|
Kontalaksky Golets
Kontalaksky Golets (russian: link=no, Конталакский Голец) is a peak in the Yablonoi Mountains. Administratively it is part of the Transbaikal Krai, Russian Federation. Geography This high mountain is the highest point of the Yablonoi Range, a long mountain chain of moderate elevations which is part of the South Siberian System of ranges. It is located in the far northeastern section of the range, just a little north of Tungokochen.Google Earth The Kontalaksky Golets is a ‘’golets’’-type of mountain with a bald peak. It rises to the west of the valley of the Karenga in a largely remote and uninhabited part of Transbaikalia. There are pillar-like rock formations in this mountain similar to the kigilyakhs of Yakutia. See also *List of mountains in Russia This is a list of mountains and hills of Russia. List by elevation Over 5000 meters 4000 to 4999 meters 3000 to 3999 meters 2000 to 2999 meters 1000 to 1999 meters Under 1000 metres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transbaikal Krai
Zabaykalsky Krai ( rus, Забайкальский край, r=Zabaikal'skii krai, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲskʲɪj kraj, lit. "Transbaikal krai"; bua, Yбэр Байгалай хизаар, Uber Baigalai Xizaar) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that was created on March 1, 2008 as a result of a merger of Chita Oblast and Agin-Buryat Autonomous Okrug, after a referendum held on the issue on March 11, 2007. The Krai is now part of the Russian Far East as of November 2018 in accordance with a decree issued by Russian President Vladimir Putin. The administrative center of the krai is located in the city of Chita. As of the 2010 Census, the population was 1,107,107. Geography The krai is located within the historical region of Transbaikalia (Dauria) and has extensive international borders with China (Inner Mongolia and Heilongjiang) (998 km) and Mongolia (Dornod Province, Khentii Province and Selenge Province) (868 km); its internal borders are with Irkutsk and Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is administered as part of the Far Eastern Federal District, which is located between Lake Baikal in eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. The Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia (previously during the Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as just "Far East" (). What is known in English as the Far East is usually referred to as "the Asia-Pacific Region" (, abbrevia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yablonoi Mountains
The Yablonoi Mountains or Yablonovy Mountains ( rus, Яблоновый хребет, bua, Яабланай шэлэ нуруу, ; mn, Яблоны нуруу, ''Yablony nuruu'') are a mountain range, in Transbaikal (mainly in Zabaykalsky Krai), Siberia, Russia. The range is sparsely inhabited with most settlements engaged in mining. The area is especially rich in tin. The city of Chita lies between the Yablonoi Mountains to the west and the Chersky Range to the east.Google Earth The Trans-Siberian Railroad passes the mountains at Chita and runs parallel to the range before going through a tunnel to bypass the heights. Geography The Yablonoi Mountains stretch for about in a northeast–southwest direction. They rise mostly in the western part of the Zabaikalsky Krai, with a small section in the southeastern part of Buryatia. The width of the range varies between and . The Vitim Plateau lies to the north and the Borshchovochny Range to the east of the range. The tallest pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Siberian System
The South Siberian Mountains ( rus, Южно-Сибирские горы) are one of the largest mountain systems of the Russian Federation. The total area of the system of mountain ranges is more than 1.5 million km². The South Siberian Mountains are located in the Siberian and Far Eastern Federal Districts of Russia, as well as partly in Mongolia. The territory of the mountain system is one of the Great Russian Regions. Geography The system is composed of a number of ranges aligned in an east–west direction stretching for almost . Part of them are near the border with Mongolia and China, while others rise further north. To the south the South Siberian ranges merge with the Mongolian and Chinese mountain chains and plateaus. In the west lies the Dzungarian Basin and to the east the Mongolian Plateau. To the north the South Siberian Mountains merge with the West Siberian Lowland and the Central Siberian Plateau, both on the Russian side. To the southeast the Baikal Range is sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungokochen
Tungokochen (russian: Тунгокочен) is a rural locality in Tungokochensky District of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia. Population: Geography The village is about NNE of the district administrative center of Verkh-Usugli. It lies on the left bank of the Karenga river, to the southeast of the slopes of the Yablonoi Mountains. History Tungokochen was founded in the 1930s as the capital of Tungokochensky District. In 1976, the administrative center was moved to the village of Verkh-Usugli. The village had an airport which was functional until the 1990s. See also *Kontalaksky Golets Kontalaksky Golets (russian: link=no, Конталакский Голец) is a peak in the Yablonoi Mountains. Administratively it is part of the Transbaikal Krai, Russian Federation. Geography This high mountain is the highest point of the Y ... References {{Authority control Rural localities in Zabaykalsky Krai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungokochensky District
Tungokochensky District (russian: Тунгокоченский райо́н) is an administrativeRegistry of the Administrative-Territorial Units and the Inhabited Localities and municipalLaw #316-ZZK district (raion), one of the thirty-one in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia. It is located in the central northern part of the krai, and borders with Kalarsky District in the north, Tungiro-Olyokminsky District in the east, and with Chernyshevsky District in the south. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the rural locality (a '' selo'') of Verkh-Usugli. Population: 14,207 ( 2002 Census); The population of Verkh-Usugli accounts for 20.7% of the district's total population. Geography The Chersky and Yablonoi ranges stretch from NE to SW across the district, forming the watershed of rivers flowing to the Arctic Ocean on the northern side and rivers flowing to the Pacific Ocean in the southern side. Kontalaksky Golets, the highest peak of the Yablonoi is located in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Earth
Google Earth is a computer program that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geographic information system, GIS data onto a 3D globe, allowing users to see cities and landscapes from various angles. Users can explore the globe by entering addresses and coordinates, or by using a Computer keyboard, keyboard or computer mouse, mouse. The program can also be downloaded on a smartphone or Tablet computer, tablet, using a touch screen or stylus to navigate. Users may use the program to add their own data using Keyhole Markup Language and upload them through various sources, such as forums or blogs. Google Earth is able to show various kinds of images overlaid on the surface of the earth and is also a Web Map Service client. In 2019, Google has revealed that Google Earth now covers more than 97 percent of the world, and has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golets (geography)
Golets ( rus, голец), plural Goltsy ( rus, Гольцы), is a type of bald mountain summit of certain areas of Siberia. The term is part of the geographical name of several peaks in the region. Description ''Golets'' protrude above the treeline and are usually round or blunt. They are barren, rocky or stony, and only rarely lichens or stunted small scrubs such as Siberian pine, may grow on them. Bare rock slopes, kurums and cliffs are common. The term is usually found in the names of mountaintops in the South Siberian System, especially in Transbaikalia and the Sayan Mountains. The zone below the golets is normally the highest of the altitudinal vegetation zones, above the mountain tundra of the alpine belt.Sizykh, A. (2016) ''Formation of an Ecotone at the Boundary of Forest and Mountain Tundra—Morskoy Ridge as an Example, Middle Part of Eastern Coast of Lake Baikal.'' Open Access Library Journal, 3, 1-4. This kind of mountains may consist in single high peaks connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
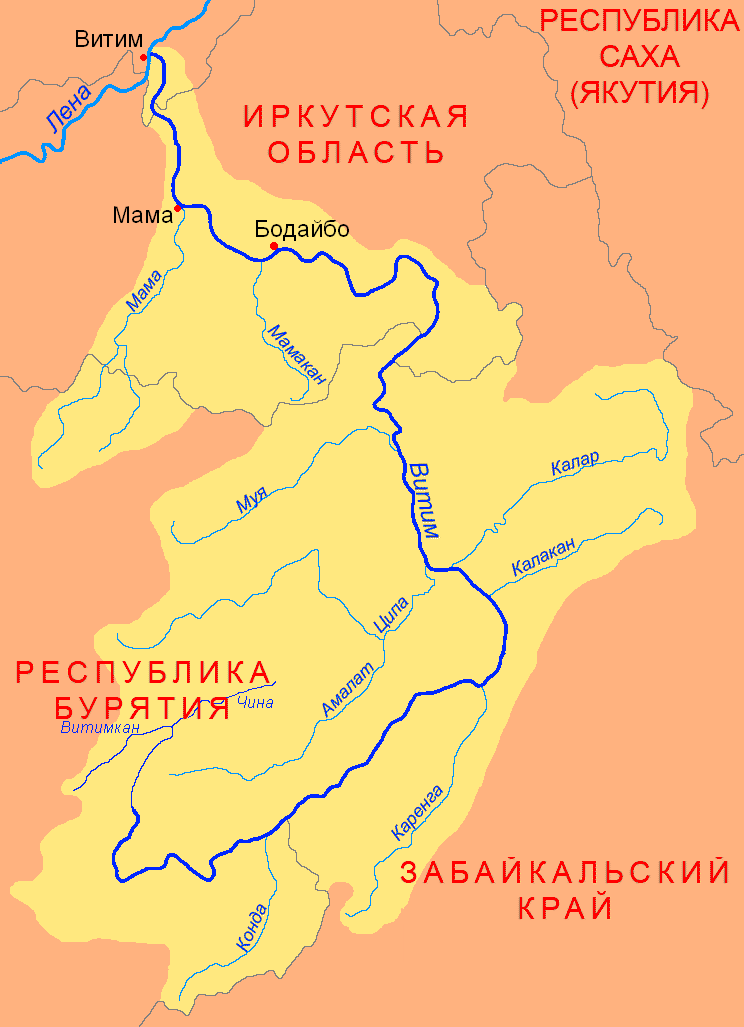
Karenga (river)
The Karenga (russian: Каренга) is a river in Zabaykalsky Krai, southern East Siberia, Russia. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The area through which the river flows is inhabited by indigenous Tungus people. There are Neolithic archaeological sites near the mouth of the river where ancient ceramic remains belonging to the Ust-Karenga Culture have been found. Course The Karenga is a right tributary of the Vitim. Its sources are in the Chingikhan Saddle, located between the Yablonoi Mountains and the Chersky Range. Kontalaksky Golets, the highest peak of the Yablonoi rises to the NW of the river valley, near Tungokochen.Google Earth It flows in a mainly northeastern direction within a winding channel. The vegetation along the banks of the river is mainly sparse larch taiga. Its lower course is at the eastern end of the Vitim Plateau. Finally, at the border with Buryatia it meets the Vitim from its mouth in the Lena. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Formation
A rock formation is an isolated, scenic, or spectacular surface rock outcrop. Rock formations are usually the result of weathering and erosion sculpting the existing rock. The term ''rock formation'' can also refer to specific sedimentary strata or other rock unit in stratigraphic and petrologic studies. A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination: * Igneous rocks are created when molten rock cools and solidifies, with or without crystallisation. They may be either plutonic bodies or volcanic extrusive. Again, erosive forces sculpt their current forms. * Metamorphic rocks are created by rocks that have been transformed into another kind of rock, usually by some combination of heat, pressure, and chemical alteration. * Sedimentary rocks are created by a variety of processes but usually involving deposition, grain by grain, layer by layer, in water or, in the case of terrestrial sediments, on land through the action of wind or sometimes moving ice. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kigilyakh
Kigilyakh or kisiliyakh ( rus, кигиляхи; sah, киһилээх, meaning "stone person") are tall, pillar-like natural rock formations looking like tall monoliths standing more or less isolated. Usually they are composed of granite or sandstone shaped as a result of cryogenic weathering. Most kigilyakhs formed during the Cretaceous period and are about 120 million years old. Cultural significance and etymology These anthropomorphic rock pillars are an important feature in Yakut culture. Often they are slightly scattered, protruding from the surface of smooth mountains and giving the impression of a standing crowd of people. According to Yakut legends kigilyakhs originated in very ancient people. The Yakut word ''"kisiliy"'' means "a place where there are people". ''Kisilyakh'' means "mountain having a man" or "mountain married". The term "kigilyakh" is a distorted form of the original Yakut ''"kisilyakh"''. Locations Such stones are found in different places of Sakha ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)