|
LSm
In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation. The Sm proteins were first discovered as antigens targeted by so-called anti-Sm antibodies in a patient with a form of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a debilitating autoimmune disease. They were named Sm proteins in honor of Stephanie Smith, a patient who suffered from SLE. Other proteins with very similar structures were subsequently discovered and named LSm proteins. New members of the LSm protein family continue to be identified and reported. Proteins with similar structures are gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LSm 1I5L 1
In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation. The Sm proteins were first discovered as antigens targeted by so-called anti-Sm antibodies in a patient with a form of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a debilitating autoimmune disease. They were named Sm proteins in honor of Stephanie Smith, a patient who suffered from SLE. Other proteins with very similar structures were subsequently discovered and named LSm proteins. New members of the LSm protein family continue to be identified and reported. Proteins with similar structures are grouped into a hierarchy of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SnRNP
snRNPs (pronounced "snurps"), or small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, are RNA-protein complexes that combine with unmodified pre-mRNA and various other proteins to form a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. The action of snRNPs is essential to the removal of introns from pre-mRNA, a critical aspect of post-transcriptional modification of RNA, occurring only in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Additionally, '' U7 snRNP'' is not involved in splicing at all, as U7 snRNP is responsible for processing the 3′ stem-loop of histone pre-mRNA. The two essential components of snRNPs are protein molecules and RNA. The RNA found within each snRNP particle is known as ''small nuclear RNA'', or snRNA, and is usually about 150 nucleotides in length. The snRNA component of the snRNP gives specificity to individual introns by " recognizing" the sequences of critical splicing signals at the 5' and 3' ends and branch site of introns. The snRN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U6 SnRNA
U6 snRNA is the non-coding small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U6 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein''), an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex that catalyzes the excision of introns from pre-mRNA. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes. The RNA sequence of U6 is the most highly conserved across species of all five of the snRNAs involved in the spliceosome, suggesting that the function of the U6 snRNA has remained both crucial and unchanged through evolution. It is common in vertebrate genomes to find many copies of the U6 snRNA gene or U6-derived pseudogenes. This prevalence of "back-ups" of the U6 snRNA gene in vertebrates further implies its evolutionary importance to organism viability. The U6 snRNA gene has been isolated in many organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmunity
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, post-infectious IBS, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), Alopecia Areata and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids. Autoimmunity means presence of antibodies or T cells that react with self-protein and is present in all individuals, even in normal health state. It causes autoimmune diseases if self-reactivity can lead to tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spliceosome
A spliceosome is a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) and numerous proteins. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules bind to specific proteins to form a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex (snRNP, pronounced “snurps”), which in turn combines with other snRNPs to form a large ribonucleoprotein complex called a spliceosome. The spliceosome removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA, a type of primary transcript. This process is generally referred to as splicing. An analogy is a film editor, who selectively cuts out irrelevant or incorrect material (equivalent to the introns) from the initial film and sends the cleaned-up version to the director for the final cut. However, sometimes the RNA within the intron acts as a ribozyme, splicing itself without the use of a spliceosome or protein enzymes. History In 1977, work by the Sharp and Roberts labs reveale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quantity relative molecular mass, as defined by IUPAC, is the ratio of the mass of a molecule to the unified atomic mass unit (also known as the dalton) and is unitless. The molecular mass and relative molecular mass are distinct from but related to the molar mass. The molar mass is defined as the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of a substance and is expressed in g/mol. That makes the molar mass an average of many particles or molecules, and the molecular mass the mass of one specific particle or molecule. The molar mass is usually the more appropriate figure when dealing with macroscopic (weigh-able) quantities of a substance. The definition of molecular weight is most authoritatively synonymous with relative molecular mass; ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U5 SnRNA
U5 snRNA is a small nuclear RNA (snRNA) that participates in RNA splicing as a component of the spliceosome. It forms the U5 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein'') by associating with several proteins including Prp8 - the largest and most conserved protein in the spliceosome, Brr2 - a helicase Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separatin ... required for spliceosome activation, Snu114, and the 7 Sm proteins. U5 snRNA forms a coaxially-stacked series of helices that project into the active site of the spliceosome. Loop 1, which caps this series of helices, forms 4-5 base pairs with the 5'-exon during the two chemical reactions of splicing. This interaction appears to be especially important during step two of splicing, exon ligation. References Further reading * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
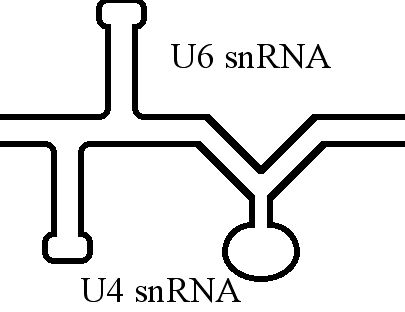
U4 SnRNA
The U4 small nuclear Ribo-Nucleic Acid (U4 snRNA) is a non-coding RNA component of the major or U2-dependent spliceosome – a eukaryotic molecular machine involved in the splicing of pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA). It forms a duplex with U6, and with each splicing round, it is displaced from the U6 snRNA (and the spliceosome) in an ATP-dependent manner, allowing U6 to re-fold and create the active site for splicing catalysis. A recycling process involving protein Brr2 releases U4 from U6, while protein Prp24 re-anneals U4 and U6. The crystal structure of a 5′ stem-loop of U4 in complex with a binding protein has been solved. Biological role The U4 snRNA has been shown to exist in a number of different formats including: bound to proteins as a small nuclear Ribo-Nuclear Protein snRNP, involved with the U6 snRNA in the di-snRNP, as well as involved with both the U6 snRNA and the U5 snRNA in the tri-snRNP. The different formats have been proposed to coincide with different temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U2 SnRNA
U2 spliceosomal snRNAs are a species of small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules found in the major spliceosomal (Sm) machinery of virtually all eukaryotic organisms. ''In vivo'', U2 snRNA along with its associated polypeptides assemble to produce the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP), an essential component of the major spliceosomal complex. The major spliceosomal-splicing pathway is occasionally referred to as U2 dependent, based on a class of Sm intron—found in mRNA primary transcripts—that are recognized exclusively by the U2 snRNP during early stages of spliceosomal assembly. In addition to U2 dependent intron recognition, U2 snRNA has been theorized to serve a catalytic role in the chemistry of pre-RNA splicing as well. Similar to ribosomal RNAs ( rRNAs), Sm snRNAs must mediate both RNA:RNA and RNA:protein contacts and hence have evolved specialized, highly conserved, primary and secondary structural elements to facilitate these types of interactions. Shortly after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U1 SnRNA
U1 spliceosomal RNA is the small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U1 snRNP (''small nuclear ribonucleoprotein''), an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification, and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes. Structure and function In humans, the U1 spliceosomal RNA is 164 bases long, forms four stem-loops, and possesses a 5'-trimethylguanosine five-prime cap. Bases 3 to 10 are a conserved sequence that base-pairs with the 5' splice site of introns during RNA splicing, and bases 126 to 133 form the Sm site, around which the Sm ring is assembled. Stem-loop I binds to the U1-70K protein, stem-loop II binds to the U1 A protein, stem-loops III and IV bind to the core RNP domain, a heteroheptameric Sm ring consisting of SmB/B', S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR. The number of non-coding RNAs within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest that there are thousands of non-coding transcripts. Many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function. There is no consensus in the literature on how much of non-coding transcription is functional. Some researchers have argued that many ncRNAs are non-functional (sometimes referred to as "junk RNA"), spurious transcriptions. Others, however, disagree, arguing instead that many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |