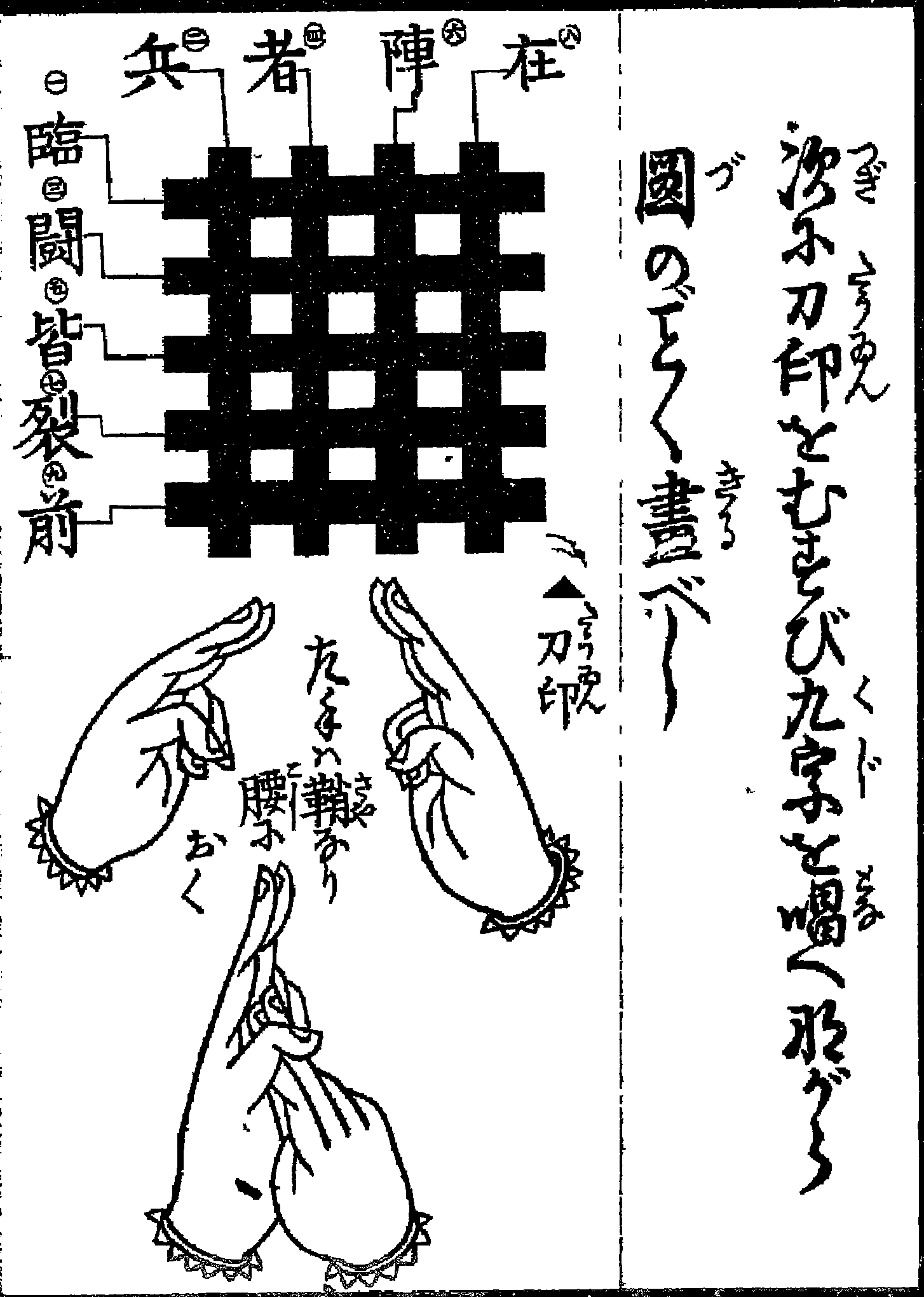
|
Kuji-kiri
is a practice of using hand gestures found today in Shugendō and Shingon Mikkyō. It is also present in some old and traditional schools (" ryūha") of Japanese martial arts including but not exclusive to schools that have ties with ninjutsu. The Nine Cuts * (臨) Rin – Power over oneself & others * (兵) Pyō – Direction of energy * (闘) Toh – Harmony with nature * (者) Sha – Healing of oneself & others * (皆) Kai – Premonition of danger * (陣) Jin– Knowing the thoughts of others * (列) Retsu – Dimension * (在) Zai - Creation * (前) Zen – Enlightenment Religious symbolism and meanings The ''Kuji-in'' were created from the gesture of both the hands. The left hand ''Taizokai'' represents a receptive valence, and the right hand ''Kongokai'' conveys an emitter valence. The ''Kuji Kiri'' performed with the right hand are to emphasize the cut of the ignorance of the Maya (illusion) (that is the deceptive sensory world) through the ''Sword of the Wisdom''. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuji-in
The ''kuji-in'' () also known as ''Nine Hand Seals'' is a system of mudras and associated mantras that consist of nine syllables. The mantras are referred to as ''kuji'' (九字), which literally translates as ''nine characters'' The syllables used in kuji are numerous, especially within Japanese esoteric Mikkyō. Scholars have stated that kuji is of Taoist origin, not Buddhist. There is no mention of the kuji in any of the Shingon or Tendai records that were brought back from China. The use of kuji is largely a layman’s practice, and is uncommon in many orthodox Buddhist traditions. It is however, found extensively in Shugendō, the ascetic mountain tradition of Japan, and Ryōbu Shintō, which is the result of blending Shingon Buddhism and Shinto. History The kuji are first introduced in the Bàopǔzǐ (), a Chinese Taoist text written by Gé Hóng c.280–340 CE). He introduces the kuji in chapter 17, entitled ''Dēngshè'' (登涉; lit. "Climbing ountainsand crossing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuji-kiri02
is a practice of using hand gestures found today in Shugendō and Shingon Mikkyō. It is also present in some old and traditional schools (" ryūha") of Japanese martial arts including but not exclusive to schools that have ties with ninjutsu. The Nine Cuts * (臨) Rin – Power over oneself & others * (兵) Pyō – Direction of energy * (闘) Toh – Harmony with nature * (者) Sha – Healing of oneself & others * (皆) Kai – Premonition of danger * (陣) Jin– Knowing the thoughts of others * (列) Retsu – Dimension * (在) Zai - Creation * (前) Zen – Enlightenment Religious symbolism and meanings The ''Kuji-in'' were created from the gesture of both the hands. The left hand ''Taizokai'' represents a receptive valence, and the right hand ''Kongokai'' conveys an emitter valence. The ''Kuji Kiri'' performed with the right hand are to emphasize the cut of the ignorance of the Maya (illusion) (that is the deceptive sensory world) through the ''Sword of the Wisdom''. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Japanese Buddhism
This is the glossary of Japanese Buddhism, including major terms the casual (or brand-new) reader might find useful in understanding articles on the subject. Words followed by an asterisk (*) are illustrated by an image in one of the photo galleries. Within definitions, words set in boldface are defined elsewhere in the glossary. __NOTOC__ A * ''agyō''* (阿形) – A type of statue (of a Niō, komainu, etc.) with its mouth open to pronounce the sound "a", first letter of the Sanskrit alphabet and symbol of the beginning of all things. See also ''ungyō''. * Amida Nyorai (阿弥陀如来) – Japanese name of Amitabha, deity worshiped mainly by the Pure Land sect.''Kōjien Japanese dictionary'' * – A Hermitage. * arhat – see arakan. * ''arakan*'' (阿羅漢) – the highest level of Buddhist ascetic practice, or someone who has reached it. The term is often shortened to just ''rakan'' (羅漢). B *bay – see ken. *''bettō'' (別当) – Previously the title of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Shinto
This is the glossary of Shinto, including major terms on the subject. Words followed by an asterisk (*) are illustrated by an image in one of the photo galleries. __NOTOC__ A * – A red papier-mâché cow bobblehead toy; a kind of ''engimono'' and an ''omiyage'' (a regional souvenir in Japan) that is considered symbolic of Aizu. * – A type of fan held by aristocratic women of the Heian period when formally dressed; it is brightly painted with tassels and streamers on the ends. Held today in Shinto by a ''miko'' in formal costume for festivals. See also ''hiôgi''. * – The term's meaning is not limited to moral evil, and includes misfortune, inferiority and unhappiness. * - A malevolent fire spirit, demon or devil. * - Also known as the ''Akujin'', the ''Kibi-no-Ananowatari-no-Kami'' and as the ''Anato-no-Kami'', ''Akuru'' is a malevolent ''kami'' that is mentioned in the ''Keikoki'' (records regarding the time of the Emperor Keiko), the ''Nihonshoki'' (Chronicles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudra
A mudra (; sa, मुद्रा, , "seal", "mark", or "gesture"; ,) is a symbolic or ritual gesture or pose in Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism. While some mudras involve the entire body, most are performed with the hands and fingers. As well as being spiritual gestures employed in the iconography and spiritual practice of Indian religions, mudras have meaning in many forms of Indian dance, and yoga. The range of mudras used in each field (and religion) differs, but with some overlap. In addition, many of the Buddhist mudras are used outside South Asia, and have developed different local forms elsewhere. In hatha yoga, mudras are used in conjunction with pranayama (yogic breathing exercises), generally while in a seated posture, to stimulate different parts of the body involved with breathing and to affect the flow of prana. It is also associated with bindu, bodhicitta, amrita, or consciousness in the body. Unlike older tantric mudras, hatha yogic mudras are generally inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin And Yang
Yin and yang ( and ) is a Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosophical concept that describes opposite but interconnected forces. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and yang and formed into objects and lives. Yin is the receptive and yang the active principle, seen in all forms of change and difference such as the annual cycle (winter and summer), the landscape (north-facing shade and south-facing brightness), sexual coupling (female and male), the formation of both men and women as characters and sociopolitical history (disorder and order). Taiji (philosophy), Taiji or Tai chi () is a Chinese cosmological term for the "Supreme Ultimate" state of undifferentiated absolute and infinite potential, the oneness before duality, from which yin and yang originate. It can be compared with the old ''Wuji (philosophy), wuji'' (, "without pole"). In the cosmology pertaining to yin and yang, the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninjutsu Skills
, sometimes used interchangeably with the modern term , is the martial art strategy and military tactics, tactics of unconventional warfare, guerrilla warfare and espionage purportedly practised by the ninja. ''Ninjutsu'' was a separate discipline in some traditional Japanese martial arts, Japanese schools, which integrated study of more conventional martial arts (''taijutsu'') along with ''shurikenjutsu'', ''kenjutsu'', ''sōjutsu'', ''bōjutsu'' and others. While there is an Bujinkan, international martial arts organization representing several Modern schools of ninjutsu, modern styles of ''ninjutsu'', the historical lineage of these styles is disputed. Some schools claim to be the only legitimate heir of the art, but ''ninjutsu'' is not centralized like modernized martial arts such as judo or karate. Togakure-ryū claims to be the oldest recorded form of ninjutsu, and claims to have survived past the 16th century. History Spying in Japan dates as far back as Prince Shōtoku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Martial Arts Terminology
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of Philosophy, philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of China, Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the ''Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later Zhuangzi (book), writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shugendō
is a highly syncretic religion, a body of ascetic practices that originated in the Nara Period of Japan having evolved during the 7th century from an amalgamation of beliefs, philosophies, doctrines and ritual systems drawn from local folk-religious practices, Shinto mountain worship and Buddhism. The final purpose of ''Shugendō'' is for practitioners to find supernatural power and save themselves and the masses by conducting religious training while treading through steep mountain ranges. Practitioners are called or . The mountains where ''shugenja'' practiced were all over Japan, and include various mountains of the Ōmine mountain range such as Mount Hakkyō and Mount Ōmine. The ''Shugendō'' worldview includes a large pantheon of deities (which include Buddhist and Shinto figures). Some of the most important figures are the tantric Buddhist figures of Fudō Myōō and Dainichi Nyorai. Other key figures are , which are considered to be the manifestation of Buddhas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya (illusion)
''Maya'' (; Devanagari: , IAST: ), literally "illusion" or "magic", has multiple meanings in Indian philosophies depending on the context. In later Vedic texts, connotes a "magic show, an illusion where things appear to be present but are not what they seem"; the principle which shows "attributeless Absolute" as having "attributes". also connotes that which "is constantly changing and thus is spiritually unreal" (in opposition to an unchanging Absolute, or Brahman), and therefore "conceals the true character of spiritual reality".Lynn Foulston and Stuart Abbott (2009), ''Hindu Goddesses: Beliefs and Practices'', Sussex Academic Press, , pp. 14-16. In the Advaita Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy, , "appearance", is "the powerful force that creates the cosmic illusion that the phenomenal world is real." In this nondualist school, at the individual level appears as the lack of knowledge () of the real Self, ''Atman-Brahman'', mistakingly identifying with the body-mind comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |