|
Kudumi Mahato
The Kudmi are a community in the states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Bihar of India. They were primarily agriculturalist. . Classification Kudmi were classified as a Notified Tribe by the British Raj under the terms of the Indian Succession Act introduced in 1865 as they have customary rules of succession. Subsequently, in 1913, they were classified as a Primitive tribe. Then they were omitted from the list of communities listed as tribes in the 1931 census. Again, they were omitted from the Scheduled Tribe list drawn up in 1950. In 2004, the Government of Jharkhand recommended that they should be listed as a Scheduled Tribe rather than Other Backward Class. The Tribal Research Institute of Government of India recommended against this proposal, claiming they are a sub-caste of the Kunbi and thus different to tribal people. Therefore, In 2015, the Government of India refused to approve the recommendation of Jharkhand government to list the Kudmi Mahato as Schedule Tribe. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurmi
Kurmi is traditionally a non-elite tiller caste in the lower Gangetic plain of India, especially southern regions of Awadh, eastern Uttar Pradesh and parts of Bihar. The Kurmis came to be known for their exceptional work ethic, superior tillage and manuring, and gender-neutral culture, bringing praise from Mughal and British administrators alike. Etymology There are several late-19th century theories of the etymology of ''Kurmi''. According to Jogendra Nath Bhattacharya (1896), the word may be derived from an Indian tribal language, or be a Sanskrit compound term ''krishi karmi'', "agriculturalist." A theory of Gustav Salomon Oppert (1893) holds that it may be derived from ''kṛṣmi'', meaning "ploughman". History Eighteenth and nineteenth centuries With the continued waning of Mughal rule in the early 18th century, the Indian subcontinent's hinterland dwellers, many of whom were armed and nomadic, began to appear more frequently in settled areas and interact with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Other Backward Class
The Other Backward Class is a collective term used by the Government of India to classify castes which are educationally or socially backward. It is one of several official classifications of the population of India, along with General castes, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (SCs and STs). The OBCs were found to comprise 52% of the country's population by the Mandal Commission report of 1980, and were determined to be 41% in 2006 when the National Sample Survey Organisation took place. There is substantial debate over the exact number of OBCs in India; it is generally estimated to be sizable, but many believe that it is higher than the figures quoted by either the Mandal Commission or the National Sample Survey. In the Indian Constitution, OBCs are described as socially and educationally backward classes (SEBC), and the Government of India is enjoined to ensure their social and educational development — for example, the OBCs are entitled to 27% reservations in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhumair
Jhumair or Jhumar is an Indian folk dance from the Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Bihar and West Bengal. It is folk dance of Sadan, the Indo-Aryan ethnic groups of Chotanagpur. It is mainly performed during harvest season. The musical instruments used are Mandar, Dhol, Nagara, Bansuri. Varieties The Jhumair/Jhumar from different region vary from each other in style. There are variety of Jhumar in the region of Chotanagpur such as: * Khortha Jhumar * Kurmali Jhumar * Panch Pargarnia Jhumar * Nagpuri Jhumar ** Mardani Jhumar ** Janani Jhumar Notable exponent * Govind Sharan Lohra, folk artist from Jharkhand * Mukund Nayak, folk artist from Jharkhand See also *Circle dance Circle dance, or chain dance, is a style of social dance done in a circle, semicircle or a curved line to musical accompaniment, such as rhythm instruments and singing, and is a type of dance where anyone can join in without the need of par ... References Indian fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandna
Bandna (spelt as Bāndnā, Hindi: बांदना) is a agriculture-oriented festival of the Kurmali ethnolinguistic and other related communities, in which domestic cattle and agriculture appliances are worshiped. The festival mostly observed in the state of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Assam, and celebrated annually as per Hindu calendar in the month of Amavashya of Kartik. Overview Bandna is a celebration of the paddy seeds that are sown by the region's agrarian communities. This festival is celebrated by the Hindu and Tribal cultivator communities like Bagal, Rajuar, Kumhar, Kudmi Mahato and other Kurmali-speaking communities of East India. It is one of many Indian festivals during which cattle are worshiped. Ritual Bandna is a seven-day festival: the first three days are Chumaan; the fourth day is Goth Puja; the fifth day is Goriyaa Puja; the sixth day is Borod Khuntaan; and the seventh day is Budhi Bandna. The rituals of the first three days are sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karam (festival)
Karam is a harvest festival celebrated in Indian states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Assam, Odisha and Bangladesh. It is dedicated to the worship of Karam-Devta (Karam-Lord/God), the god of power, youth and youthfulness. It celebrated for good harvest and health. The festival is held on the 11th day of a full moon (Purnima) of the Hindu month of Bhado, which falls between August and September. Unmarried girls fast and grow seedlings for 7-9 days. Then next day, groups of young villagers go to the jungle and collect wood, fruits, and flowers. These are required during the puja (worship) of the Karam God. During this period, people sing and dance together in groups. The entire valley dances to the drumbeat "day of the phases". The Karam festival celebrated by diverse groups of people, including: Korwa, Sadan, Bagal, Baiga, Binjhwari, Bhumij, Oraon, Kharia, Munda, Kudmi, Karmali, Lohra and many more. Summary of the ritual This festiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jivitputrika
Jitiya (also called Jivitputrika) is a three-day-long Hindu festival which is celebrated from the seventh to ninth lunar day of Krishna-Paksha in Ashwin month. It is celebrated mainly in the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Jharkhand and the country of Nepal as well as Nepali people of West Bengal. Mothers fast (without water) for well being of their children. It is celebrated for eight days in Jharkhand from first moon day to eight moon day in the first half of Ashwin month. Rituals Uttar pradesh and Bihar It is a three day long festival. * Nahai-Khai : The first day is Nahai-Khai, where mothers eat food only after taking bath. The food has to be vegetarian, prepared with ghee and pink salt. * Khur-Jitiya or Jiviputrika day: This is the second day and mothers observe strict fasting without drinking water. * Parana: This is the third day when mothers break fasting. Variety of delicacies are prepared such as Curry Rice, Noni (portulaca oleracea) saag and Marua(Eleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tusu Festival
Tusu Festival is a folk festival held on the last day of the Bengali month of Poush, i.e., Makar Sankranti. It is mainly river centric.It is a unifying form of common faith and belief of the agrarian society in joy of harvesting crops. At the end of the festivities, the immersion of the image of Tusu is done vividly and with songs which have a melancholic ring. Rural fairs are also organised during the festival. The festival Tusu, is mostly celebrated in Southwest of West Bengal, Southeast of Jharkhand, Northeastern Odisha as well in the Tea-State of Assam.https://www.wehindu.com/?event=tusu-puja Etymology There are different theories about the origin of the word Tusu. Many believe that the word 'tusu' originates from rice bran, which is called Tush in Bengali. See also * Bhadu References External links * * *{{Cite web , title=Tusu - A tribal Festival , url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8Mink-E6zg , website=YouTube YouTube is a global online video sharing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Lingua francas have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th centuries. A world language – a language spoken internationally and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of First language, first-speakers are Hindustani language, Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
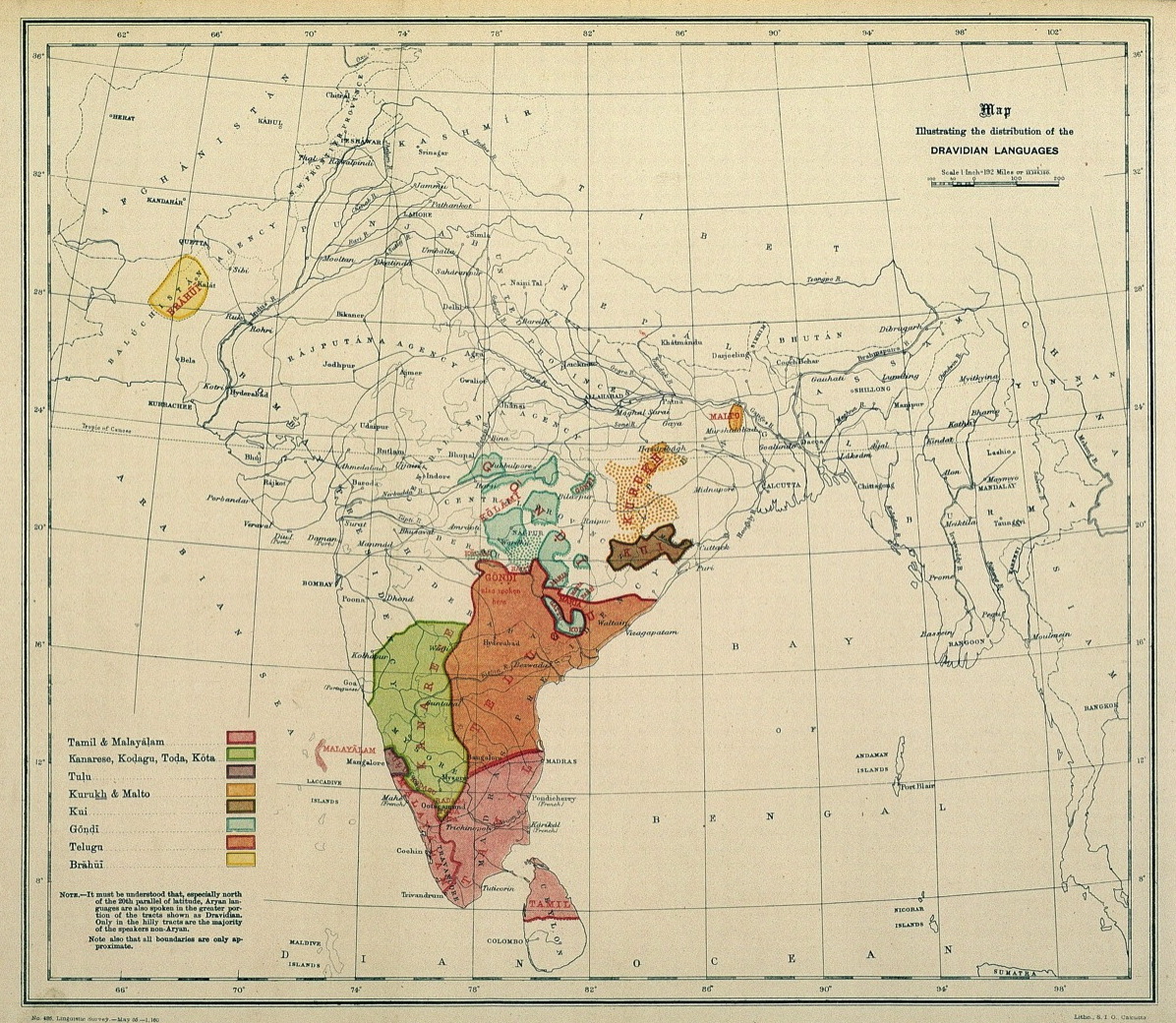
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages (or sometimes Dravidic) are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in southern India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan. Since the colonial era, there have been small but significant immigrant communities in Mauritius, Myanmar, Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United Kingdom, Australia, France, Canada, Germany, South Africa, and the United States. The Dravidian languages are first attested in the 2nd century BCE, as Tamil-Brahmi script, inscribed on the cave walls in the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Tamil Nadu. The Dravidian languages with the most speakers are (in descending order of number of speakers) Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam, all of which have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu and Kodava. There are also a number of Dravidian-speaking scheduled tribes, such as the Kurukh in Eastern India and Gondi in Central India. Outside of India, Brahui is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munda Languages
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about nine million people in India and Bangladesh. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages. The family is generally divided into two branches: North Munda, spoken in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Odisha, and South Munda, spoken in central Odisha and along the border between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. North Munda, of which Santali is the most widely spoken, has twice as many speakers as South Munda. After Santali, the Mundari and Ho languages rank next in number of speakers, followed by Korku and Sora. The re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |