|
LGBT History In India
The LGBTQ community has a long recorded history in Ancient India due to the prevalence of the accepting Hindu spiritual traditions and cultures across the subcontinent, with a turbulent period following Islamic Turkic rule and Christian European colonialism that introduced homophobic and transphobic laws, thus criminalizing homosexuality and transsexuality. In the 21st century following independence, there has been a significant amount of progress made on liberalizing LGBTQ laws and reversing the homophobia and transphobia of the previous colonial era. Ancient period Hinduism provides a wide breadth of literary and artistic sources showing LGBTQ life in Ancient India. Hinduism does not have explicit morals condemning homosexuality nor transsexuality, and has taken various positions on the topic, ranging from containing positive descriptions of homosexual characters, acts and themes in its texts to being neutral or antagonistic towards it. The concept of sexual minorities was widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosexuality In Khajuraho Sculpture
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to people of the same sex. It "also refers to a person's sense of identity based on those attractions, related behaviors, and membership in a community of others who share those attractions." Along with bisexuality and heterosexuality, homosexuality is one of the three main categories of sexual orientation within the heterosexual–homosexual continuum. Scientists do not yet know the exact cause of sexual orientation, but they theorize that it is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental influences and do not view it as a choice. Although no single theory on the cause of sexual orientation has yet gained widespread support, scientists favor biologically based theories. There is considerably more evidence suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the later overseas territories governed by Portugal. It was one of the longest-lived empires in European history, lasting almost six centuries from the conquest of Ceuta in North Africa, in 1415, to the transfer of sovereignty over Macau to China in 1999. The empire began in the 15th century, and from the early 16th century it stretched across the globe, with bases in North and South America, Africa, and various regions of Asia and Oceania. The Portuguese Empire originated at the beginning of the Age of Discovery, and the power and influence of the Kingdom of Portugal would eventually expand across the globe. In the wake of the Reconquista, Portuguese sailors began exploring the coast of Africa and the Atlantic archipelagos in 1418–1419, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catamite
In Homosexuality in ancient Greece, ancient Greece and Homosexuality in ancient Rome, Rome, a catamite (Latin: ''catamitus'') was a Puberty, pubescent boy who was the intimate companion of an older male, usually in a pederastic relationship. It was generally a term of affection and literally means "Ganymede (mythology), Ganymede" in Latin, but it was also used as a term of insult when directed toward a grown man. The word derives from the proper noun ''Catamitus'', the Latinisation of names, Latinized form of Ganymede, the name of the beautiful Troy, Trojan youth abducted by Zeus to be his companion and cupbearer, according to Greek mythology. The Etruscan language, Etruscan form of the name was ''Catmite'', from an alternative Greek form of the name, ''Gadymedes''. In its modern usage, the term catamite refers to a boy as the passive or receiving partner in anal intercourse with a man. References in literature and popular culture *In Plato's dialogue ''Gorgias (dialogue), G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Orifice
The anus (Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, the residual semi-solid waste that remains after food digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, includes: matter which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; Summary at food material after the nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts. Amphibians, reptiles, and birds use the same orifice (known as the cloaca) for excreting liquid and solid wastes, for copulation and egg-laying. Monotreme mammals also have a cloaca, which is thought to be a feature inherited from the earliest amniotes via the therapsids. Marsupials have a single orifice for excreting both solids and liquids and, in females, a separate vagina for reproduction. Female placental ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Drummond
Edmund Drummond (17 January 1814 – 10 January 1895) was a British civil servant in India. He was the third son of James Drummond, 6th Viscount Strathallan (''de jure'' 8th Viscount) and the brother of William Drummond, 7th Viscount Strathallan. He was educated at Magdalene College, Cambridge. He studied law at the Middle Temple and was called to the bar in 1848. From 7 March 1863 to 10 March 1868 he held position of Lieutenant-Governor of the North-Western Provinces. In 1875, he became a member of the Council of India The Council of India was the name given at different times to two separate bodies associated with British rule in India. The original Council of India was established by the Charter Act of 1833 as a council of four formal advisors to the Governor ... His son Edmund Charles Drummond was an admiral. (thePeerage. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal Tribes Act
Since the 1870s, various pieces of colonial legislation in India during British rule were collectively called the Criminal Tribes Act (CTA), which criminalized entire communities by designating them as habitual criminals. Under these acts, ethnic or social communities in India were defined as "addicted to the systematic commission of non-bailable offences" such as thefts, and were registered by the government. Adult males of the groups were forced to report weekly to local police, and had restrictions on their movement imposed. The first CTA, the ''Criminal Tribes Act 1871'', applied mostly in North India, before it was extended to the Bengal Presidency and other areas in 1876, and updated to the ''Criminal Tribes Act 1911'', which included the Madras Presidency. The Act went through several amendments in the next decade, and, finally, the ''Criminal Tribes Act 1924'' incorporated all of them. At the time of Indian independence in 1947, thirteen million people in 127 communiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Section 377
Section 377 of the British colonial penal code criminalized all sexual acts "against the order of nature". The law was used to prosecute people engaging in oral and anal sex along with homosexual activity. The penal code remains in many former colonies, such as India (but has been repealed in Singapore) and has been used to criminalize third gender people, such as the '' apwint'' in Myanmar. In 2018, British Prime Minister Theresa May acknowledged how the legacies of British colonial anti-sodomy laws continue to persist today in the form of discrimination, violence, and death. History Although the act of sodomy was sometimes prosecuted in England under British common law, it was first codified in the British empire as Section 377 in the Indian Penal Code as "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" in 1860. Section 377 was then exported to other colonies and even to England itself, providing the legal model for the act of ' buggery' in the Offenses Against the Person Act ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Penal Code
The Indian Penal Code (IPC) is the official criminal code of India. It is a comprehensive code intended to cover all substantive aspects of criminal law. The code was drafted on the recommendations of first law commission of India established in 1834 under the Charter Act of 1833 under the chairmanship of Thomas Babington Macaulay. It came into force in British India during the early British Raj period in 1862. However, it did not apply automatically in the Princely states, which had their own courts and legal systems until the 1940s. The Code has since been amended several times and is now supplemented by other criminal provisions. After the partition of the British Indian Empire, the Indian Penal Code was inherited by India and Pakistan, where it continues independently as the Pakistan Penal Code. After the independece of Bangladesh from Pakistan, the code continued in force there. The Code was also adopted by the British colonial authorities in Colonial Burma, Ceylon (mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijra And Companions In Eastern Bengal
Hijra, Hijrah, Hegira, Hejira, Hijrat or Hijri may refer to: Islam * Hijrah (often written as ''Hejira'' in older texts), the migration of Muhammad from Mecca to Medina in 622 CE * Migration to Abyssinia or First Hegira, of Muhammad's followers in 615 CE * Lunar Hijri calendar (widely known as "the Islamic calendar", although there is more than one Islamic calendar), the lunar calendar used by the majority of Muslims ** Hijri year (, AH), the number of a year in the Hijri calendar * Solar Hijri calendar, a solar Islamic calendar used primarily in Iran and Afghanistan Literature * ''Hijra'', by the Malayalam poet Moyinkutty Vaidyar * ''Hegira'' (novel), by Greg Bear, 1979 *Hegira, a fictional exodus from Earth in the ''Hyperion Cantos'' novels Music * ''Hejira'' (album), by Joni Mitchell, 1976 * ''Hijrah'', a 2016 album by George Hirsch Other uses * HIJRA (Humanitarian Initiative Just Relief Aid), an African organization * Hijra (South Asia), a term for eunuchs, and interse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burhanpur
Burhanpur'' is a historical city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the administrative seat of Burhanpur District. It is situated on the north bank of the Tapti River and northeast of city of Mumbai, southwest of the state's capital city of Bhopal. The city is a Municipal Corporation. History Pre-Mughal period Burhanpur was an important city under the Rashtrakuta Dynasty from 753–982. Excavations of the Tapti River and Asirgarh Fort have discovered many coins, goddess idols and temples from the prehistoric era. However, Burhanpur came to prominence during the medieval period. In 1388, Malik Nasir Khan, the Faruqi dynasty Sultan of Khandesh, discovered Burhanpur, at the behest of Shaikh Zainuddin and named it after a well-known medieval Sufi saint, Burhan-ud-Din. Burhanpur became the capital of the Khandesh sultanate. Later, Miran Adil Khan II (reigned 1457–1501), another sultan of this dynasty, built a citadel and a number of palaces in Burhanpur. Dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



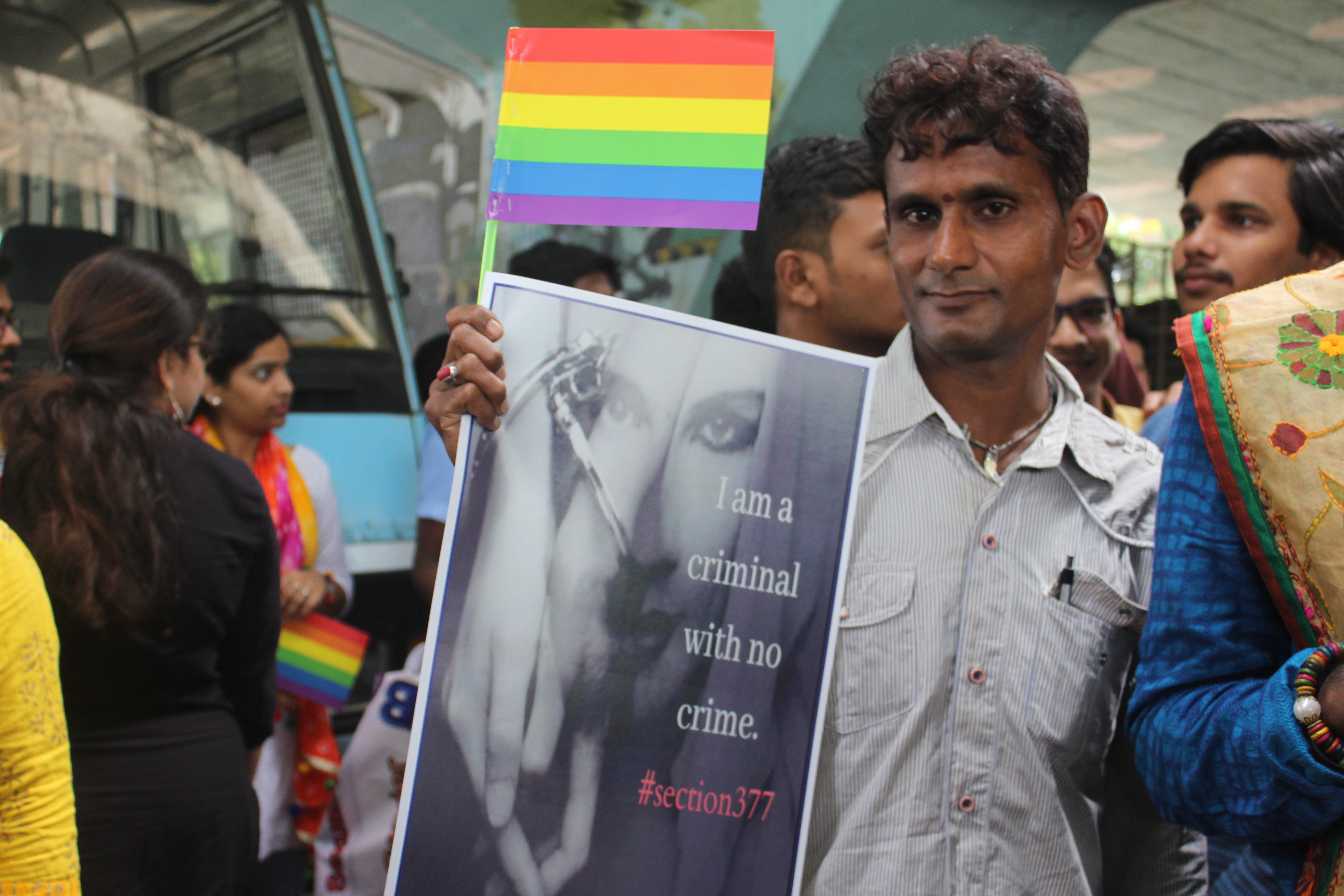

.jpg)
.png)