|
Kopp's Law
Kopp's law can refer to either of two relationships discovered by the German chemist Hermann Franz Moritz Kopp (1817–1892). #Kopp found "that the molecular heat capacity of a solid compound is the sum of the atomic heat capacities of the elements composing it; the elements having atomic heat capacities lower than those required by the Dulong–Petit law retain these lower values in their compounds." #In studying organic compounds, Kopp found a regular relationship between boiling points and the number of CH2 groups present.See page 942 of Kopp–Neumann law The Kopp–Neumann law, named for Kopp and Franz Ernst Neumann, is a common approach for determining the specific heat ''C'' (in J·kg−1·K−1) of compounds using the following equation: C = \sum_^N C_i f_i, where ''N'' is the total number of compound constituents, and ''Ci'' and ''fi'' denote the specific heat and mass fraction of the ''i''-th constituent. This law works surprisingly well at room-temperature conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rule Of Mixtures
In materials science, a general rule of mixtures is a weighted mean used to predict various properties of a composite material . It provides a theoretical upper- and lower-bound on properties such as the elastic modulus, mass density, ultimate tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity. In general there are two models, one for axial loading (Voigt model), and one for transverse loading (Reuss model). In general, for some material property E (often the elastic modulus), the rule of mixtures states that the overall property in the direction parallel to the fibers may be as high as : E_c = fE_f + \left(1-f\right)E_m where * f = \frac is the volume fraction of the fibers * E_f is the material property of the fibers * E_m is the material property of the matrix It is a common mistake to believe that this is the upper-bound modulus for Young's modulus. The real upper-bound Young's modulus is larger than E_c given by this formula. Even if both constituents are is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Kopp 01
Hermann or Herrmann may refer to: * Hermann (name), list of people with this name * Arminius, chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe in the 1st century, known as Hermann in the German language * Éditions Hermann, French publisher * Hermann, Missouri, a town on the Missouri River in the United States ** Hermann AVA, Missouri wine region * The German SC1000 bomb of World War II was nicknamed the "Hermann" by the British, in reference to Hermann Göring * Herrmann Hall, the former Hotel Del Monte, at the Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California * Memorial Hermann Healthcare System, a large health system in Southeast Texas * The Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI), a system to measure and describe thinking preferences in people * Hermann station (other), stations of the name * Hermann (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the western Oceanus Procellarum * Hermann Huppen, a Belgian comic book artist * Hermann 19, an American sailboat design built by Ted Herman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Franz Moritz Kopp
Hermann Franz Moritz Kopp (30 October 1817 – 20 February 1892), German chemist, was born at Hanau, where his father, Johann Heinrich Kopp (1777–1858), a physician, was professor of chemistry, physics and natural history at the local lyceum. After attending the gymnasium of his native town, he studied at Marburg and Heidelberg, and then, attracted by the fame of Liebig, went in 1839 to Gießen, where he became a ''privatdozent'' in 1841, and professor of chemistry twelve years later. In 1864 he was called to Heidelberg in the same capacity, and he remained there till his death. Kopp devoted himself especially to physico-chemical inquiries, and in the history of chemical theory his name is associated with several of the most important correlations of the physical properties of substances with their chemical constitution. Much of his work was concerned with specific volumes, the conception of which he set forth in a paper published when he was only twenty-two years of age; a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
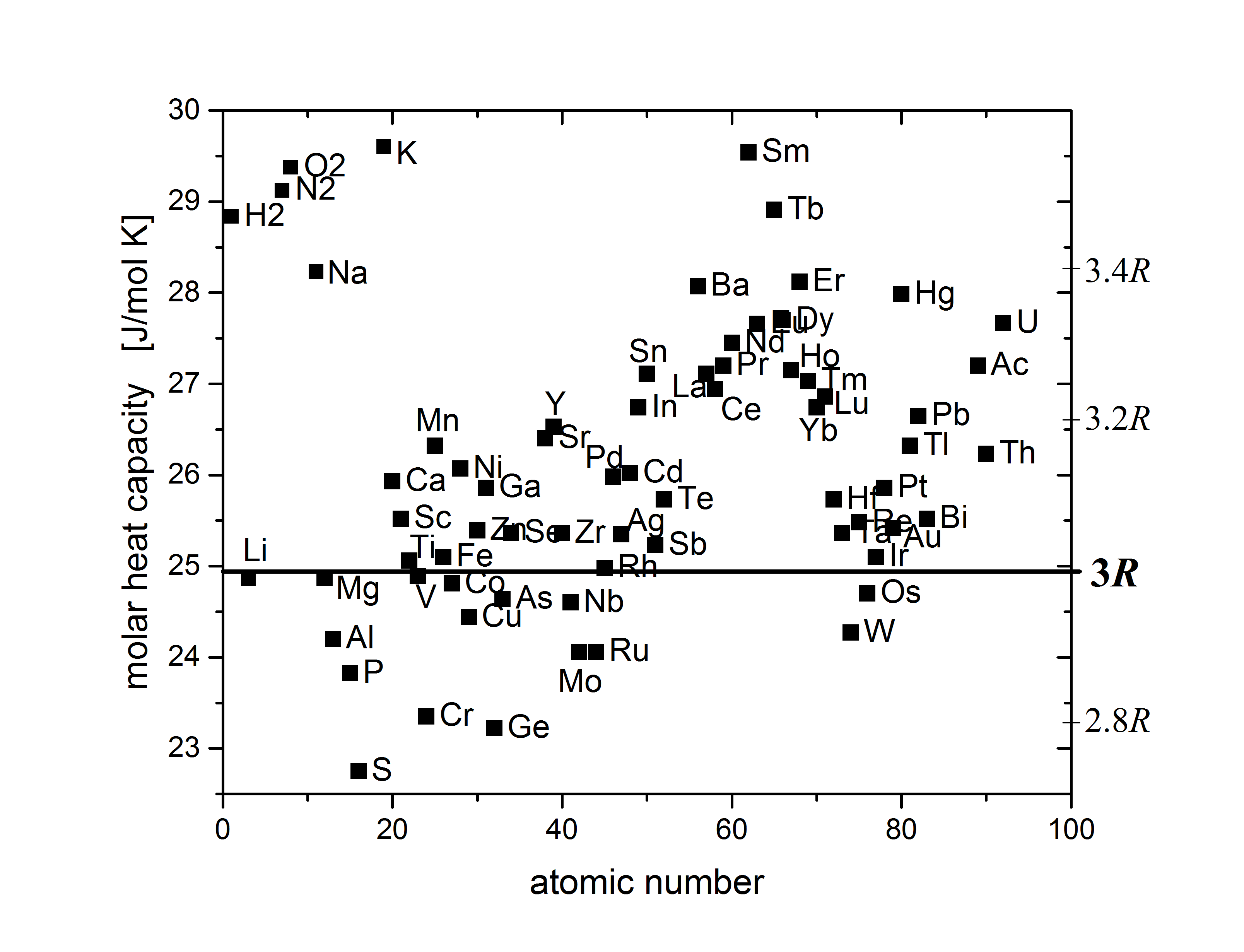
Dulong–Petit Law
The Dulong–Petit law, a thermodynamic law proposed by French physicists Pierre Louis Dulong and Alexis Thérèse Petit, states that the classical expression for the molar specific heat capacity of certain chemical elements is constant for temperatures far from the absolute zero. In modern terms, Dulong and Petit found that the heat capacity of a mole of many solid elements is about 3''R'', where ''R'' is the universal gas constant. The modern theory of the heat capacity of solids states that it is due to lattice vibrations in the solid. History Experimentally Pierre Louis Dulong and Alexis Thérèse Petit had found in 1819 that the heat capacity per weight (the mass-specific heat capacity) for 13 measured elements was close to a constant value, after it had been multiplied by a number representing the presumed relative atomic weight of the element. These atomic weights had shortly before been suggested by John Dalton and modified by Jacob Berzelius. Dulong and Petit were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Ernst Neumann
Franz Ernst Neumann (11 September 1798 – 23 May 1895) was a German mineralogist, physicist and mathematician. Biography Neumann was born in Joachimsthal, Margraviate of Brandenburg, near Berlin. In 1815 he interrupted his studies at Berlin to serve as a volunteer in the Hundred Days against Napoleon, and was wounded in the Battle of Ligny. Subsequently, he entered Berlin University as a student of theology, but soon turned to scientific subjects. His earlier papers were mostly concerned with crystallography, and the reputation they gained him led to his appointment as Privatdozent at the University of Königsberg, where in 1828 he became extraordinary, and in 1829 ordinary, professor of mineralogy and physics. His 1831 study on the specific heats of compounds included what is now known as Neumann's Law: the molecular heat of a compound is equal to the sum of the atomic heats of its constituents. Devoting himself next to optics, he produced memoirs which earned him a high place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Heat
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the mass of the sample, also sometimes referred to as massic heat capacity. Informally, it is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature. The SI unit of specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram, J⋅kg−1⋅K−1. For example, the heat required to raise the temperature of of water by is , so the specific heat capacity of water is . Specific heat capacity often varies with temperature, and is different for each state of matter. Liquid water has one of the highest specific heat capacities among common substances, about at 20 °C; but that of ice, just below 0 °C, is only . The specific heat capacities of iron, granite, and hydrogen gas are about 449 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1, 790 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1, and 14300 J⋅kg−1⋅K−1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Fraction (chemistry)
In chemistry, the mass fraction of a substance within a mixture is the ratio w_i (alternatively denoted Y_i) of the mass m_i of that substance to the total mass m_\text of the mixture. Expressed as a formula, the mass fraction is: : w_i = \frac . Because the individual masses of the ingredients of a mixture sum to m_\text, their mass fractions sum to unity: : \sum_^ w_i = 1. Mass fraction can also be expressed, with a denominator of 100, as percentage by mass (in commercial contexts often called ''percentage by weight'', abbreviated ''wt%''; see mass versus weight). It is one way of expressing the composition of a mixture in a dimensionless size; mole fraction (percentage by moles, mol%) and volume fraction ( percentage by volume, vol%) are others. When the prevalences of interest are those of individual chemical elements, rather than of compounds or other substances, the term ''mass fraction'' can also refer to the ratio of the mass of an element to the total mass of a sampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Seitz
Frederick Seitz (July 4, 1911 – March 2, 2008) was an American physicist and a pioneer of solid state physics and lobbyist. Seitz was the 4th president of Rockefeller University from 1968–1978, and the 17th president of the United States National Academy of Sciences from 1962–1969. Seitz was the recipient of the National Medal of Science, NASA's Distinguished Public Service Award, and other honors. He founded the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign and several other material research laboratories across the United States. Seitz was also the founding chairman of the George C. Marshall Institute, a tobacco industry consultant, and a prominent climate change denier. Background and personal life Born in San Francisco on July 4, 1911, Seitz graduated from Lick-Wilmerding High School in the middle of his senior year, and went on to study physics at Stanford University obtaining his bachelor's degree in three years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASIN
Asin Thottumkal (born 26 October 1985), known mononymously as Asin, is a former Indian actress who appeared predominantly in Tamil, Hindi and Telugu films. She is a trained Bharatanatyam dancer. She has received three Filmfare Awards. She began her acting career in the South Indian film industry, but later shifted her focus to Bollywood. She speaks eight languages. Making her acting debut at the age of 15 with Sathyan Anthikkad's Malayalam film ''Narendran Makan Jayakanthan Vaka'' (2001), Asin had her first commercial success with the Telugu film ''Amma Nanna O Tamila Ammayi'' in 2003, and won a Filmfare Best Telugu Actress Award for the film. '' M. Kumaran Son of Mahalakshmi'' (2004) was her debut in Tamil and a huge success. She received her Filmfare Best Tamil Actress Award for her most noted critically acclaimed performance in her third Tamil film, '' Ghajini'' (2005). She then played the lead female roles in many successful films, the most notable being the action films ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |