|
Kurt Dittmar
Kurt Dittmar (January 5, 1891 in Magdeburg – April 26, 1959 in Stadtoldendorf) was a German general in World War II, who served as the Official Military Commentator of the German Armed Forces. Biography Dittmar entered the German Imperial Army as Officer candidate in March 1909. He was assigned to the 4th Engineer Battalion (''Magdeburgisches Pionier-Bataillon Nr.4.'') and commissioned a second lieutenant one year later. During World War I, Dittmar served with the rank of captain as a company commander and also as a temporary battalion commander. After the War, Dittmar entered the Reichswehr and continued to serve with engineers units, where he reached the rank of Colonel (''Oberst'') to the date of April 1, 1936. With the outbreak of the World War II, Dittmar served as a commander of the engineer school in Berlin-Karlshorst. He became a divisional commander in February 1941 and led the 169th Infantry Division, which was later stationed in Finland. In the summer of 1941, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river. Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdeburg, was buried in the city's cathedral after his death. Magdeburg's version of German town law, known as Magdeburg rights, spread throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In the Late Middle Ages, Magdeburg was one of the largest and most prosperous German cities and a notable member of the Hanseatic League. One of the most notable people from the city is Otto von Guericke, famous for his experiments with the Magdeburg hemispheres. Magdeburg has been destroyed twice in its history. The Catholic League sacked Magdeburg in 1631, resulting in the death of 25,000 non-combatants, the largest loss of the Thirty Years' War. During the World War II the Allies bombed the city in 1945 and destroying much of it. After World War II the city belonged t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlshorst
Karlshorst (, ; ; literally meaning ''Karl's nest'') is a locality in the borough of Lichtenberg in Berlin. Located there are a harness racing track and the Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin (''HTW''), the largest University of Applied Sciences in Berlin, and the German-Russian Museum Berlin-Karlshorst. History Established in 1895 as the ''Carlshorst'' mansion's colony, Karlshorst from 1901 had access to the railway line from Berlin to Breslau (today Wrocław, Poland) and developed to a quite affluent residential area, sometimes referred to as " Dahlem of the East". The locality encompasses the Waldsiedlung, a garden city laid out between 1919 and 1921 according to plans by Peter Behrens. In April 1945, as the Red Army approached the Reich's capital, Marshal Georgy Zhukov, commander of the 1st Belorussian Front, established his headquarters at a former Heer officer's mess hall in Karlshorst, where on May 8, the unconditional surrender of the German forces was pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Tittel
Hermann or Herrmann may refer to: * Hermann (name), list of people with this name * Arminius, chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe in the 1st century, known as Hermann in the German language * Éditions Hermann, French publisher * Hermann, Missouri, a town on the Missouri River in the United States ** Hermann AVA, Missouri wine region * The German SC1000 bomb of World War II was nicknamed the "Hermann" by the British, in reference to Hermann Göring * Herrmann Hall, the former Hotel Del Monte, at the Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California * Memorial Hermann Healthcare System, a large health system in Southeast Texas * The Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI), a system to measure and describe thinking preferences in people * Hermann station (other), stations of the name * Hermann (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the western Oceanus Procellarum * Hermann Huppen, a Belgian comic book artist * Hermann 19, an American sailboat design built by Ted Herman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Kirchheim
Heinrich Kirchheim (6 April 1882 – 14 December 1973) was a German generalleutnant who served in both World War I and World War II. He is also one of few German officers who were awarded the Pour le Mérite and the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. He also served as a deputy member on the "Court of Military Honour," a drumhead court-martial that expelled many of the officers involved in the 20 July Plot from the Army before handing them over to the People's Court. Early military career Kirchheim entered the Imperial Army as an officer candidate on May 1, 1899. He became a Leutnant with the Infanterie-Regiment Prinz Friedrich der Niederlande (2. Westfälisches) Nr. 15 in Minden on October 18, 1900. On October 1, 1904, he transferred to the Schutztruppe of German Southwest Africa, going on an eight-year tour of duty in the colony. In January 1904, the native Herero tribe of Southwest Africa rebelled against German colonial rule over the expropriation of their land and cattle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Last Battle (Cornelius Ryan Book)
''The Last Battle'' is a 1966 book by Cornelius Ryan about the events leading up to the Battle of Berlin in World War II. The book, which was published by Simon & Schuster, is structured as an historical narrative. It is based on interviews with hundreds of persons actually involved, including Americans, British, Germans and Russians. Ryan was granted unique historical access to Soviet archives and Soviet generals involved in the battle, which was rare at the time."Book--Authors". - ''New York Times''. - December 22, 1965. The book was published simultaneously in the United Kingdom, France, West Germany, Italy, Spain, Norway, Denmark, Sweden, the Netherlands, Finland and Portugal, when it appeared in March 1966. Reception ''The Last Battle'' made news at the time it was published. The book revealed that the German capture of a top-secret Allied plan for dividing and occupying Germany (Operation Eclipse) helped stiffen German resistance and prolonged World War II. Also receivin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht Long Service Award
The Wehrmacht Long Service Award () was a military service decoration of Nazi Germany issued for satisfactory completion of a number of years in military service. History On 16 March, 1936, Adolf Hitler ordered the institution of a service award in four classes, each class reflecting the completion of a select number of years of military service. The award was bestowed by each branch of the Wehrmacht (army, navy, and air force) and was issued for four years service (fourth class – silver medal), 12 years (third class – gold medal), 18 years (second class – silver cross), 25 years (first class – gold cross), and 40 years (special class). The 40 year special class was introduced on 10 March 1939. Recipients of the higher level awards wore the decoration simultaneously with one lower year award. The manner they were worn was: *3rd Class with 4th Class (gold medal with silver medal) *2nd Class with 4th Class (silver cross with silver medal) *1st Class with 3rd Class (gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Honour Cross Of The World War 1914/1918
The Honour Cross of the World War 1914/1918 (german: Das Ehrenkreuz des Weltkrieges 1914/1918), commonly, but incorrectly, known as the Hindenburg Cross or the German WWI Service Cross was established by Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, President of the German Weimar Republic, by an order dated 13 July 1934, to commemorate service of the German people during the First World War. This was Germany's first official service medal for soldiers of Imperial Germany who had taken part in the war, and where they had since died it was also awarded to their surviving next-of-kin. Shortly after its issuance, the government of Nazi Germany declared the award as the only official service decoration of the First World War and further forbade the continued wearing of German Free Corps awards on any military or paramilitary uniform of a state or Nazi Party organization. The Honour Cross was awarded in three forms: * - for front-line veterans, with swords * - for non-combatant veterans, witho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic Cross
The Hanseatic Cross (German: ''Hanseatenkreuz'') was a military decoration of the three Hanseatic city-states of Bremen, Hamburg and Lübeck, who were members of the German Empire during World War I. Each republic established its own version of the cross, but the design and award criteria were similar for each. Establishment and criteria The Hanseatic Cross was jointly instituted by agreement of the senates of the three cities, with each senate ratifying the award on different days. The Lübeck version was established first, on 21 August 1915. The Hamburg version followed on 10 September and the Bremen version on 14 September. The cross was awarded for merit in war, and could be awarded to civilians as well as military personnel. When awarded for bravery or combat merit, it was the three cities' equivalent of the Prussian Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Crown (Prussia)
The Royal Order of the Crown (german: Königlicher Kronen-Orden) was a Prussian order of chivalry. Instituted in 1861 as an honour equal in rank to the Order of the Red Eagle, membership could only be conferred upon commissioned officers (or civilians of approximately equivalent status), but there was a medal associated with the order which could be earned by non-commissioned officers and enlisted men. Officially the Order of the Red Eagle and the Order of the Crown were equal. Most officials did however prefer to be appointed in the older Order of the Red Eagle. The Order of the Crown was often used as an award for someone who had to be rewarded while the Prussian government did not want to use the Order of the Red Eagle. Classes The Order had six classes: *Grand Cross – wore the Grand Cross badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *1st Class – wore the badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *2nd Class – wore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clasp To The Iron Cross
The Clasp to the Iron Cross (Spange zum Eisernen Kreuz) was a white metal medal clasp displayed on the uniforms of German Wehrmacht personnel who had been awarded the Iron Cross in World War I, and who again qualified for the decoration in World War II. During the war, over 100,000 clasps were awarded. Description A holder of the 1914 Iron Cross could qualify for the same grade of the 1939 Iron Cross. To permit the two awards to be worn together, a "1939 Clasp" (''Spange'') was established to be worn with the original 1914 Iron Cross. It depicted a national eagle clutching an oak leaf wreath surrounding a swastika above a trapezoid bearing the year ''1939''. For the Second Class, the clasp was attached to the ribbon A ribbon or riband is a thin band of material, typically cloth but also plastic or sometimes metal, used primarily as decorative binding and tying. Cloth ribbons are made of natural materials such as silk, cotton, and jute and of synthetic mater ... of the 1914 I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
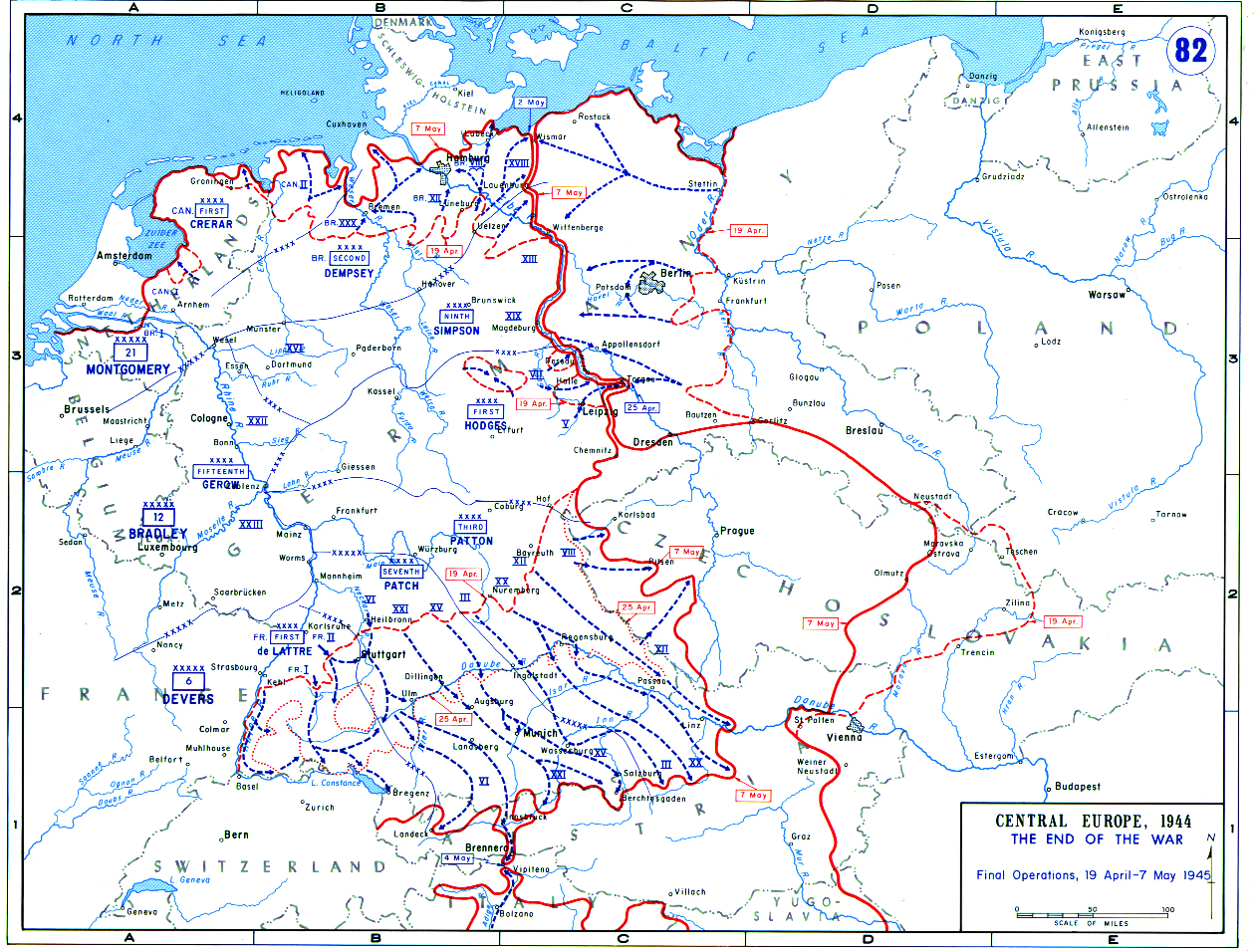
Alpine Fortress
The Alpine Fortress (german: Alpenfestung) or Alpine Redoubt was the World War II national redoubt planned by Heinrich Himmler in November and December 1943"Himmler started laying the plans for underground warfare in the last two months of 1943.... The plans are threefold, embracing (1) Open warfare directed from Hitler's mountain headquarters; (2) Sabotage and guerrilla activity conducted by partisan bands organized by districts, and (3) Propaganda warfare to be carried on by some 200,000 Nazi followers in Europe and elsewhere. Strongholds Established Already picked S.S. (elite) troops have been established in underground strongholds and hospitals in the Austrian, Bavarian and Italian Alpine area and it is the plan of Nazi leaders to flee to that region when the German military collapse comes" . for Germany's government and armed forces to retreat to an area from "southern Bavaria across western Austria to northern Italy"."But what of the top Nazis who cannot hide? With a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |