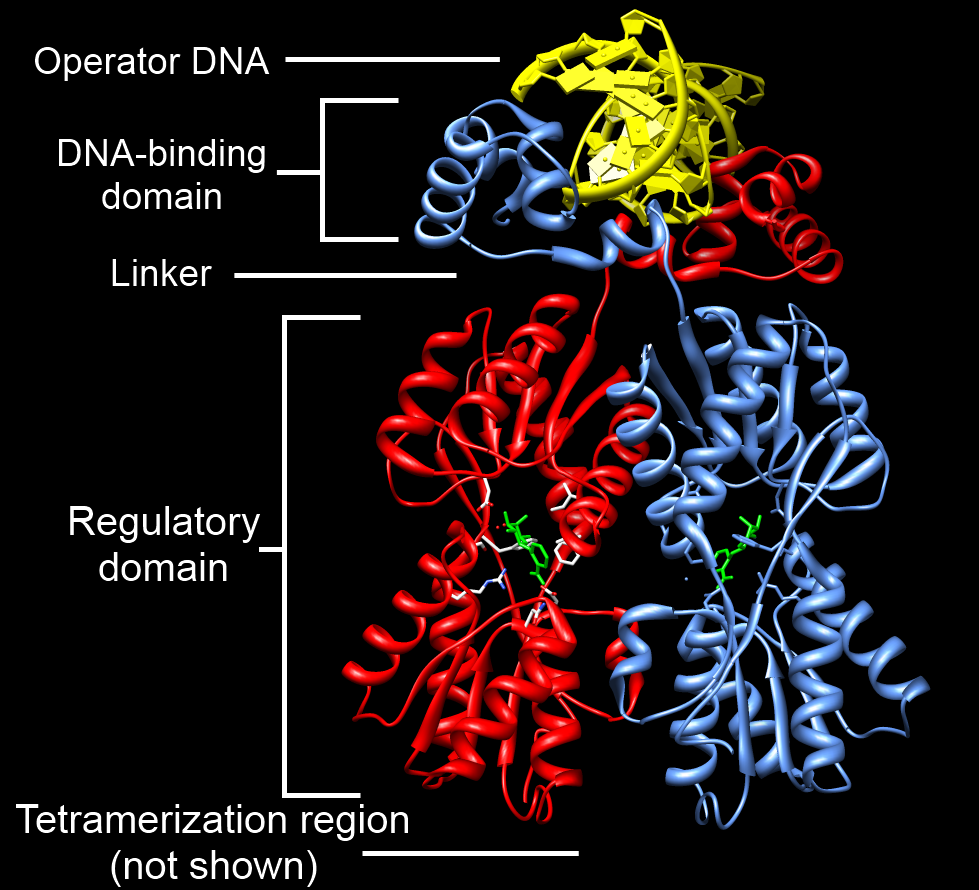
LacI Dimer Structure Annotated
The ''lac'' repressor (LacI) is a DNA-binding protein that inhibits the Gene expression, expression of genes coding for proteins involved in the metabolism of lactose in bacteria. These genes are repressed when lactose is not available to the cell, ensuring that the bacterium only invests energy in the production of machinery necessary for uptake and utilization of lactose when lactose is present. When lactose becomes available, it is firstly converted into allolactose by Beta-galactosidase, β-Galactosidase (Lac operon, lacZ) in bacteria. The DNA binding ability of lac repressor bound with allolactose is inhibited due to allosteric regulation, thereby genes coding for proteins involved in lactose uptake and utilization can be expressed. Function The ''lac'' repressor (LacI) operates by a helix-turn-helix Structural motif, motif in its DNA-binding domain, binding base-specifically to the major groove of the Operon, operator region of the lac operon, ''lac'' operon, with base co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lac Operon
The ''lactose'' operon (''lac'' operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in ''E. coli'' and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the ''lac'' operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the ''lac'' operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the ''lac'' operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965. Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lac Operon
The ''lactose'' operon (''lac'' operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in ''E. coli'' and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the ''lac'' operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the ''lac'' operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the ''lac'' operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965. Bacterial operons are polycistronic transcripts that are able to produce multiple proteins from one mRNA transcript. In this case, when l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, like in spinodal decomposition. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, and price values). The central idea of diffusion, however, is common to all of these: a substance or collection undergoing diffusion spreads out from a point or location at which there is a higher concentration of that substance or collection. A gradient is the change in the value of a quantity, for example, concentration, pressure, or temperature with the change in another variable, usually distance. A change in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site. The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site'' or ''regulatory site''. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change and/or a change in protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as ''allosteric activators'', whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called ''allosteric inhibitors''. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such as feedback from downstream products or feedforward from upstream substrates. Long-range allostery is especially important in cell signaling. Allosteric regulation is also particularly important in the cell's ability to adjust enzyme activity. The term ''allostery'' comes from the Ancient Greek ''allos'' (), "other", and ''stereos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binding And Unbinding Mechanism Of LacI
Binding may refer to: Computing * Binding, associating a network socket with a local port number and IP address * Data binding, the technique of connecting two data elements together ** UI data binding, linking a user interface element to an element of a domain model, such as a database field ** XML data binding, representing XML document data using objects and classes * Key binding, or keyboard shortcut, mapping key combinations to software functionality * Language binding, a library providing a functional interface to second library in a different programming language * Name binding, the association of code or data with an identifier in a programming language ** Late binding, name binding which is resolved at run-time rather than in pre-execution time Science * Binding problem, a term for several problems in cognitive science and philosophy ** Neural binding, synchronous activity of neurons and neuronal ensembles * Molecular binding, an attractive interaction between two molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
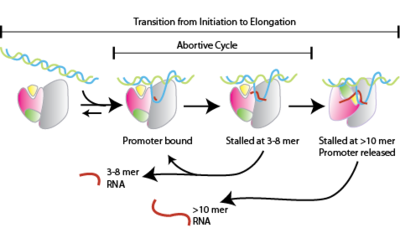
Abortive Initiation
Abortive initiation, also known as abortive transcription, is an early process of genetic transcription in which RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter and enters into cycles of synthesis of short mRNA transcripts which are released before the transcription complex leaves the promoter. This process occurs in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Abortive initiation is typically studied in the T3 and T7 RNA polymerases in bacteriophages and in ''E. coli''. Overall process Abortive initiation occurs prior to promoter clearance. # RNA polymerase binds to promoter DNA to form an RNA polymerase-promoter ''closed'' complex # RNA polymerase then unwinds one turn of DNA surrounding the transcription start site to yield an RNA polymerase-promoter ''open'' complex # RNA polymerase enters into abortive cycles of synthesis and releases short RNA products (contains less than 10 nucleotides) # RNA polymerase escapes the promoter and enters into the elongation step of transcription Mechanism Aborti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |