|
Korean Regional Cuisine
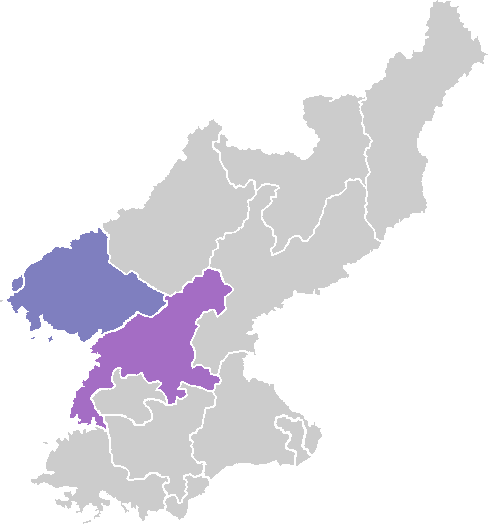
Korean regional cuisines () are characterized by local specialties and distinctive styles within Korean cuisine. The divisions reflected historical boundaries of the provinces where these food and culinary traditions were preserved until modern times. Although Korea has been divided into two nation-states since 1948 (North Korea and South Korea), it was once divided into eight provinces (''paldo'') according to the administrative districts of the Joseon Dynasty. The northern region consisted of Hamgyeong, Pyeongan, and Hwanghae provinces. The central region comprised Gyeonggi, Chungcheong, and Gangwon provinces. Gyeongsang and Jeolla provinces made up the southern region. Until the late 19th century transportation networks were not well developed, and each provincial region preserved its own characteristic tastes and cooking methods. Geographic differences are also reflected by the local specialty foodstuffs depending on the climate and types of agriculture, as well as the nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Cuisine
Korean cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient agricultural and nomadic traditions in Korea and southern Manchuria, Korean cuisine reflects a complex interaction of the natural environment and different cultural trends. Korean cuisine is largely based on rice, vegetables, seafood and (at least in South Korea) meats. Dairy is largely absent from the traditional Korean diet. Traditional Korean meals are named for the number of side dishes (반찬; 飯饌; ''banchan'') that accompany steam-cooked short-grain rice. Kimchi is served at nearly every meal. Commonly used ingredients include sesame oil, ''doenjang'' (fermented bean paste), soy sauce, salt, garlic, ginger, ''gochugaru'' (pepper flakes), '' gochujang'' (fermented red chili paste) and napa cabbage. Ingredients and dishes vary by province. Many regional dishes have become national, and dishes that were once regional have proliferated in different variations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daum (web Portal)
Daum ( ko, 다음) is a South Korean web portal. It offers many Internet services to web users, including a popular free web-based e-mail, messaging service, forums, shopping, news and webtoon service. The word "daum" means "next" and also "diverse voices". Background The popularity of Daum stems from the range of services it offers, but also from the fact that it was the first Korean web portal of significant size. Its popularity started when it merged with the then most popular e-mail service, daum.net or hanmail.net. After the merging, Daum started the forum service Daum Cafe which brought its firm status in the market. Daum received the eighth highest trust rating in a 2020 Reuters Institute survey of selected South Korean media outlets. History The former Daum Communications Corporation (Korean: ㈜다음커뮤니케이션) was founded in 1994 by and , and the company launched the namesake portal in May 1997 making it the first South Korean web portal, four months earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hankyoreh
''The Hankyoreh'' (, literally "The Korean Nation" or "One Nation") is a centre-left liberal daily newspaper in South Korea. It was established in 1988 after widespread purges forced out dissident journalists, and was envisioned as an alternative to existing newspapers, which were regarded as unduly influenced by the authoritarian government at the time. When it launched, it claimed to be "the first newspaper in the world truly independent of political power and large capital." As of 2016, it has been voted as the most trusted news organization by Korean journalists for nine consecutive years but also it is the least influential news outlet by the survey. It has online editions in English, Chinese, and Japanese. History The newspaper was originally established as ''Hankyoreh Shinmun'' () on 15 May 1988 by ex-journalists from the Dong-a Ilbo and Chosun Ilbo. At the time, government censors were in every newsroom, newspaper content was virtually dictated by the Ministry of Cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Cheese
Head cheese (Dutch: ''hoofdkaas'') or brawn is a cold cut terrine or meat jelly that originated in Europe. It is made with flesh from the head of a calf or pig (less commonly a sheep or cow), typically set in aspic, and usually eaten cold, at room temperature, or in a sandwich. Despite its name the dish is not a cheese and contains no dairy products. The parts of the head used vary, and may include the tongue and sometimes the feet and heart but do not commonly include the brain, eyes or ears. Trimmings from more commonly eaten cuts of pork and veal are often used, with gelatin added as a binder. Variations of head cheese exist throughout Europe and the rest of the world, with differences in construction and ingredients. A version pickled with vinegar is known as ''souse''. Historically, meat jellies were made of the head of an animal, less its organs, which would be simmered to produce a naturally gelatinous stock that would congeal as the dish cooled. Meat jellies made th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyongyang Naengmyeon
Naengmyeon * (, in South Korea) or raengmyŏn (, in North Korea) is a noodle dish of North Korean origin which consists of long and thin handmade noodles made from the flour and starch of various ingredients, including buckwheat (메밀, ''memil''), potatoes, sweet potatoes, arrowroot starch (darker color and chewier than buckwheat noodles), and kudzu (, ). Buckwheat predominates (despite the name, it is not a wheat but rather is more closely related to sorrel). Other varieties of naengmyeon are made from ingredients such as seaweed and green tea. In modern times, the ''mul naengmyeon'' (물 냉면) variant is commonly associated with and popularly consumed during the summer, however, it was historically a dish enjoyed during winter. History According to the 19th-century documents of ''Dongguksesigi'' (), ''naengmyeon'' has been made since the Joseon Dynasty. Originally a delicacy in northern Korea, especially in the cities of Pyongyang () and Hamhung (), ''naengmyeon'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimchi Mari
''Guk'' (), also sometimes known as ''tang'' (), is a class of soup-like dishes in Korean cuisine. ''Guk'' and ''tang'' are commonly grouped together and regarded as the same type of dish, although ''tang'' can sometimes be less watery than ''guk''. It is one of the most basic components in a Korean meal, along with ''bap'' (밥, rice), and ''banchan'' (반찬, side dishes). In Korean table setting, ''guk'' is served on the right side of ''bap'' (rice), and left side of ''sujeo'' (수저, a spoon and chopsticks). ''Guk'' is a native Korean word, while ''tang'' is a Sino-Korean word that originally meant "boiling water" or "soup". ''Tang'' has been used as an honorific term in place of ''guk'', when it denotes the same meaning as ''guk'' as in '' yeonpo-tang'' (연포탕, octopus soup), '' daegu-tang'' (대구탕, codfish soup), or ''jogae-tang'' (조개탕, clam soup). Generally, the names of lighter soups with vegetables are suffixed with ''-guk'', while heavier, thicker sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gukbap
''Gukbap'' (), hot soup with rice, is a Korean dish made by putting cooked rice into hot soup or boiling rice in soup. It is commonly served in a ttukbaegi. Whereasoupanricehave been traditionally served separately at tables in Korea, Gukbap means food putting rice into a soup. But these days, soup and rice are sometimes served separately in Korean restarurants for several reasons. As inns appear, Gukbap became popular at the end of the Joseon Dynasty. It was a food that the common people eat often. At first, ainn's ownermay have made Gukbap with vegetables that are available. After the market economy was revitalized, Gukbap with beef and pork may have appeared in inns. Later it also got popular among people in the market and even in the city. Etymology ''Gukbap'' is a compound of ''guk'' (soup) and ''bap'' (cooked rice). Varieties * ''Dwaeji-gukbap'' () – pork and rice soup. It is a Gukbap that brews pig bone in meat broth, and people eat it together witboiled pork sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongchimi
''Dongchimi'' is a variety of kimchi consisting of Korean radish, napa cabbage, scallions, jangajji, pickled green chili pepper, chilli, ginger, Pyrus pyrifolia, Korean pear and watery brine in Korean cuisine. As the name ''dong'' (hangul: 동; hanja: wikt:冬, 冬; literally "winter") and ''chimi'' (hangul: 치미, an ancient term for kimchi), suggests, this kimchi is traditionally consumed during the winter season. Dongchimi is fermented like other varieties of kimchi, but its maturing period is relatively short (2–3 days). Although it can be made at any time of the year, it is usually made during the ''gimjang'' season. The northern regions consisting of Hamgyeong-do and Pyeongan-do in North Korea are particularly famous for their dongchimi. The clear and clean taste of the watery dongchimi is used as a soup for making ''dongchimi guksu'' (동치미국수 cold noodle soup made with ''dongchimi'') and ''naengmyeon'', or served with ''tteok'' or steamed sweet potatoes to bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimchi
''Kimchi'' (; ko, 김치, gimchi, ), is a traditional Korean side dish of salted and fermented vegetables, such as napa cabbage and Korean radish. A wide selection of seasonings are used, including ''gochugaru'' (Korean chili powder), spring onions, garlic, ginger, and ''jeotgal'' (salted seafood), etc. Kimchi is also used in a variety of soups and stews. As a staple food in Korean cuisine, it is eaten as a side dish with almost every Korean meal. There are hundreds of different types of kimchi made with different vegetables as the main ingredients. Traditionally, winter kimchi, called kimjang, was stored in large earthenware fermentation vessels, called ''onggi'', in the ground to prevent freezing during the winter months and to keep it cool enough to slow down the fermentation process during summer months. The vessels are also kept outdoors in special terraces called jangdokdae. In contemporary times, household kimchi refrigerators are more commonly used. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandu (dumpling)
''Mandu'' (), or mandoo, are dumplings in Korean cuisine. * ''Mandu'' can be steamed, boiled, pan-fried, or deep-fried. The styles also vary across regions in the Korean Peninsula. ''Mandu'' were long part of Korean royal court cuisine, but are now found in supermarkets, restaurants, and snack places such as ''pojangmacha'' and ''bunsikjip'' throughout Korea. Names and etymology The name is cognate with the names of similar types of meat-filled dumplings along the Silk Road in Central Asia, such as Uyghur ''manta'' (), Turkish ', Kazakh '' mänti'' (), Uzbek ', Afghan ' and Armenian '' mantʿi'' (). Chinese ''mántou'' (; ) is also considered a cognate, which used to mean meat-filled dumplings, but now refers to steamed buns without any filling. ''Mandu'' can be divided into ''gyoja'' () type and ''poja'' () type. In Chinese, the categories of dumplings are called ''jiǎozi'' (; ) and ''bāozi'' () respectively, which are cognates with the Korean words. In Japanese, the forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naengmyeon
Naengmyeon * (, in South Korea) or raengmyŏn (, in North Korea) is a noodle dish of North Korean origin which consists of long and thin handmade noodles made from the flour and starch of various ingredients, including buckwheat (메밀, ''memil''), potatoes, sweet potatoes, arrowroot starch (darker color and chewier than buckwheat noodles), and kudzu (, ). Buckwheat predominates (despite the name, it is not a wheat but rather is more closely related to sorrel). Other varieties of naengmyeon are made from ingredients such as seaweed and green tea. In modern times, the ''mul naengmyeon'' (물 냉면) variant is commonly associated with and popularly consumed during the summer, however, it was historically a dish enjoyed during winter. History According to the 19th-century documents of ''Dongguksesigi'' (), ''naengmyeon'' has been made since the Joseon Dynasty. Originally a delicacy in northern Korea, especially in the cities of Pyongyang () and Hamhung (), ''naengmyeon'' b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steamed Rice
Cooked rice refers to rice that has been cooked either by steaming or boiling. The terms steamed rice or boiled rice are also commonly used. Any variant of Asian rice (both Indica and Japonica varieties), African rice or wild rice, glutinous or non-glutinous, long-, medium-, or short-grain, of any colour, can be used. Rice for cooking can be whole grain or milled. Cooked rice is used as a base for various fried rice dishes (e.g. chǎofàn, khao phat), rice bowls/plates (e.g. bibimbap, chazuke, curry rice, dal bhat, donburi, loco moco, panta bhat, rice and beans, rice and gravy), rice porridges (e.g. congee, juk), rice balls/rolls (e.g. gimbap, onigiri, sushi, zongzi), as well as rice cakes and desserts (e.g. mochi, tteok, yaksik). Rice is a staple food in not only Asia and Latin America, but across the globe, and is considered the most consumed food in the world. The U.S. Department of Agriculture classifies rice as part of the grains food group. Nutritionally, 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

_2.jpg)