|
Korazim Plateau
The Korazim Plateau ( he, רמת כורזים, ''Ramat Korazim'', also spelled Corazim), is a volcanic plateau, located in northern Israel. The plateau is bounded between by the Hula Valley in the north, Sea of Galilee in the south, the mountains of the Galilee to the west and by the Jordan River to the east. Semapat govmap.gov.il It is named after an ancient Jewish settlement also known as "Chorazin". The highest point is Filon Hill, which is 409 meters above sea level. The plateau is home to a few Israeli communities, including Rosh Pinna, Hatzor HaGlilit and the Bedouin town of Tuba-Zangariyye. The plateau's rural settlements make part of the regional councils of Upper Galilee, Mevo'ot HaHermon and Emek HaYarden. Several important archaeological and historical sites are located on the plateau, including Tel Hazor, Daughters of Jacob Bridge, Mount of Beatitudes and Jubb Yussef. Historically the plateau also served as a transit region for the valleys to the north and south, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus. Lava plateau Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions through numerous vents without violent explosions (quiet eruptions). These eruptions are quiet because of low viscosity of lava, so that it is very fluid and contains a small amount of trapped gases. The resulting sheet lava flows may be extruded from linear fissures or rifts or gigantic volcanic eruptions through multiple vents characteristic of the prehistoric era which produced giant flood basalts. Multiple successive and extensive lava flows cover the original landscape to eventually form a plateau, which may contain lava fields, cinder cones, shield volcanoes and other volcanic landforms. In some cases, a lava plateau may be part of a single volcano. An example is the massive Level Mountain shield volcano in northern British Columbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
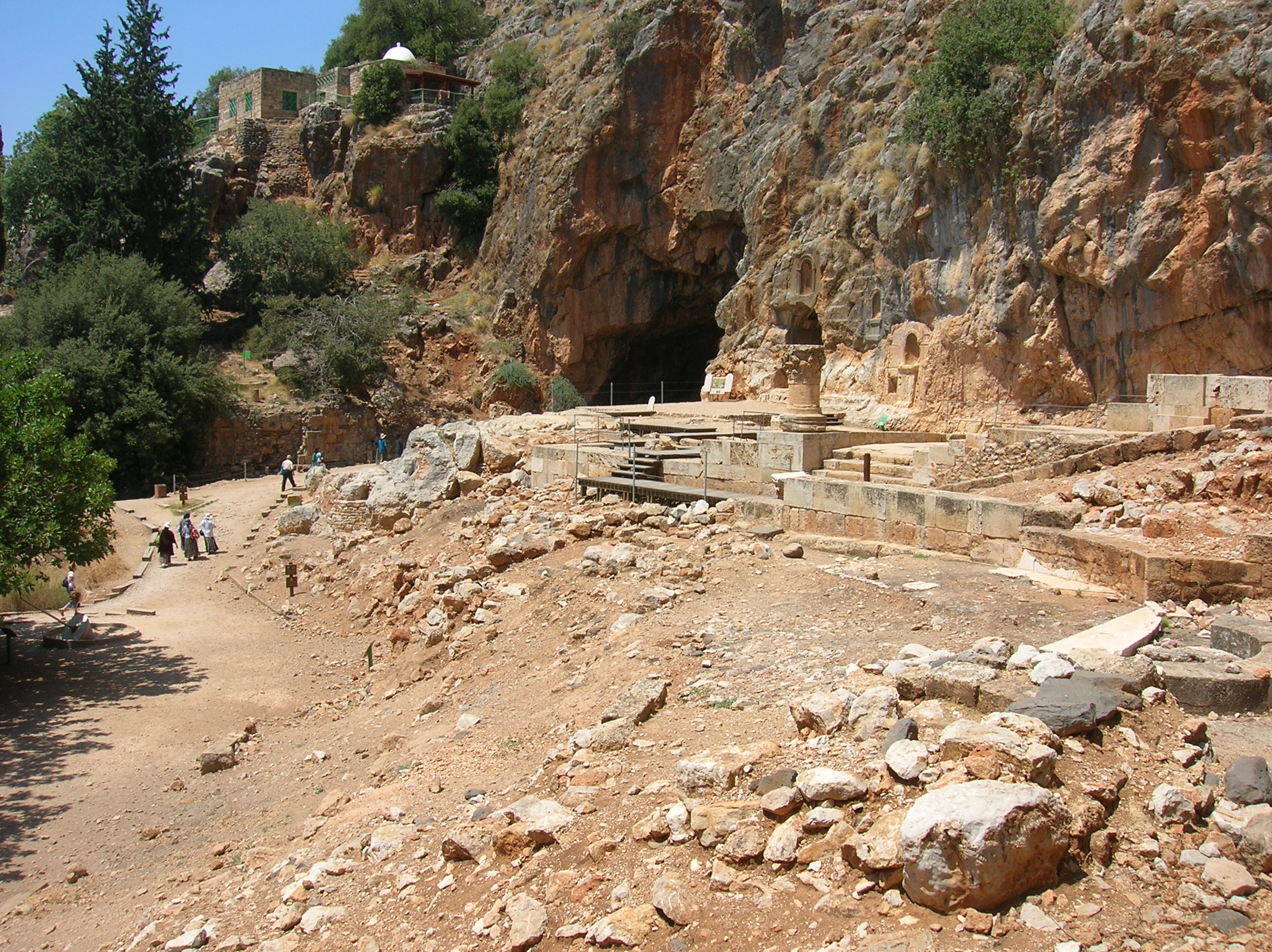
Mount Of Beatitudes
The Mount of Beatitudes ( he, הר האושר, ''Har HaOsher'') is a hill in northern Israel, in the Korazim Plateau. It is the traditional site of Jesus' Sermon on the Mount. Location The site known as the Mount of Beatitudes is on the northwestern shore of the Sea of Galilee, between Capernaum and the archeological site of Gennesaret (Ginosar), on the southern slopes of the Korazim Plateau. Its negative altitude (around 25 metres below sea level, nearly 200 metres above the Sea of Galilee) makes it one of the lowest summits of the world. This site, very near Tabgha and also known as Mount Eremos, has been commemorated for more than 1600 years. Other suggested locations for the Jesus' Sermon on the Mount have included the nearby Mount Arbel, or even the Horns of Hattin. Churches A Byzantine church was erected lower down the slope from the current site in the 4th century, and it was used until the 7th century. Remains of a cistern and a monastery are still visible. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea Transform
The Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system, also sometimes referred to as the Dead Sea Rift, is a series of faults that run from the Maras Triple Junction (a junction with the East Anatolian Fault in southeastern Turkey) to the northern end of the Red Sea Rift (just offshore of the southern tip of the Sinai Peninsula). The fault system forms the transform boundary between the African Plate to the west and the Arabian Plate to the east. It is a zone of left lateral displacement, signifying the relative motions of the two plates. Both plates are moving in a general north-northeast direction, but the Arabian Plate is moving faster, resulting in the observed left lateral motions along the fault of approximately 107 km at its southern end. A component of extension is also present in the southern part of the transform, which has contributed to a series of depressions, or pull-apart basins, forming the Gulf of Aqaba, Dead Sea, Sea of Galilee, and Hula basins. A component of shortenin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure-ridge
A pressure ridge is a topographic ridge produced by compression. Depending on the affected material, "pressure ridge" may refer to: * Pressure ridge (ice), between ice floes * Pressure ridge (lava), in a lava flow * Pressure ridge (seismic), in a fault zone In a seismic context, a pressure ridge can range in size from a few-metres-long mound, to a kilometres-long lateral ridge. It is the result of one or several earthquakes occurring on certain types of fault geometries, such as compressional bends or stepovers along strike-slip faults. A pressure ridge can for instance be the result of a deep-set obstruction on the fault plane, which leads to material being pushed up during earthquakes. See also * Ridge (meteorology) A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticy ..., an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand why landscapes look the way they do, to understand landform and terrain history and dynamics and to predict changes through a combination of field observations, physical experiments and numerical modeling. Geomorphologists work within disciplines such as physical geography, geology, geodesy, engineering geology, archaeology, climatology, and geotechnical engineering. This broad base of interests contributes to many research styles and interests within the field. Overview Earth's surface is modified by a combination of surface processes that shape landscapes, and geologic processes that cause tectonic uplift and subsidence, and shape the coastal geography. Surface processes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel Antiquities Authority
The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA, he, רשות העתיקות ; ar, داﺌرة الآثار, before 1990, the Israel Department of Antiquities) is an independent Israeli governmental authority responsible for enforcing the 1978 Law of Antiquities. The IAA regulates excavation and conservation, and promotes research. The Director-General is Mr. Eli Escusido, and its offices are housed in the Rockefeller Museum. The Israel Antiquities Authority plans to move into a new building for the National Campus for the Archaeology of Israel in Jerusalem, next to the Israel Museum. History The Israel Department of Antiquities and Museums (IDAM) of the Ministry of Education was founded on July 26, 1948, after the establishment of the State of Israel. It took over the functions of the Department of Antiquities of the British Mandate in Israel and Palestine. Originally, its activities were based on the British Mandate Department of Antiquities ordinances. IDAM was the statutory aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between disciplines: as a geological and biogeographical region, the term refers to a basaltic plateau bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west, the Anti-Lebanon with Mount Hermon in the north and Wadi Raqqad in the east. As a geopolitical region, it refers to the border region captured from Syria by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967; the territory has been occupied by the latter since then and was subject to a de facto Israeli annexation in 1981. This region includes the western two-thirds of the geological Golan Heights and the Israeli-occupied part of Mount Hermon. The earliest evidence of human habitation on the Golan dates to the Upper Paleolithic period. According to the Bible, an Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naftali Mountains
Naftali Mountains ( he, הרי נפתלי) is a mountain range between Lebanon and Upper Galilee, Israel. The western side gradually changes into the highlands of southern Lebanon. The eastern side sharply descends into the Hula Valley of Israel. They are a part of the watershed between the basins of the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. The area was the place of heavy fighting in 1948 during the Israel War of Independence. M. M. Silver, ''The History of Galilee, 1538–1949. Mysticism, Modernization, and War'', 2022, p.320-322/ref> Israeli populated places in the mountains (from north to south) are: Misgav Am, Margaliot, Manara, Ramot Naftali, Malkia, Avivim Avivim ( he, אֲבִיבִים), is a moshav in the far north of Israel, in the Upper Galilee. It is located less than one kilometre (3,000 feet) from the Blue Line with Lebanon. In its population was . History Mandatory period In 1920, Salih ..., Dishon. References External linksNaftali Mountains For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Map Of Ramat Korazim
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane. When a relief is carved into a flat surface of stone (relief sculpture) or wood (relief carving), the field is actually lowered, leaving the unsculpted areas seeming higher. The approach requires a lot of chiselling away of the background, which takes a long time. On the other hand, a relief saves forming the rear of a subject, and is less fragile and more securely fixed than a sculpture in the round, especially one of a standing figure where the ankles are a potential weak point, particularly in stone. In other materials such as metal, clay, plaster stucco, ceramics or papier-mâché the form can be simply added to or raised up from the background. Monumental bronze reliefs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yom Kippur War
The Yom Kippur War, also known as the Ramadan War, the October War, the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, or the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, was an armed conflict fought from October 6 to 25, 1973 between Israel and a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria. The majority of combat between the two sides took place in the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights—both of which were occupied by Israel in 1967—with some fighting in African Egypt and northern Israel. Egypt's initial objective in the war was to seize a foothold on the eastern bank of the Suez Canal and subsequently leverage these gains to negotiate the return of the rest of the Israeli-occupied Sinai Peninsula. The war began on October 6, 1973, when the Arab coalition jointly launched a surprise attack against Israel on the Jewish holy day of Yom Kippur, which had occurred during the 10th of the Islamic holy month of Ramadan in that year. Following the outbreak of hostilities, both the United States and the Soviet U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
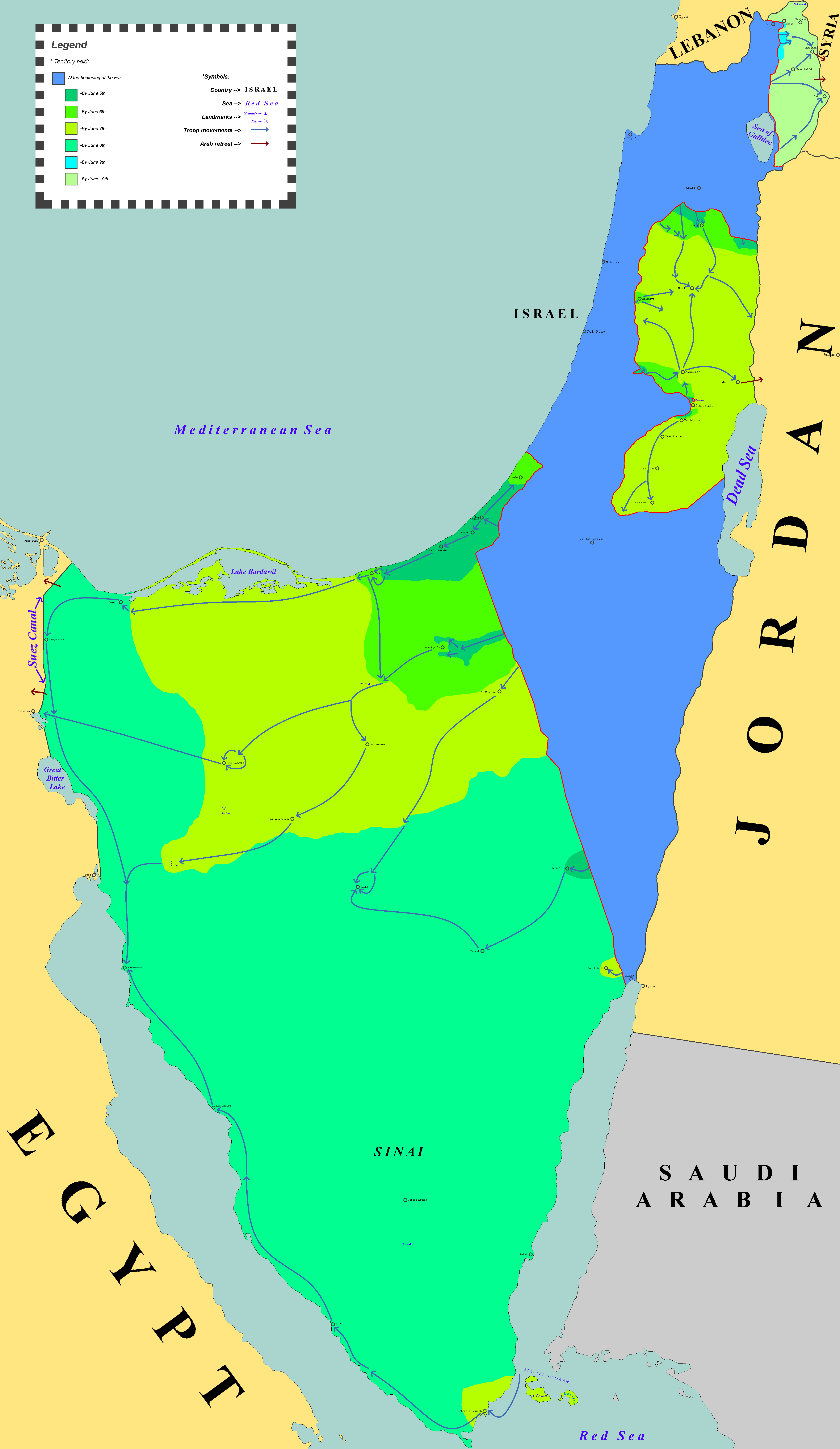
Six Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 June 1967. Escalated hostilities broke out amid poor relations between Israel and its Arab neighbours following the 1949 Armistice Agreements, which were signed at the end of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, First Arab–Israeli War. Earlier, in 1956, regional tensions over the Straits of Tiran escalated in what became known as the Suez Crisis, when Israel invaded Egypt over the Israeli passage through the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran, Egyptian closure of maritime passageways to Israeli shipping, ultimately resulting in the re-opening of the Straits of Tiran to Israel as well as the deployment of the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) along the Borders of Israel#Border with Egypt, Egypt–Israel border. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had been issued earlier that day, and a military coalition of Arab states entered the territory of British Palestine in the morning of 15 May. The day after the 29 November 1947 adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine – which planned to divide Palestine into an Arab state, a Jewish state, and the Special International Regime encompassing the cities of Jerusalem and Bethlehem – an ambush of two buses carrying Jews took place in an incident regarded as the first in the civil war which broke out after the UN decision. The violence had certain continuities with the past, the Fajja bus attack being a direct response to a Lehi massacre on 19 November of five members of an Arab family, suspected of being British informan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |