|
Kurdish Democratic Union Party
The Democratic Union Party ( ku, Partiya Yekîtiya Demokrat (PYD) ; ar, حزب الاتحاد الديمقراطي, translit=Ḥizb al-Ittiḥad al-Dimuqraṭiy; syc, ܓܒܐ ܕܚܘܝܕܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܐܛܝܐ, translit=Gabo d'Ḥuyodo Demoqraṭoyo) is a Kurdish left-wing political party established on 20 September 2003 in northern Syria. It is a founding member of the National Coordination Body for Democratic Change. Carnegie Middle East Center, 1 March 2012The Kurdish Democratic Union Party/ref> It is the leading political party among Syrian Kurds. The PYD was established as a Syrian branch of the Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) in 2003, and both organizations are still closely affiliated through the Kurdistan Communities Union (KCK). Finland and Sweden’s alleged support for the PYD, is one of the points which caused Turkey to oppose Finland and Sweden’s NATO accession bid. Ideology On its website, the PYD describes itself as believing in "social equality, justice and the free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PYD Logo
PYD or pyd may refer to: * "PYD" (song), a 2013 single by Justin Bieber * Democratic Union Party (Syria) (''Partiya Yekîtiya Demokrat''), a Kurdish Syrian political party * Pyrin domain (PYD), or the protein domain * Positive youth development Positive youth development (PYD) programs are designed to optimize youth developmental progress. ''Youth.gov'' states that "PYD is an intentional, prosocial approach that engages youth within their communities, schools, organizations, peer groups, ... * .pyd, a file extension for the Python programming language {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Middle East Center
The Malcolm H. Kerr Carnegie Middle East Center, previously known as The Carnegie Middle East Center (CMEC) is a think tank and research center dealing with public policy in the Middle East. It was established in Beirut, Lebanon in November 2006 by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace The center is part of the network of Carnegie regional centers, including the Carnegie Moscow Center, the Carnegie–Tsinghua Center for Global Policy in Beijing, and Carnegie Europe, located in Brussels. In 2009 and 2015, the University of Pennsylvania’s Global “Go-To Think Tanks” annual report listed the Carnegie Middle East Center as the number one think tank in the Middle East and North Africa. Background The Carnegie Middle East Center is an independent policy research institute based in Beirut, Lebanon, and part of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. The center's scope of work includes political and economic developments in the Arab world, Turkey and Iran. It incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Nationalism
Kurdish nationalism (, ) is a nationalist political movement which asserts that Kurds are a nation and espouses the creation of an independent Kurdistan from Iran, Iraq, Syria and Turkey. Early Kurdish nationalism had its roots in the Ottoman Empire, within which Kurds were a significant ethnic group. With the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire, its Kurdish-majority territories were divided between the newly formed states of Turkey, Iraq, and Syria, making Kurds a significant ethnic minority in each state. Kurdish nationalist movements have long been suppressed by Turkey and the Arabs, Arab-majority states of Iraq, Iran and Syria, all of whom fear a potential independent Kurdistan. Since the 1970s, Iraqi Kurds have pursued the goal of greater autonomy and even outright independence against the Iraqi nationalist Ba'ath Party regimes, which responded with brutal repression, including the massacre of 182,000 Kurds in the Anfal genocide. The Kurdish–Turkish conflict (1978–pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of people),Anthony D. Smith, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, Ideology, History''. Polity (publisher), Polity, 2010. pp. 9, 25–30; especially with the aim of gaining and maintaining the nation's sovereignty (self-governance) over its homeland to create a nation-state. Nationalism holds that each nation should govern itself, free from outside interference (self-determination), that a nation is a natural and ideal basis for a polity, and that the nation is the only rightful source of political power. It further aims to build and maintain a single national identity, based on a combination of shared social characteristics such as culture, ethnicity, geographic location, language, politics (or the government), religion, traditions and belief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Rojava
The de facto Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria, sometimes referred to as "Rojava", is divided into several self-governing regions. The Afrin, Jazira and Euphrates Regions followed from the cantons established in January 2014 and were envisioned as sub-divisions for a future federalisation of Syria. The three cantons were later reorganized into three regions with subordinate cantons, areas, districts and communes. In March 2018, most of the Afrin Region was captured by the Turkish Armed Forces (TAF) and Syrian National Army (SNA) in Operation Olive Branch, becoming part of the Turkish occupation of northern Syria. The Afrin Region was reduced to an area around Tell Rifaat. In September 2018, the regions of Raqqa, Tabqa, Manbij and Deir ez-Zor were incorporated into the de facto autonomous region as well. Parts of the Euphrates and Jazira Regions also became occupied by the TAF and SNA after the October 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria The 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdullah Öcalan
Abdullah Öcalan ( ; ; born 4 April 1949), also known as Apo (short for Abdullah in Turkish and Kurdish for "uncle"), is a political prisoner and founding member of the militant Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK). Öcalan was based in Syria from 1979 to 1998. He helped found the PKK in 1978, and led it into the Kurdish–Turkish conflict in 1984. For most of his leadership, he was based in Syria, which provided sanctuary to the PKK until the late 1990s. After being forced to leave Syria, Öcalan was abducted in Nairobi in 1999 by the Turkish National Intelligence Agency (MIT) (with assistance of the USA) and taken to Turkey, where after a trial he was sentenced to death under Article 125 of the Turkish Penal Code, which concerns the formation of armed organizations. The sentence was commuted to aggravated life imprisonment when Turkey abolished the death penalty. From 1999 until 2009, he was the sole prisoner in İmralı prison in the Sea of Marmara, where he is still held. Ö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray Bookchin
Murray Bookchin (January 14, 1921 – July 30, 2006) was an American social theorist, author, orator, historian, and political philosopher. A pioneer in the environmental movement, Bookchin formulated and developed the theory of social ecology and urban planning within anarchist, libertarian socialist, and ecological thought. He was the author of two dozen books covering topics in politics, philosophy, history, urban affairs, and social ecology. Among the most important were ''Our Synthetic Environment'' (1962), ''Post-Scarcity Anarchism'' (1971), ''The Ecology of Freedom'' (1982) and ''Urbanization Without Cities'' (1987). In the late 1990s, he became disenchanted with what he saw as an increasingly apolitical " lifestylism" of the contemporary anarchist movement, stopped referring to himself as an anarchist, and founded his own libertarian socialist ideology called "communalism", which seeks to reconcile and expand Marxist, syndicalist, and anarchist thought. Bookchin wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Confederalism
Democratic confederalism ( ku, Konfederalîzma demokratîk), also known as Kurdish communalism or Apoism, is a political concept theorized by Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) leader Abdullah Öcalan about a system of democratic self-organization with the features of a confederation based on the principles of autonomy, direct democracy, political ecology, feminism, multiculturalism, self-defense, self-governance and elements of a cooperative economy. Influenced by social ecology, libertarian municipalism, Middle Eastern history and general state theory, Öcalan presents the concept as a political solution to Kurdish national aspirations, as well as other fundamental problems in countries in the region deeply rooted in class society, and as a route to freedom and democratization for people around the world. Although the liberation struggle of the PKK was originally guided by the prospect of creating a Kurdish nation state on a Marxist–Leninist basis, Öcalan became disil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Nikkei, with core editorial offices across Britain, the United States and continental Europe. In July 2015, Pearson sold the publication to Nikkei for £844 million (US$1.32 billion) after owning it since 1957. In 2019, it reported one million paying subscriptions, three-quarters of which were digital subscriptions. The newspaper has a prominent focus on financial journalism and economic analysis over generalist reporting, drawing both criticism and acclaim. The daily sponsors an annual book award and publishes a " Person of the Year" feature. The paper was founded in January 1888 as the ''London Financial Guide'' before rebranding a month later as the ''Financial Times''. It was first circulated around metropolitan London by James Sherid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobin
, logo = JacobinVignette03.jpg , logo_size = 180px , logo_caption = Seal of the Jacobin Club (1792–1794) , motto = "Live free or die"(french: Vivre libre ou mourir) , successor = Panthéon Club , formation = 1789 , founder = Maximilien Robespierre , founding_location = Versailles, France , dissolved = , type = Parliamentary group , status = Inactive , purpose = Establishment of a Jacobin society * 1789–1791: abolition of the Ancien Régime, creation of a parliament, introduction of a Constitution and separation of powers * 1791–1795: establishment of a republic, fusion of powers into the National Convention and establishment of an authoritarian-democratic state , headquarters = Dominican convent, Rue Saint-Honoré, Paris , region = France , methods = From democratic initiatives to public violence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
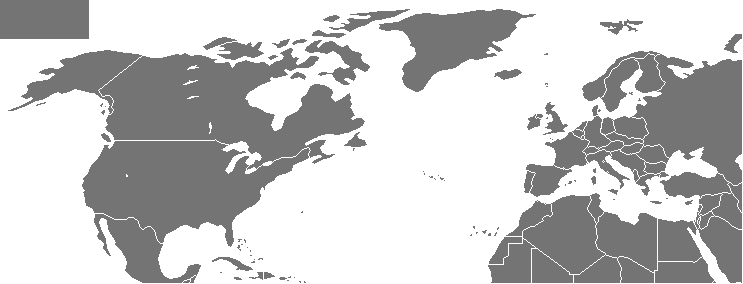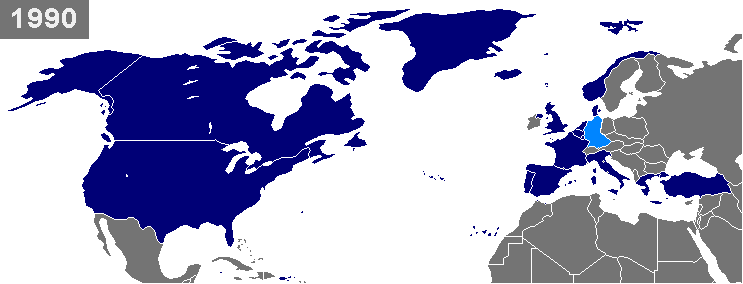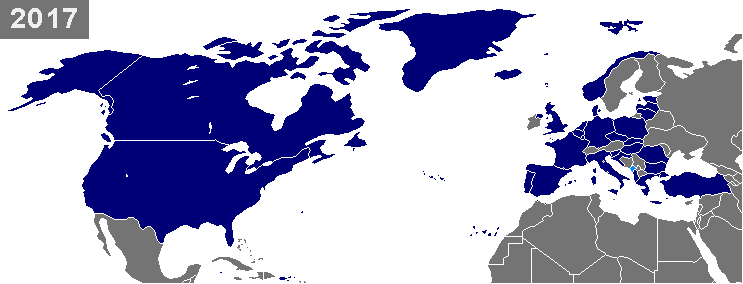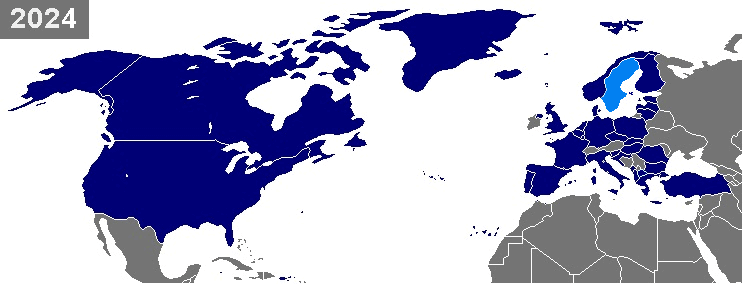
Enlargement Of NATO
NATO is a military alliance of twenty-eight European and two North American countries that constitutes a system of collective defense. The process of joining the alliance is governed by Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which allows for the invitation of "other European States" only and by subsequent agreements. Countries wishing to join must meet certain requirements and complete a multi-step process involving political dialog and military integration. The accession process is overseen by the North Atlantic Council, NATO's governing body. NATO was formed in 1949 with twelve founding members and has added new members eight times. The first additions were Greece and Turkey in 1952. In May 1955, West Germany joined NATO, which was one of the conditions agreed to as part of the end of the country's occupation by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, prompting the Soviet Union to form their own collective security alliance (commonly called the Warsaw Pact) la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey In NATO
Turkey has been a member of NATO since 1952, has its second largest army and is the host of the Allied Land Command headquarters. The Incirlik Air Base, Incirlik and Konya Air Base, Konya Airbases have both been involved in several NATO military operations since their establishment. The current Ambassador to NATO is Basat Öztürk. Background Turkey sought to become a member of NATO because it wanted a security guarantee against a potential invasion by the Soviet Union, which made several overtures towards control of the Dardanelles, Straits of the Dardanelles. In March 1945, the Soviets terminated the Treaty of Friendship and Non-aggression pact, Non Aggression to which the Soviet Union and Turkey had agreed on in 1925.Aydin, Mustafa (2000).p.107 In June 1945, the Soviets demanded the establishment of Soviet bases on the Straits in exchange for a reinstatement of this treaty. The Turkish President İsmet İnönü, Ismet Inönu and the Speaker of the Parliament responded decisive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |