|
Kure Naval Arsenal
was one of four principal naval shipyards owned and operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. History The Kure Naval District was established at Kure, Hiroshima in 1889, as the second of the naval districts responsible for the defense of the Japanese home islands. Along with the establishment of the navy base, a ship repair facility was also constructed, initially by moving the equipment from the Onohama shipyards near Kobe. Construction was supervised by the French engineer Louis-Émile Bertin. The first warship constructed at Kure, '' Miyako'', was launched in 1897. The "Kure Shipyards" were officially renamed the "Kure Naval Arsenal" in 1903. Kure developed into one of the largest shipbuilding facilities in the Empire of Japan, capable of working with the largest vessels. The Arsenal included a major steel works (built with British assistance), and also facilities for producing naval artillery and projectiles. The battleships ''Yamato'' and '' Nagato'' were designed and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamato Battleship Under Fitting-out Works
was originally the area around today's Sakurai City in Nara Prefecture of Japan, which became Yamato Province and by extension a name for the whole of Japan. Yamato is also the dynastic name of the ruling Imperial House of Japan. Japanese history * Yamato people, the dominant ethnic group of Japan * Yamato period, when the Japanese Imperial court ruled from Yamato Province * Yamato clan, clan active in Japan since the Kofun period * ''Yamato-damashii'', the "Japanese spirit", or ''Yamato-gokoro'', the "Japanese heart/mind" * Yamato nadeshiko, the ideology of the perfect Japanese woman * Yamato Takeru, a legendary Japanese prince of the Yamato dynasty * Yamato-e, classical Japanese painting * ''Yamato-uta'', alternative term for ''waka'' (poetry) * Yamatai, ancient geographical term that may be associated with Yamato * Daiwa (other) is spelled using the same kanji as Yamato Geography Japan * Yamato Province, Japan, former province, present-day Nara Prefecture * Yama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Nagato
, named for Nagato Province, was a super-dreadnought battleship built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). Completed in 1920 as the lead ship of her class, she carried supplies for the survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923. The ship was modernized in 1934–1936 with improvements to her armor and machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. ''Nagato'' briefly participated in the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during the attack on Pearl Harbor. She covered the withdrawal of the attacking ships and did not participate in the attack itself. Other than participating in the Battle of Midway in June 1942, where she did not see combat, the ship spent most of the first two years of the Pacific War training in home waters. She was transferred to Truk in mid-1943, but did not see any combat until the Battle of the Philippine Sea in mid-1944 when she was attacked by American aircraft. ''Nagato'' did not fire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amagi-class Battlecruiser
The was a series of four battlecruisers planned for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) as part of the Eight-eight fleet in the early 1920s. The ships were to be named ''Amagi'', , ''Atago'', and ''Takao''. The ''Amagi'' design was essentially a lengthened version of the battleship, but with a thinner armored belt and deck, a more powerful propulsion system, and a modified secondary armament arrangement. They were to have carried the same main battery of ten guns and been capable of a top speed of . Limitations imposed by the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty prevented the class from being completed as designed. However, the treaty had a limited allowance for hulls already under construction to be converted into aircraft carriers. ''Amagi'' and ''Akagi'' were both intended for conversion, but an earthquake damaged the hull of ''Amagi'' so extensively that the ship was scrapped. ''Akagi'' was reconstructed as an aircraft carrier and served with distinction as part of the ''Kido But ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
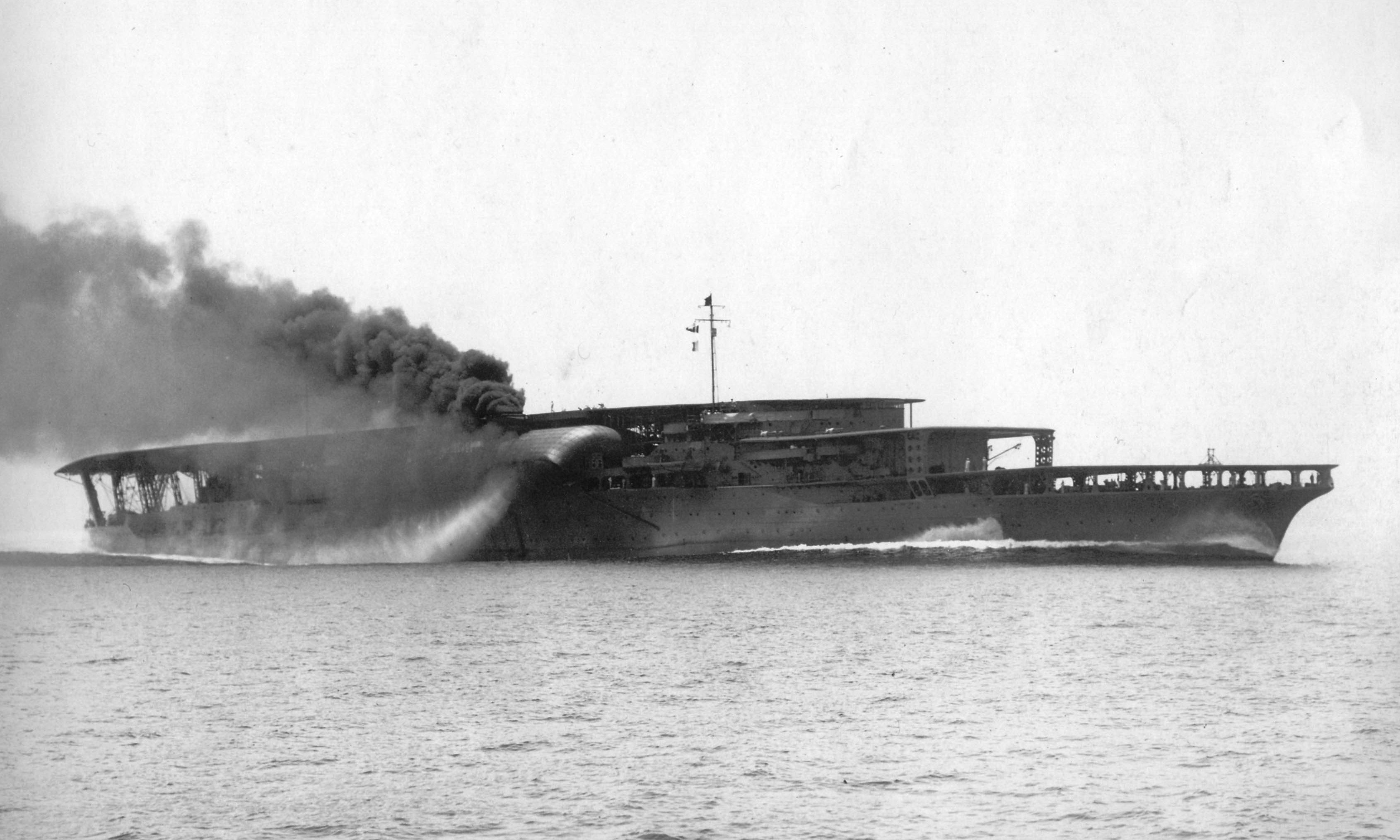
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Akagi
''Akagi'' (Japanese: 赤城, "red castle") was an aircraft carrier built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), named after Mount Akagi in present-day Gunma Prefecture. Though she was laid down as an , ''Akagi'' was converted to an aircraft carrier while still under construction to comply with the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty. The ship was rebuilt from 1935 to 1938 with her original three flight decks consolidated into a single enlarged flight deck and an island superstructure. The second Japanese aircraft carrier to enter service, and the first large or "fleet" carrier, ''Akagi'' and the related '' Kaga'' figured prominently in the development of the IJN's new carrier striking force doctrine that grouped carriers together, concentrating their air power. This doctrine enabled Japan to attain its strategic goals during the early stages of the Pacific War from December 1941 until mid-1942. ''Akagi''s aircraft served in the Second Sino-Japanese War in the late 1930s. Upon the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Aircraft Carrier Soryu 1937
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawachi-class Battleship
The was a two-ship class of dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the first decade of the 20th century. Both ships bombarded German fortifications at Tsingtao during the Battle of Tsingtao in 1914, but saw no other combat in World War I. sank in 1918 after an explosion in her ammunition magazine with the loss of over 600 officers and crewmen. was disarmed in 1922 and converted into a target ship two years later to meet the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty and served until she was sunk in 1945 by American carrier aircraft. The ship was refloated after the war and scrapped in 1946–1947. Background The ''Kawachi'' class was ordered on 22 June 1907 under the 1907 Warship Supplement Program after the Russo-Japanese War as Japan's first dreadnoughts,Lengerer, p. 74 although their construction was delayed by a severe depression. They were one of the first steps in the fulfillment of the recently adopted Eight-Eight Fleet Program that required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Battleship Settsu
was the second and last of the dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) in the first decade of the 20th century. Following the Japanese ship-naming conventions, ''Settsu'' was named after Settsu Province, now a part of Osaka prefecture. During World War I she bombarded German fortifications at Tsingtao during the Battle of Tsingtao in 1914, but saw no other combat. She was placed in reserve in 1919 and was disarmed in 1922 in accordance with the terms of the Washington Naval Treaty. Two years later, ''Settsu'' was converted into a target ship and she played a minor role at the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937. At the beginning of the Pacific War in 1941, the ship was used in an attempt to deceive the Allies as to the locations and activities of the Japanese aircraft carriers. ''Settsu'' reverted to her normal role as a target ship for the rest of the war; she was badly damaged when Allied aircraft carriers struck the naval base at Kure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagato-class Battleship
The were a pair of dreadnought battleships built for the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) towards the end of World War I, although they were not completed until after the war. The last of Japan's pre-Treaty capital ships, they were the first class to carry guns, the largest afloat and the first bigger than . , the lead ship of the class, frequently served as a flagship. Both ships carried supplies for the survivors of the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923. They were modernized in 1933–1936 with improvements to their armor and machinery and a rebuilt superstructure in the pagoda mast style. ''Nagato'' and her sister ship briefly participated in the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1937 and ''Nagato'' was the flagship of Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto during the attack on Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941 that began the Pacific War. The sisters participated in the Battle of Midway in June 1942, although they did not see any combat. ''Mutsu'' saw more active service than her sister because she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamato-class Battleship
The were two battleships of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), and , laid down leading up to World War II and completed as designed. A third hull laid down in 1940 was converted to an aircraft carrier, , during construction. Displacing nearly at full load, the completed battleships were the heaviest ever constructed. The class carried the largest naval artillery ever fitted to a warship, nine 460-mm (18.1 in) naval guns, each capable of firing shells over . Due to the threat of U.S. submarines and aircraft carriers, both ''Yamato'' and ''Musashi'' spent the majority of their careers in naval bases at Brunei, Truk, and Kure—deploying on several occasions in response to U.S. raids on Japanese bases. All three ships were sunk by the U.S. Navy; ''Musashi'' while participating in the Battle of Leyte Gulf in October 1944, the ''Shinano'' while under way from Yokosuka to Kure for fitting out in November 1944, and the ''Yamato'' while en route from Japan to Okinawa as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Marine United
(informally JMU) is a Japanese ship building marine engineering and service company headquartered in Yokohama, Japan. It's Japan’s second largest shipbuilder after Imabari Shipbuilding, with shipyard facilities in Kure, Hiroshima, Yokohama, Nagasu, Kumamoto, Maizuru, Kyoto and Mie prefectures. JMU's products include the design, manufacture, purchase and sale of both merchant and naval ships, offshore engineering and ship life cycle services. History Osaka Iron Works (Hitachi Zosen) established in 1881. Nippon Kokan (NKK) established by Asano zaibatsu in 1912. Both united and became Universal Shipbuilding Corporation in 2002. Ishikawajima Shipyard established in 1853. Uraga Dock ( Sumitomo Heavy Industries) established in 1893. Both united and became IHI Marine United in 2002, part of Ishikawajima-Harima Heavy Industries Co., Ltd., later renamed IHI Corporation Universal Shipbuilding Corporation and IHI Marine United Inc. united and became Japan Marine United in 2013. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender Of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) had become incapable of conducting major operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent. Together with the United Kingdom and China, the United States called for the unconditional surrender of the Japanese armed forces in the Potsdam Declaration on 26 July 1945—the alternative being "prompt and utter destruction". While publicly stating their intent to fight on to the bitter end, Japan's leaders (the Supreme Council for the Direction of the War, also known as the "Big Six") were privately making entreaties to the publicly neutral Soviet Union to mediate peace on terms more favorable to the Japanese. While maintaining a sufficient level of diplomatic engagement with the Japanese to give them the impression they might be wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
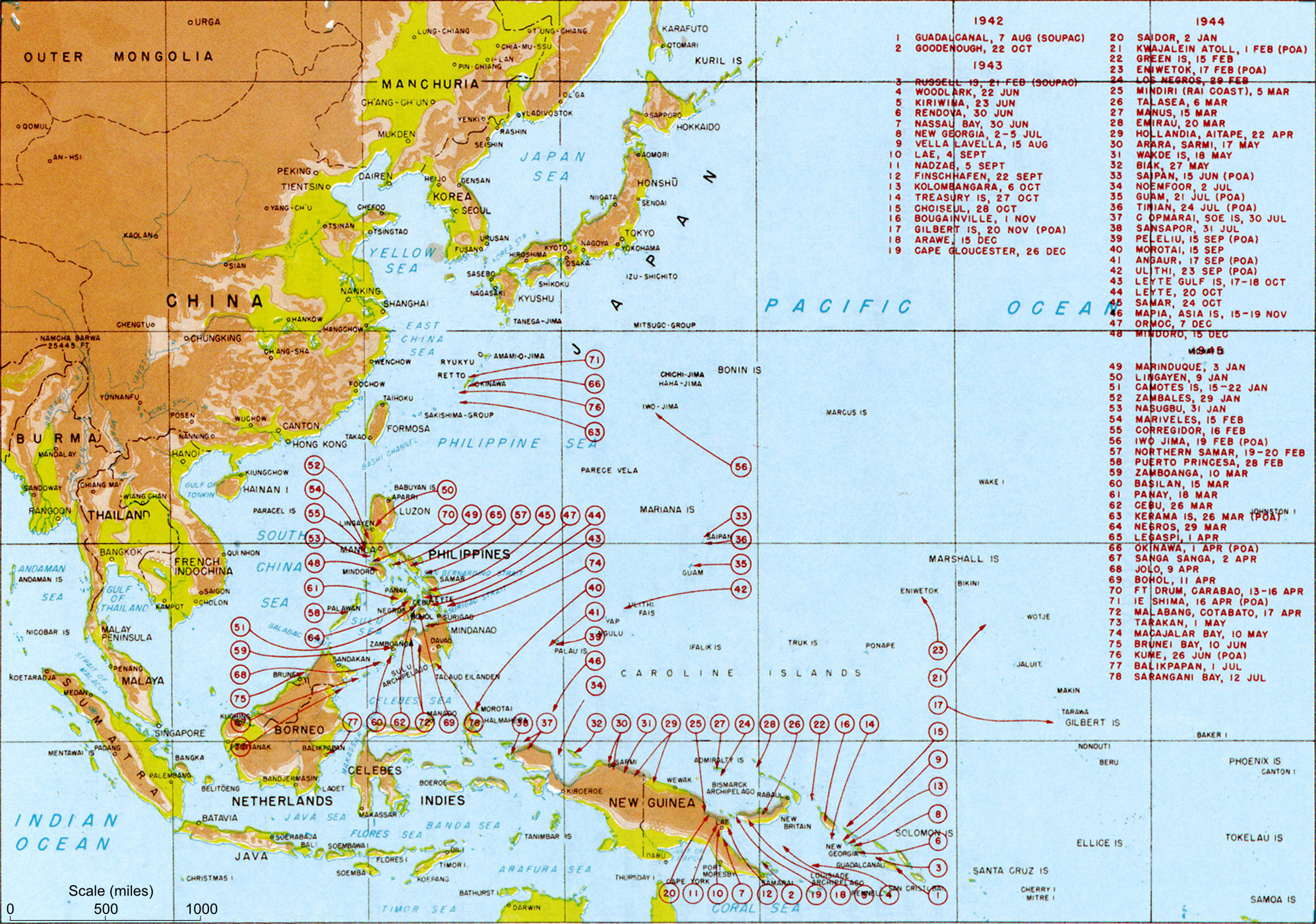
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War. The Second Sino-Japanese War between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China had been in progress since 7 July 1937, with hostilities dating back as far as 19 September 1931 with the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. However, it is more widely accepted that the Pacific War itself began on 7 December (8 December Japanese time) 1941, when the Japanese simultaneously invaded Thailand, attacked the British colonies of Malaya, Singapore, and Hong Kong as well as the United States military and naval bases in Hawaii, Wake Island, Guam, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw the Allies pitted against Japan, the latter ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |