|
Kishangarh State
Kishangarh State was a princely state of India from 1611 to 1948. It was founded by the Jodhpur State, Jodhpur prince Kishan Singh of Kishangarh, Kishan Singh in 1609. Prior to Kishan Singh this area was ruled by Raja Samokhan Singh. Kishangarh State was located between 25° 49′ and 26° 59′ in the north, and 70° 49′ and 75° 11′ east. Bordered on the North and northwest by Jodhpur; on the east by Jaipur; on the west and southeast by the Ajmer District and on the extreme south by Shahpura State, Shahpura. History Kishan Singh of Kishangarh, Kishen Singh, who was the son of Udai Singh of Marwar, Udai Singh of Jodhpur State, Jodhpur left his family's lands for Ajmer in 1596. From the Mughal Emperor Akbar he received the district of ''Hindaun'' (now in Jaipur); and later, the grant of ''Setholao'' along with certain other districts. In 1611, he founded the town of Kishangarh which name was then also given to the state. The 13th Chief succeeding Udai Singh was Kalyan Singh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a population of 3.1 million, making it the List of cities in India by population, tenth most populous city in the country. Jaipur is also known as the ''Pink City'', due to the dominant colour scheme of its buildings. It is also known as the Paris of India, and C. V. Raman called it the ''Island of Glory''. It is located from the national capital New Delhi. Jaipur was founded in 1727 by the Kachhwaha Rajput ruler Jai Singh II, the ruler of Amer, India, Amer, after whom the city is named. It was one of the earliest planned cities of modern India, designed by Vidyadhar Bhattacharya. During the British Colonial period, the city served as the capital of Jaipur State. After independence in 1947, Jaipur was made the capital of the newly formed s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1611 Establishments In India
Events January–June * February 27 – Sunspots are observed by telescope, by Frisians, Frisian astronomers Johannes Fabricius and David Fabricius. Johannes publishes the results of these observations, in ''De Maculis in Sole observatis'' in Wittenberg, later this year. Such early discoveries are overlooked, however, and the first sighting is claimed a few months later, by Galileo Galilei and Christoph Scheiner. * March 4 – George Abbot (bishop), George Abbot is enthroned as Archbishop of Canterbury. * March 9 – Battle of Segaba in Begemder: Yemana Kristos, brother of Emperor of Ethiopia Susenyos I, ends the rebellion of Melka Sedeq. * April 4 – Denmark-Norway declares Kalmar War, war on Sweden, then captures Kalmar. * April 28 – The ''Colegio de Nuestra Señora del Santísimo Rosario'' is established in Manila, the Philippines (later renamed Colegio de Santo Tomas, now known as the University of Santo Tomas). * May 2 – The Authori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajputs
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Rajput covers various patrilineal clans historically associated with warriorhood: several clans claim Rajput status, although not all claims are universally accepted. According to modern scholars, almost all Rajput clans originated from peasant or pastoral communities. Over time, the Rajputs emerged as a social class comprising people from a variety of ethnic and geographical backgrounds. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the membership of this class became largely hereditary, although new claims to Rajput status continued to be made in the later centuries. Several Rajput-ruled kingdoms played a significant role in many regions of central and northern India from seventh century onwards. The Rajput population and the former Rajput states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princely States Of India
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown. There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large ( Hyderabad State, Mysore State, Jammu and Kashmir State, and Baroda State). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off. At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates and jagirs. In 1947, princely states covered 40% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naubat Khan
Naubat Khan (also known as Ali Khan Karori) was an Indian classical music composer, musician and instrumentalist who was made a Mansabdar by Mughal Emperor Akbar. He is known today for his skills with the ''rudra veena'' or ''bīn'', which he is shown playing in paintings by Mughal court artists.Naubat Khan was the contemporary and son in law of legendary Tansen. Early life and background Naubat Khan was the grandson of Raja Samokhan Singh of Kishangarh. Samokhan Singh, a Jodhpur prince, was himself a great veena player of his time. As the Mughal Emperor Akbar fought his wars of conquest in India, he fought against Raja Samokhan Singh. Singh was defeated in the battle and his grandson Misri Singh (Naubat Khan) was kept under house arrest. Misri Singh later accepted Islam and was named Ali. He was trained under Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana, the son of Bairam Khan to get an understanding of the Mughal court procedures. Ali was given the title of Khan by Mughal Emperor Akbar, and the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajputana Agency
The Rajputana Agency was a political office of the British Indian Empire dealing with a collection of native states in Rajputana (now in Rajasthan, northwestern India), under the political charge of an Agent reporting directly to the Governor-General of India and residing at Mount Abu in the Aravalli Range. The total area of the states falling within the Rajputana Agency was , with eighteen states and two estates or chiefships. Subdivisions and (e)states * Mewar Residency, with headquarters at Udaipur, dealt with the state of Mewar (title Maharana of Udaipur), a salute state entitled to a hereditary gun salute of 19 guns (21 local). * Southern Rajputana States Agency, which was part of Mewar Residency until 1906, when it was separated, covered three salute states: ** Banswara, title Maharawal, hereditary 15 guns ** Dungarpur, title Maharawal, hereditary 15 guns ** Pratapgarh, title Maharawat, hereditary 15 guns * Jaipur Residency, with headquarters at Jaipur, dealt with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
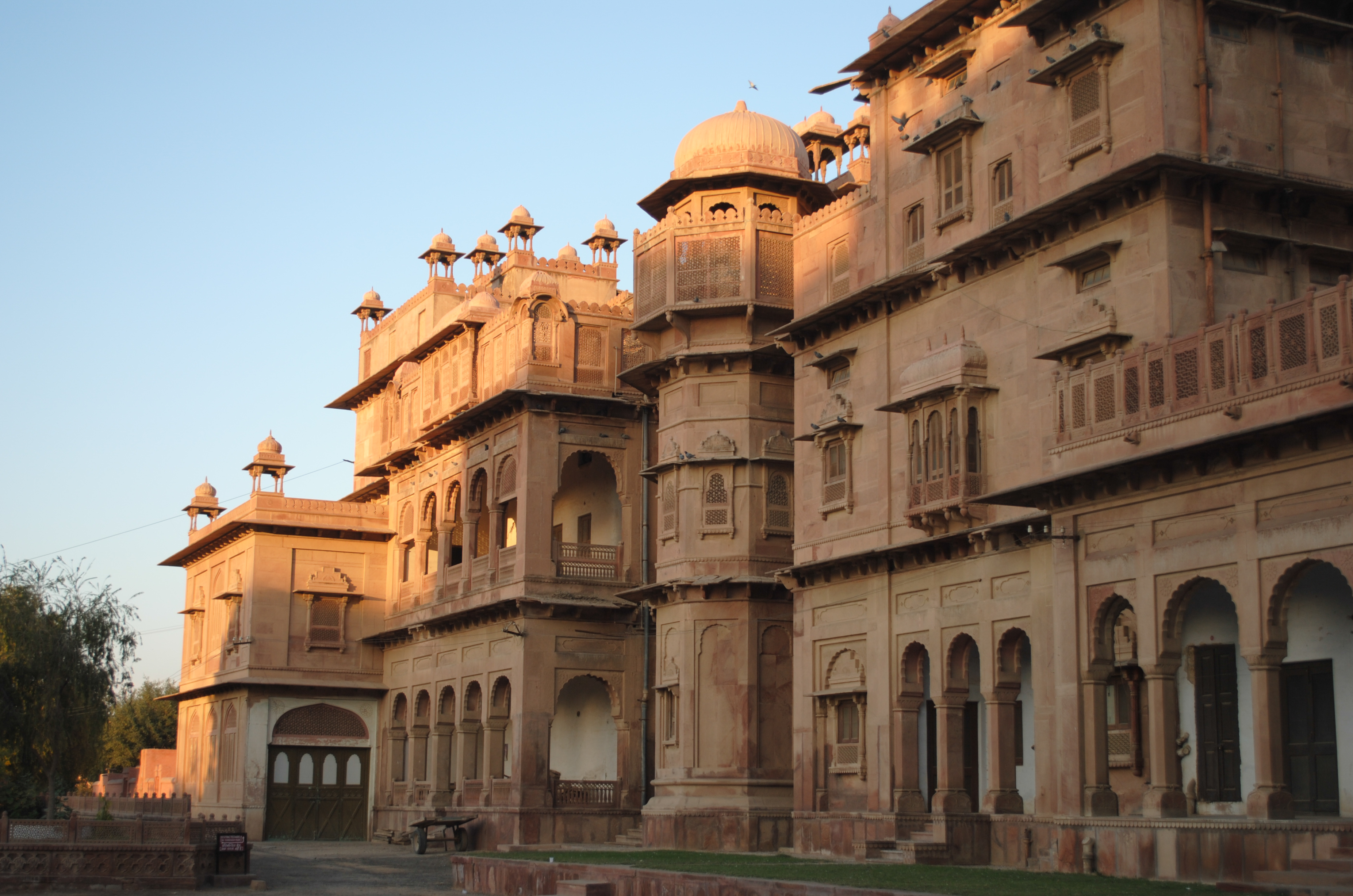
Kishangarh
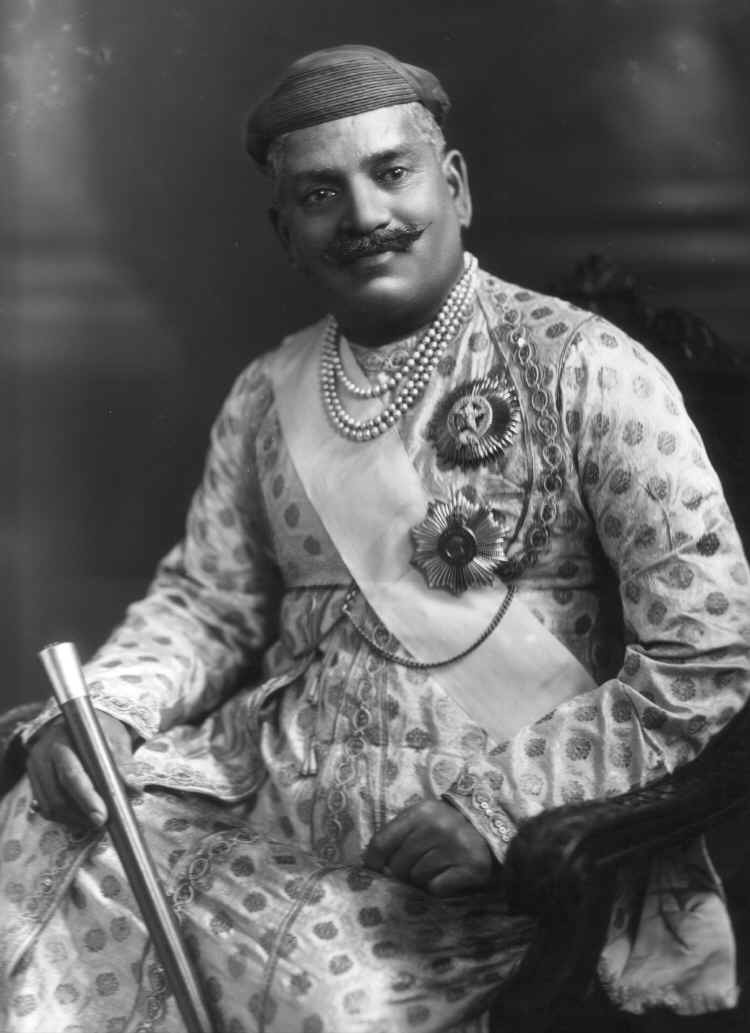
Kishangarh is a city and a Municipal Council in Ajmer district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. History Kishangarh State was founded by the Jodhpur prince Kishan Singh in 1609. Prior to the rule of Kishan Singh this area was ruled by Raja Samokhan Singh. Kishangarh was the capital of the eponymous princely state during the British Raj, which was located in the Rajputana Agency. It had an area of 2210 km2 (858 miles²) and a population in 1901 of 90,970. This figure for population represented a decrease of 27% over the census figure of 1891, something presumably attributable to the famine of 1899-1900. The state enjoyed an estimated revenue of £.34,000/- and paid no tribute to the British Raj. In 1840, ''Prithvi Singh'', became the 15th Maharaja of Kishangarh, and reigned till his death in 1879, after which he was succeeded by his son, ''Sardul Singh''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja Kalyan Singh (Reigned 1798-1838) LACMA M
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king". A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, and Chandragupta Maurya. 'Title inflation' soon led to most being rather mediocre or even petty in real power, which led to compound titles (among other efforts) being used in an attempt to distinguish some among their ranks. The female equivalent, Maharani (or Maharanee, Mahārājñī, Maharajin), denotes either the wife of a Maharaja (or Maharana etc.) or also, in states where it was customary, a woman ruling without a husband. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajmata, "queen mother". Maharajakumar generally denotes a son of a Maharaja, but more specific titulatures are often used at each court, including Yuvaraja for the heir (the crown prince). The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Of Ustad Mansur, British Museum
Work may refer to: * Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community ** Manual labour, physical work done by humans ** House work, housework, or homemaking ** Working animal, an animal trained by humans to perform tasks * Work (physics), the product of force and displacement ** Work (electric field), the work done on a charged particle by an electric field ** Work (thermodynamics), energy transferred by the system to its surroundings * Creative work, a manifestation of creative effort **Work of art Broadcast call signs * WORK (FM), now WRFK (FM), an American radio station in Vermont * WORK-LP, an American low-power TV station in New Hampshire * WOYK, an American AM radio station in Pennsylvania, known as WORK 1932–1973 Music * The Work (band), an English post-punk rock group * Work Group, an American record label Albums and EPs * ''Work'' (EP), a 2015 EP by Marcus Marr and Chet Faker * ''Work!'', a 1986 album by Mulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






%2C_15th_Maharaja_of_Kishangarh%2C_early_1870s.jpg)
