|
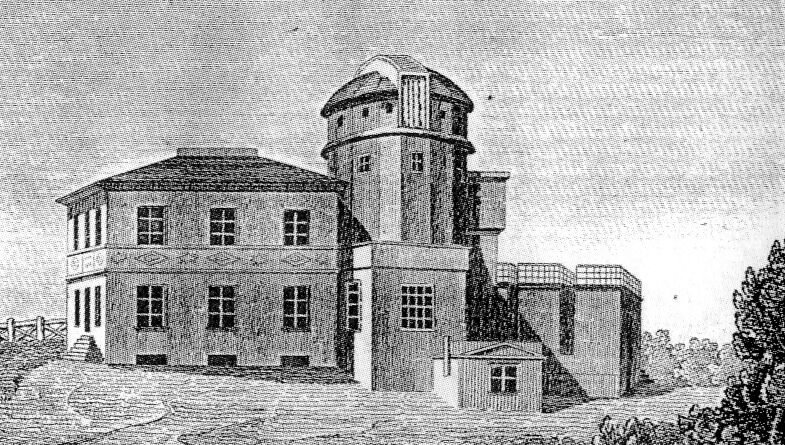
Koenigsberg Observatory
Koenigsberg Observatory (german: Sternwarte Königsberg; Königsberger Universitätssternwarte; obs. code: 058) was an astronomical observatory and research facility which was attached to the Albertina University in Königsberg, what is now Kaliningrad, Russia. The observatory was destroyed by Royal Air Force bombs in August 1944 during the Second World War. Only the reduit (interior of the building) remained from the bastion. The building is a semicircular two-storey building with a brick vault. Nowadays, the building is considered a regional architectural monument. Description It was founded in 1810 and started working in 1813. Well-known astronomers who used the observatory included Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel, Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander, Arthur Auwers and Hermann Struve. In 1838, the parallax of a star was determined successfully for first time by Bessel using a heliometer A heliometer (from Greek ἥλιος ''hḗlios'' "sun" and ''measure'') is an instrument origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Observatory Codes
This is a list of observatory codes (IAU codes or MPC codes) published by the Minor Planet Center. For a detailed description, ''see observations of small Solar System bodies Observations of minor planets as well as comets and natural satellites of the Solar System are made by astronomical observatories all over the world and reported to the Minor Planet Center (MPC), a service of the International Astronomical Unio ...''. List References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Observatory codes * Astronomy-related lists Technology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander
Friedrich Wilhelm August Argelander (22 March 1799 – 17 February 1875) was a German astronomer. He is known for his determinations of stellar brightnesses, positions, and distances. Life and work Argelander was born in Memel in the Kingdom of Prussia (now Klaipėda in Lithuania), the son of a father of Finnish descent, Johann Gottlieb Argelander, and German (Prussian) mother, Dorothea Wilhelmina Grünlingen. He studied with Friedrich Bessel, whose assistant he became in 1820, and obtained his Ph.D. in 1822 at University of Königsberg. From 1823 until 1837, Argelander was the head of the Finnish observatory, first in Turku and then in Helsinki. He then moved to Bonn, Germany. There he designed and built a new observatory at the University of Bonn with funding approved directly by King Frederick William IV whom Argelander had become friends with in his childhood. This lifelong friendship had started when the then crown prince temporarily lived in Argelander's parents house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Astronomical Observatories
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Königsberg
The University of Königsberg (german: Albertus-Universität Königsberg) was the university of Königsberg in East Prussia. It was founded in 1544 as the world's second Protestant academy (after the University of Marburg) by Duke Albert of Prussia, and was commonly known as the Albertina. Following World War II, the city of Königsberg was transferred to the Soviet Union according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement, and renamed Kaliningrad in 1946. The Albertina was closed and the remaining non-Lithuanian population either executed or expelled, by the terms of the Potsdam Agreement. Today, the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University in Kaliningrad claims to maintain the traditions of the Albertina. History Albert, former Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights and first Duke of Prussia since 1525, had purchased a piece of land behind Königsberg Cathedral on the Kneiphof island of the Pregel River from the Samland chapter, where he had an academic gymnasium (school) erected in 154 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Von Fraunhofer
Joseph Ritter von Fraunhofer (; ; 6 March 1787 – 7 June 1826) was a German physicist and optical lens manufacturer. He made optical glass, an achromatic telescope, and objective lenses. He also invented the spectroscope and developed diffraction grating. In 1814, he discovered and studied the dark absorption lines in the spectrum of the sun now known as Fraunhofer lines. The German research organization Fraunhofer Society, which is Europe's biggest Society for the advancement of applied research, is named after him. Biography Joseph Fraunhofer was the 11th child, born into a Roman Catholic family in Straubing, in the Electorate of Bavaria, to Franz Xaver Fraunhofer and Maria Anna Fröhlich. He was orphaned at the age of 11 and started working as an apprentice to a harsh glassmaker named Philipp Anton Weichelsberger. In 1801, the workshop in which he was working collapsed, and he was buried in the rubble. The rescue operation was led by Prince-Elector Maximilian Joseph. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
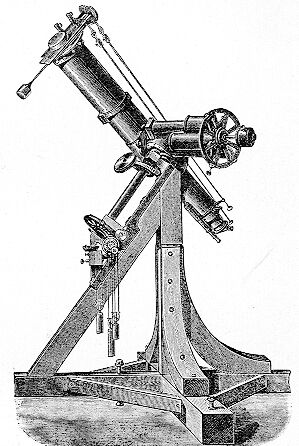
Heliometer
A heliometer (from Greek ἥλιος ''hḗlios'' "sun" and ''measure'') is an instrument originally designed for measuring the variation of the sun's diameter at different seasons of the year, but applied now to the modern form of the instrument which is capable of much wider use. The basic concept is to introduce a split element into a telescope's optical path so as to produce a double image. If one element is moved using a screw micrometer, precise angle measurements can be made. The simplest arrangement is to split the object lens in half, with one half fixed and the other attached to the micrometer screw and slid along the cut diameter. To measure the diameter of the sun, for example, the micrometer is first adjusted so that the two images of the solar disk coincide (the "zero" position where the split elements form essentially a single element). The micrometer is then adjusted so that diametrically opposite sides of the two images of the solar disk just touch each other. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Parallax
Stellar parallax is the apparent shift of position of any nearby star (or other object) against the background of distant objects, and a basis for determining (through trigonometry) the distance of the object. Created by the different orbital positions of Earth, the extremely small observed shift is largest at time intervals of about six months, when Earth arrives at opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit, giving a baseline distance of about two astronomical units between observations. The parallax itself is considered to be half of this maximum, about equivalent to the observational shift that would occur due to the different positions of Earth and the Sun, a baseline of one astronomical unit (AU). Stellar parallax is so difficult to detect that its existence was the subject of much debate in astronomy for hundreds of years. Thomas Henderson, Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, and Friedrich Bessel made first successful parallax measurements in 1832-1838, for the stars alpha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Struve
Karl Hermann von Struve ( – 12 August 1920) was a Baltic German astronomer. In Russian, his name is sometimes given as ''German Ottovich Struve'' (Герман Оттович Струве) or ''German Ottonovich Struve'' (Герман Оттонович Струве). Hermann von Struve was a part of the famous group of astronomers from the Struve family, which also included his grandfather Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve, father Otto Wilhelm von Struve, brother Ludwig Struve and nephew Otto Struve. Unlike other astronomers of the Struve family, Herman spent most of his career in Germany. Continuing the family tradition, Struve's research was focused on determining the positions of stellar objects. He was particularly known for his work on satellites of planets of the Solar System and development of the intersatellite method of correcting their orbital position. The mathematical Struve function is named after him. Biography Herman was born in 1854 in Tsarskoye Selo, a forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Auwers
Georg Friedrich Julius Arthur von Auwers (12 September 1838 – 24 January 1915) was a German astronomer. Auwers was born in Göttingen to Gottfried Daniel Auwers and Emma Christiane Sophie (née Borkenstein). He attended the University of Göttingen and worked at the University of Königsberg. He specialized in astrometry, making very precise measurements of stellar positions and motions. He detected the companion stars of Sirius and Procyon from their effects on the main star's motion, before telescopes were powerful enough to visually observe them. He was from 1866 Secretary to the Prussian Academy of Sciences, Berlin Academy, and directed expeditions to measure the Astronomical transit, transits of Venus, in order to measure the distance from the earth to the Sun more accurately, and therefore be able to calculate the dimensions of the Solar System more accurately and with greater precision. He began a project to unify all available sky charts, an interest that began with h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the sun to another star by the method of parallax. A special type of mathematical functions were named Bessel functions after Bessel's death, though they had originally been discovered by Daniel Bernoulli and then generalised by Bessel. Life and family Bessel was born in Minden, Westphalia, then capital of the Prussian administrative region Minden-Ravensberg, as second son of a civil servant into a large family. At the age of 14 Bessel was apprenticed to the import-export concern Kulenkamp at Bremen. The business's reliance on cargo ships led him to turn his mathematical skills to problems in navigation. This in turn led to an interest in astronomy as a way of determining longitude. Bessel came to the attention of a major figure of German astronomy at the time, Heinrich Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Code
This is a list of observatory codes (IAU codes or MPC codes) published by the Minor Planet Center. For a detailed description, ''see observations of small Solar System bodies Observations of minor planets as well as comets and natural satellites of the Solar System are made by astronomical observatories all over the world and reported to the Minor Planet Center (MPC), a service of the International Astronomical Unio ...''. List References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Observatory codes * Astronomy-related lists Technology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |