|
Konstantinos I
Constantine I ( el, Κωνσταντίνος Αʹ, ''Konstantínos I''; – 11 January 1923) was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army during the unsuccessful Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and led the Greek forces during the successful Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, in which Greece expanded to include Thessaloniki, doubling in area and population. He succeeded to the throne of Greece on 18 March 1913, following his father's assassination. Constantine’s disagreement with Eleftherios Venizelos over whether Greece should enter World War I led to the National Schism. He forced Venizelos to resign twice, but in 1917 he left Greece, after threats by the Entente forces to bombard Athens; his second son, Alexander, became king. After Alexander's death, Venizelos' defeat in the 1920 legislative elections, and a plebiscite in favor of his return, Constantine was reinstated. He abdica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of The Hellenes
The Kingdom of Greece was ruled by the House of Wittelsbach between 1832 and 1862 and by the House of Glücksburg from 1863 to 1924, temporarily abolished during the Second Hellenic Republic, and from 1935 to 1973, when it was once more abolished and replaced by the Third Hellenic Republic. Only the first king, Otto, King of Greece, Otto, was actually styled ''Basileus#Modern Greece, King of Greece'' (). His successor, George I of Greece, George I, was styled ''King of the Hellenes'' (), as were all other modern Greek monarchs. Second Hellenic Republic, A republic was briefly established from 1924 to 1935. The restored monarchy was abolished weeks before the 1973 Greek republic referendum, referendum in 1973 conducted under the auspices of the then-ruling Regime of the Colonels, military regime, which confirmed the abolishment. It was re-confirmed by 1974 Greek republic referendum, a second referendum in 1974, after the metapolitefsi, restoration of democratic rule. House of Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gardes Du Corps
A ''Garde du Corps'' (French for lifeguard) is a military unit, formed of guards. A ''Garde du Corps'' was first established in France in 1445. From the 17th century onwards, the term was used in several German states and also, for example, in the Kingdom of Two Sicilies for several regiments of heavy cavalry, whose proprietary colonel was usually the sovereign. *In the Electorate of Brandenburg, the Trabant Guards were given the title ''Garde du Corps'' in 1692, but were disbanded again around 1715. In 1740, King Frederick II established a cuirassier regiment as his '' Gardes du Corps'', which existed until the Prussian Army was disbanded in 1918. (Only in Prussia was the unit known as the ''Regiment der Gardes du Corps'', as opposed to simply a ''Garde du Corps'' in other German states.) *The Saxon ''Garde du Corps'' was formed in 1620, initially going under various names. From 1707 it was permanently titled the ''Garde du Corps'' and was stationed in Dresden and the sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kilkis-Lachanas
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counter-attacked, entering Bulgaria. With Bulgaria also having previously engaged in territorial disputes with Romania and the bulk of Bulgarian forces engaged in the south, the prospect of an easy victory incited Romanian intervention against Bulgaria. The Ottoman Empire also took advantage of the situation to regain some lost territories from the previous war. When Romanian troops approached the capital Sofia, Bulgaria asked for an armistice, resulting in the Treaty of Bucharest, in which Bulgaria had to cede portions of its First Balkan War gains to Serbia, Greece and Romania. In the Treaty of Constantinople, it lost Adrianople to the Ottomans. The political developments and military preparations f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bizani
The Battle of Bizani (, ''Máchi tou Bizaníou''; tr, Bizani Muharebesi, italic=no) took place in Epirus on . The battle was fought between Greek and Ottoman forces during the last stages of the First Balkan War, and revolved around the forts of Bizani, which covered the approaches to Ioannina, the largest city in the region. At the outbreak of the war, the Hellenic Army on the Epirus front did not have the numbers to initiate an offensive against the German-designed defensive positions in Bizani. However, after the campaign in Macedonia was over, many Greek troops were redeployed to Epirus, where Crown Prince Constantine himself assumed command. In the battle that followed the Ottoman positions were breached and Ioannina taken. Despite having a slight numerical advantage, this was not the decisive factor in the Greek victory. Rather, "solid operational planning" by the Greeks was key as it helped them implement a well-coordinated and executed assault that did not allow the Ott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
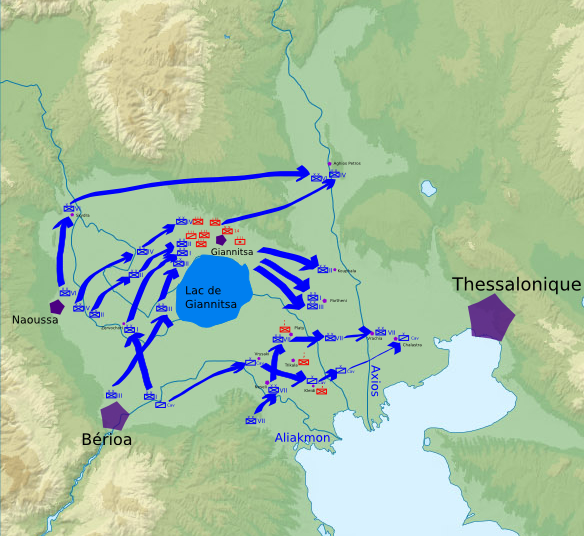
Battle Of Yenidje
The Battle of Yenidje, also transliterated as Yenice ( el, Μάχη των Γιαννιτσών, Battle of Giannitsa), was a major battle between Greek forces under Crown Prince Constantine and Ottoman forces under General Hasan Tahsin Pasha and took place between October 19–20 ( O.S.), 1912 during the First Balkan War. The battle began when the Greek army attacked the Ottoman fortified position at Yenidje (now Giannitsa, Greece), which was the last line of defense for the city of Thessaloniki. The rough and swampy terrain surrounding Yenidje significantly complicated the advance of the Greek army, most notably its artillery. In the early morning of 20 October, an infantry charge by the Greek 9th Evzone Battalion caused the Greek army to gain momentum, leading to the collapse of the entire western wing of the Ottomans. Ottoman morale plunged and the bulk of the defenders began fleeing two hours later. The Greek victory at Yenidje opened the way for the capture of Thessaloniki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sarantaporo
The Battle of Sarantaporo, also variously transliterated as Sarantaporon or Sarandaporon ( el, Μάχη του Σαρανταπόρου, tr, Sarantaporo Muharebesi, links=no), took place on 9–10 October, 1912. It was the first major battle fought between Greek forces under Crown Prince Constantine and Ottoman forces under General Hasan Tahsin Pasha during the First Balkan War. The battle began when the Greek army attacked the Ottoman defensive line at the Sarantaporo pass, which connected Thessaly with central Macedonia. Despite being perceived as impregnable by its defenders, the main body of the Greek forces managed to advance deep inside the pass, while auxiliary units broke through the Ottoman flanks. The Ottomans abandoned their defensive line during the night, fearing encirclement. The Greek victory at Sarantaporo opened the way for the capture of Servia and Kozani. Background Following the conclusion of the Greek War of Independence, the Megali Idea (Great Idea) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and involved actions of the Balkan League (the Kingdoms of Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Greece, Greece and Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro) against the Ottoman Empire. The Balkan states' combined armies overcame the initially numerically inferior (significantly superior by the end of the conflict) and strategically disadvantaged Ottoman armies, achieving rapid success. The war was a comprehensive and unmitigated disaster for the Ottomans, who lost 83% of their European territories and 69% of their European population. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defeated it, in the process stripping the Ottomans of its European provinces, leaving only Eastern Thrace under the Ottoman Empire's control. In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria fought against the other four original combatants of the first war. It also faced an attack from Romania from the north. The Ottoman Empire lost the bulk of its territory in Europe. Although not involved as a combatant, Austria-Hungary became relatively weaker as a much enlarged Serbia pushed for union of the South Slavic peoples. The war set the stage for the Balkan crisis of 1914 and thus served as a "prelude to the First World War". By the early 20th century, Bulgaria, Greece, Montenegro and Serbia had achieved independence from the Ottoman Empire, but large eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Domokos
The Battle of Domokos ( tr, Dömeke Savaşı) was a battle between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Greece. This battle was a part of the Greco-Turkish War (1897). Background After Greece tried to annex the island Crete the Ottoman porte declared war on Greece. The commander of the Ottoman army at Elassona ( tr, Alasonya) was Edhem Pasha (later gained the title Gazi) . He was one of the younger generals of the Ottoman Army (then 46) and his appointment perplexed many. The commander of the Greek army was the Prince Constantine. The Ottoman army in Domokos was 45000 strong and the Greek army was 40000 strong The Greek side also had 2000 Italian irregulars under the command of Ricciotti Garibaldi. The battle According to a contemporary source following initial victories, Ethem Pasha had some of his troops in Velestino (which was the theatre of a battle) and most in Pharsala. But there was a momentary pause after the second battle of Valestino. The new Greek prime minist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Turkish War (1897)
The Greco-Turkish War of 1897 or the Ottoman-Greek War of 1897 ( or ), also called the Thirty Days' War and known in Greece as the Black '97 (, ''Mauro '97'') or the Unfortunate War ( el, Ατυχής πόλεμος, Atychis polemos), was a war fought between the Kingdom of Greece and the Ottoman Empire. Its immediate cause involved the status of the Ottoman province of Crete, whose Greek-majority population had long desired union with Greece. Despite the Ottoman victory on the field, an autonomous Cretan State under Ottoman suzerainty was established the following year (as a result of the intervention of the Great Powers after the war), with Prince George of Greece and Denmark as its first High Commissioner. The war put the military and political personnel of Greece to test in an official open war for the first time since the Greek War of Independence in 1821. For the Ottoman Empire, this was also the first war-effort to test a re-organized military system. The Ottoman a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Army
The Hellenic Army ( el, Ελληνικός Στρατός, Ellinikós Stratós, sometimes abbreviated as ΕΣ), formed in 1828, is the land force of Greece. The term ''Hellenic'' is the endogenous synonym for ''Greek''. The Hellenic Army is the largest of the three branches of the Hellenic Armed Forces, also constituted by the Hellenic Air Force (HAF) and the Hellenic Navy (HN). The army is commanded by the chief of the Hellenic Army General Staff (HAGS), which in turn is under the command of Hellenic National Defence General Staff (HNDGS). The motto of the Hellenic Army is ('Freedom stems from valour'), from Thucydides's '' History of the Peloponnesian War (2.43.4)'', a remembrance of the ancient warriors that defended Greek lands in old times. The Hellenic Army Emblem is the two-headed eagle with a Greek Cross escutcheon in the centre. The Hellenic Army is also the main contributor to, and "lead nation" of, the Balkan Battle Group, a combined-arms rapid-response force under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |