|
Kodungallur Bhagavathy Temple
Sree Kurumba Bhagavati Temple (alternatively Kodungallur Devi Temple) is a Hindu temple at Kodungallur, Thrissur District, Kerala state, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Bhadrakali, a form of Mahakali or simply Durga or Aadi Parashakthi worshipped and significantly revered in Kerala. The goddess is known also by the names "Sri Kurumba"" (The Mother of Kodungallur). This temple is the head of 64 Bhadrakali temples in Kerala especially Malabar. This Mahakali temple is one of the oldest functioning temples in India. This is attested by numerous Tamil poems and inscriptions of different times. The goddess of the temple represents the goddess in her fierce ('ugra') form, facing North, featuring eight hands with various attributes. One is holding the head of the demon king Daruka, another a sickle-shaped sword, next an anklet, another a bell, among others. Routine worship at the temple every day at 03:00 and ends at 21:00 local time. The temple is often accredited as the original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sri Chakra
The Sri Yantra, Shri Yantra, or Shri Chakra is a form of mystical diagram (''yantra'') used in the Shri Vidya school of Hinduism. It consists of nine interlocking triangles - four upward ones which represent Shiva, and five downward ones representing Shakti. All these surround the central point, the ''bindu''. These triangles represent the cosmos and the human body. Because of its nine triangles, Shri Yantra is also known as the ''Navayoni Chakra''. When the two-dimensional Shri Yantra is represented in three dimensions, it is called a ''Mahameru''. Mount Meru derives its name from this shape. In addition to Mount Meru, all other yantras derive from the Shri Yantra. Appearance In the 2009 issue of Brahmavidya (the journal of the Adyar Library), Subhash Kak argues that the description of Shri Yantra is identical to the ''yantra'' described in the Śrī Sūkta in the Rigveda. The Sri Yantra's 9 constituent triangles vary in size and shape and intersect to form 43 smaller triangles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
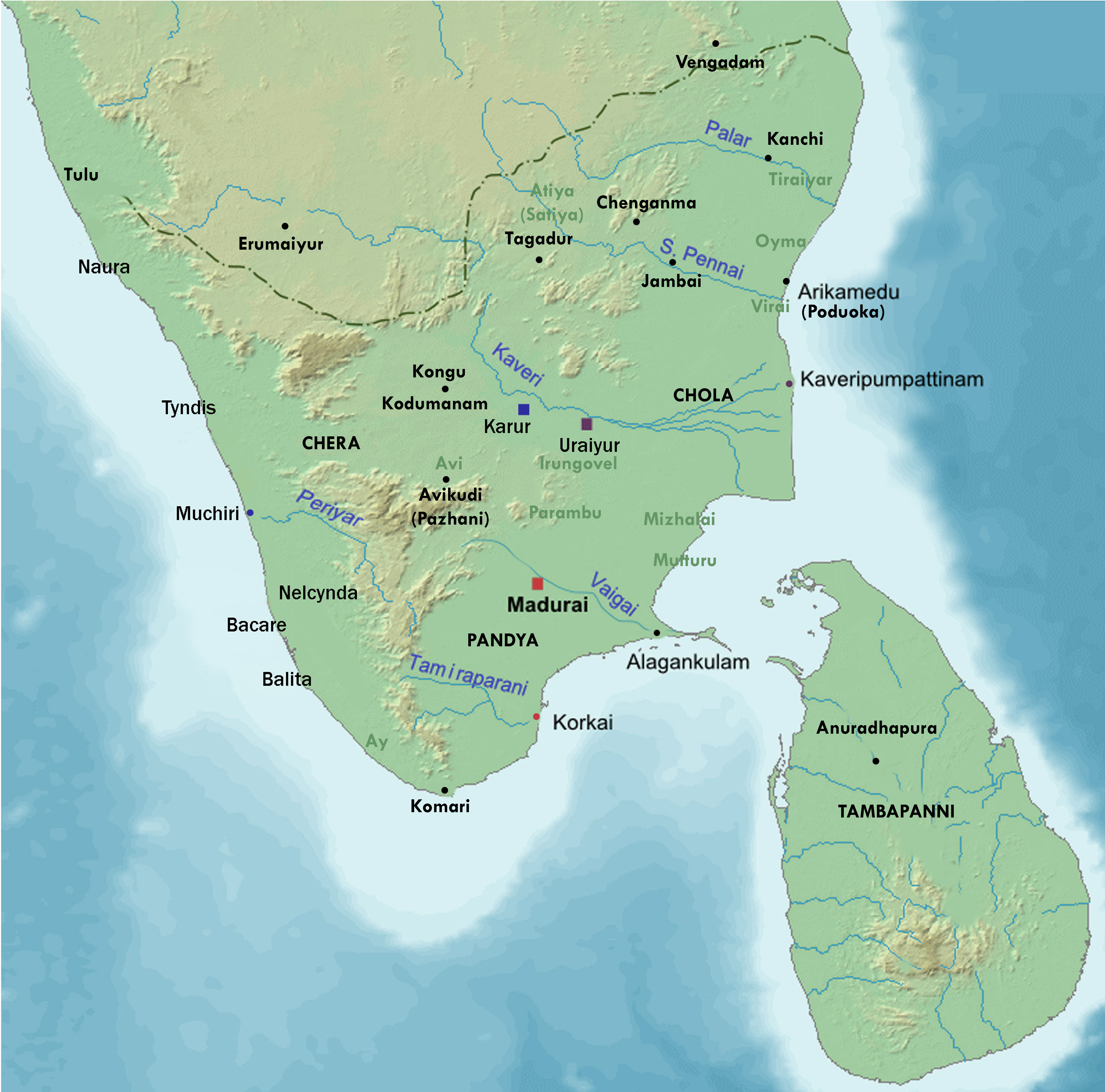
Kodungallur Thiyya Tara
Kodungallur (; also Cranganore, Portuguese: Cranganor; formerly known as Mahodayapuram, Shingly, Vanchi, Muchiri, Muyirikkode, and Muziris) is a historically significant town situated on the banks of river Periyar on the Malabar Coast in Thrissur district of Kerala, India. It is north of Kochi (Cochin) by National Highway 66 and from Thrissur. Kodungallur, being a port city at the northern end of the Kerala lagoons, was a strategic entry point for the naval fleets to the extensive Kerala backwaters. As of the 2011 India Census, Kodungallur Municipality had a population of 33,935. It had an average literacy rate of 95.10%. Around 64% of the population follows Hinduism, 32% Islam and 4% Christianity. Schedule Caste (SC) constitutes 7.8% while Schedule Tribe (ST) were 0.1% of total population in Kodungallur. Kodungallur is the headquarters of the Kodungallur sub-district (tehsil) in Thrissur district. Kodungallur Kerala Legislative Assembly constituency is a part of Chala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhoti
The dhoti, also known as veshti, vetti, dhuti, mardani, chaadra, dhotar, jaiñboh, panchey, is a type of sarong, tied in a manner that outwardly resembles "loose trousers". It is a lower garment forming part of the ethnic costume for men in the Indian subcontinent. The ''dhoti'' is fashioned out of a rectangular piece of unstitched cloth, usually around long, wrapped around the waist and the legs and knotted, either in the front or the back. The ''dhoti'' is touted as the male counterpart of the ''sari'' worn by females to religious and secular ceremonies ( functions). is a yellow silk dhoti, worn on auspicious occasions. The dhoti which is worn around the lower waist and drawn up in between the legs, is a 5-yard-long piece of woven fabric; it must not be confused with pre- stitched "dhoti pants", which are a new ready to wear trend these days, popular among women and typical of children. Etymology The word ''dhoti'' is derived from ''dhauti'' (Sanskrit: धौती), transl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrikas
Matrikas (Sanskrit: मातृका (singular), IAST: mātṝkās, lit. "divine mothers") also called Matar or Matri, are a group of mother goddesses who are always depicted together in Hinduism. The Matrikas are often depicted in a group of seven, the Saptamatrika(s) (Seven Mothers). However, they are also depicted as a group of eight, the Ashtamatrika(s). In the '' Brihat Samhita'', Varahamihira says that "Mothers are to be made with cognizance of (different major Hindu) gods corresponding to their names." They are associated with these gods as their spouses or their energies (''Shaktis''). Brahmani emerged from Brahma, Vaishnavi from Vishnu, Maheshvari from Shiva, Indrani from Indra, Kaumari from Skanda, Varahi from Varaha and Chamunda from Devi. and additionals are Narasimhi from Narasimha and Vinayaki from Ganesha. Originally believed to be a personification of the seven stars of the star cluster the Pleiades, they became quite popular by the seventh century and a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and includes Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Indonesia (Java and Bali), Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, and Bangladesh and in countries with large ethnic Indian populations including Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, and Trinidad and Tobago. Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his elephant head. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and thought to bring good luck; the patron of arts and sciences; and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked as a patron of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. Starting in the early centuries of the common era, newly revealed Tantras centering on Vishnu, Shiva or Shakti emerged. There are tantric lineages in all main forms of modern Hinduism, such as the Shaiva Siddhanta tradition, the Shakta sect of Sri-Vidya, the Kaula, and Kashmir Shaivism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheraman Perumal
Perumal (the 'Great One') is the name of a Hindu deity. It was also a medieval Indian royal title of: *Western Ganga dynasty Narayanan, M. G. S. ''Perumāḷs of Kerala''. Thrissur (Kerala): CosmoBooks, 2013. 171. **Sripurusha **Rajamalla **Nitimarga * Pandya dynasty **Maran Chatayan * Chola dynasty **Parantaka * Pallava dynasty **Paramesvara Varma II of Kanchi * Chera Perumals of MakotaiNoburu Karashmia (ed.), ''A Concise History of South India: Issues and Interpretations.'' New Delhi: Oxford University Press, 2014 ** Rama "Rajasekhara" (Cheraman Perumal Nayanar) **Sthanu Ravi (Kulasekhara Alvar Kulasekhara (Tamil: ''குலசேகரர்'') (''fl.'' 9th century CE), one of the twelve Vaishnavite alvars, was a bhakti theologian and devotional poet from medieval south India (Kerala). He was the author of Perumal Tirumoli in Tamil a ...) **Bhaskara Ravi "Manukuladitya" ** Rama "Kulasekhara" References {{Reflist Hindu dynasties Indian surnames Dynasties of India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappathikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannaki Amman
Kannaki Amman ( ta, கண்ணகி அம்மன், IAST: , si, පත්තිනි දෙවියෝ, ml, കണ്ണകി ഭഗവതി ''kaṇṇaki bhagavati'') is the deified form of Kannagi, the heroine of the Tamil epic '' Cilappatikāram.'' She is worshipped in parts of Sri Lanka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala. As a goddess of chastity, she is venerated by Indian Tamils and Malayalis, Sri Lankan Tamil Shaivites, and also by the Sinhalese Buddhists as Pattini Deviyo. In regional Hindu tradition, her tale is interpreted as the story of Durga demanding justice after the death of her husband, Kovalan, who is identified as a form of Shiva. Origin Cilappatikāram, the literary work of Ilango Adigal, describes the poor life of Kannaki with her husband merchant Kovalan, who lost all his wealth during his life with a lavish courtesan dancer called Madhavi, and travelled to Madurai to start a new life. While Kovalan sold the anklets of Kannaki for money in Madur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskritisation
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek 'upward' mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper castes. It is a process similar to "passing" in sociological terms. This term was made popular by Indian sociologist M. N. Srinivas in the 1950s. In a broader sense, also called Brahmanisation, it is a historical process in which "local" Indian religious traditions become syncretised, or aligned to and absorbed within the Brahmanical religion, resulting in the pan-Indian religion of Hinduism. Definition Srinivas defined ''Sanskritisation'' as a process by which In a broader sense, Sanskritisation is In this process, local traditions ("little traditions") become integrated into the "great tradition" of Brahmanical religion, disseminating Sanskrit texts and Brahmanical ideas throughout India, and abroad. This facilitated the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nair
The Nair , also known as Nayar, are a group of Indian Hindu castes, described by anthropologist Kathleen Gough as "not a unitary group but a named category of castes". The Nair include several castes and many subdivisions, not all of whom historically bore the name 'Nair'. Fuller (1975) p. 309 These people lived, and continue to live, in the area which is now the Indian state of Kerala. Their internal caste behaviours and systems are markedly different between the people in the northern and southern sections of the area, although there is not very much reliable information on those inhabiting the north. Fuller (1975) p. 284 Historically, Nairs lived in large family units called ''tharavads'' that housed descendants of one common female ancestor. These family units along with their unusual marriage customs, which are no longer practiced, have been much studied. Although the detail varied from one region to the next, the main points of interest to researchers of Nair marriage custo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |