|
Kingdom Of Cilicia (ancient)
The Kingdom of Cilicia was an independent state that existed from 612 BC to 549 BC. The state was governed by the Syennesis dynasty, possibly from Greeks that moved into Cilicia towards the end of the Bronze Age. Prior to and after the independent kingdom, the Syennesis dynasty ruled Cilicia as autonomous state under the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Achaemenid Empire and the Kingdom of Alexander. History The Cilicians were able to protect themselves from Assyrian domination and with the dissolution of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 612 BC, they managed to establish a fully independent kingdom. Due to having a significant strategical geography, the Cilicians were able to expand their kingdom to the Halys River in a short period. With these expansions, the Cilician Kingdom established itself as one of the strong powers of the time. In 585 BC, Herodotus praised the Cilician king Syennesis I, the founder of the kingdom, for his efforts in leading negotiations ending the 5 years' war between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus, Mersin
Tarsus (Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒅈𒊭 ; grc, Ταρσός, label=Ancient Greek, Greek ; xcl, Տարսոն, label=Old Armenian, Armenian ; ar, طَرسُوس ) is a historic city in south-central Turkey, inland from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean. It is part of the Adana-Mersin metropolitan area, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Turkey with a population of 3 million people. Tarsus forms an administrative district in the eastern part of Mersin Province, Mersin province and lies at the heart of the region. With a history going back over 6,000 years, Tarsus has long been an important stop for traders and a focal point of many civilisations. During the Roman Empire, it was the capital of the province of Cilicia (Roman province), Cilicia. It was the scene of the first meeting between Mark Antony and Cleopatra, and the birthplace of Paul the Apostle, St Paul the Apostle. Tarsus is home to one of Turkey's most famous high schools, the Tarsus American College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyaxares
Cyaxares (Median: ; Old Persian: ; Akkadian: ; Old Phrygian: ; grc, Κυαξαρης, Kuaxarēs; Latin: ; reigned 625–585 BCE) was the third king of the Medes. Cyaxares collaborated with the Babylonians to destroy the Assyrian Empire, and united most of the Iranian tribes of ancient Iran, thereby transforming Media into a regional power. Name The name is the Latinised form of the Greek (), which was itself the Hellenisation of the Median name (), meaning "good ruler." The Greek author Diodorus Siculus named Cyaxares as (), which is the Hellenisation of the Median name , meaning "spear bearer." This name is similar to the Median form of his son Astyages's name, , meaning "spear thrower." Life and reign According to Herodotus, Cyaxares was the son of the Median king Phraortes. In the middle of the 7th century BCE, Phraortes led the Medes in a revolt against Assyria and was killed in battle, either against the Assyrians under their king Ashurbanipal, or against t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
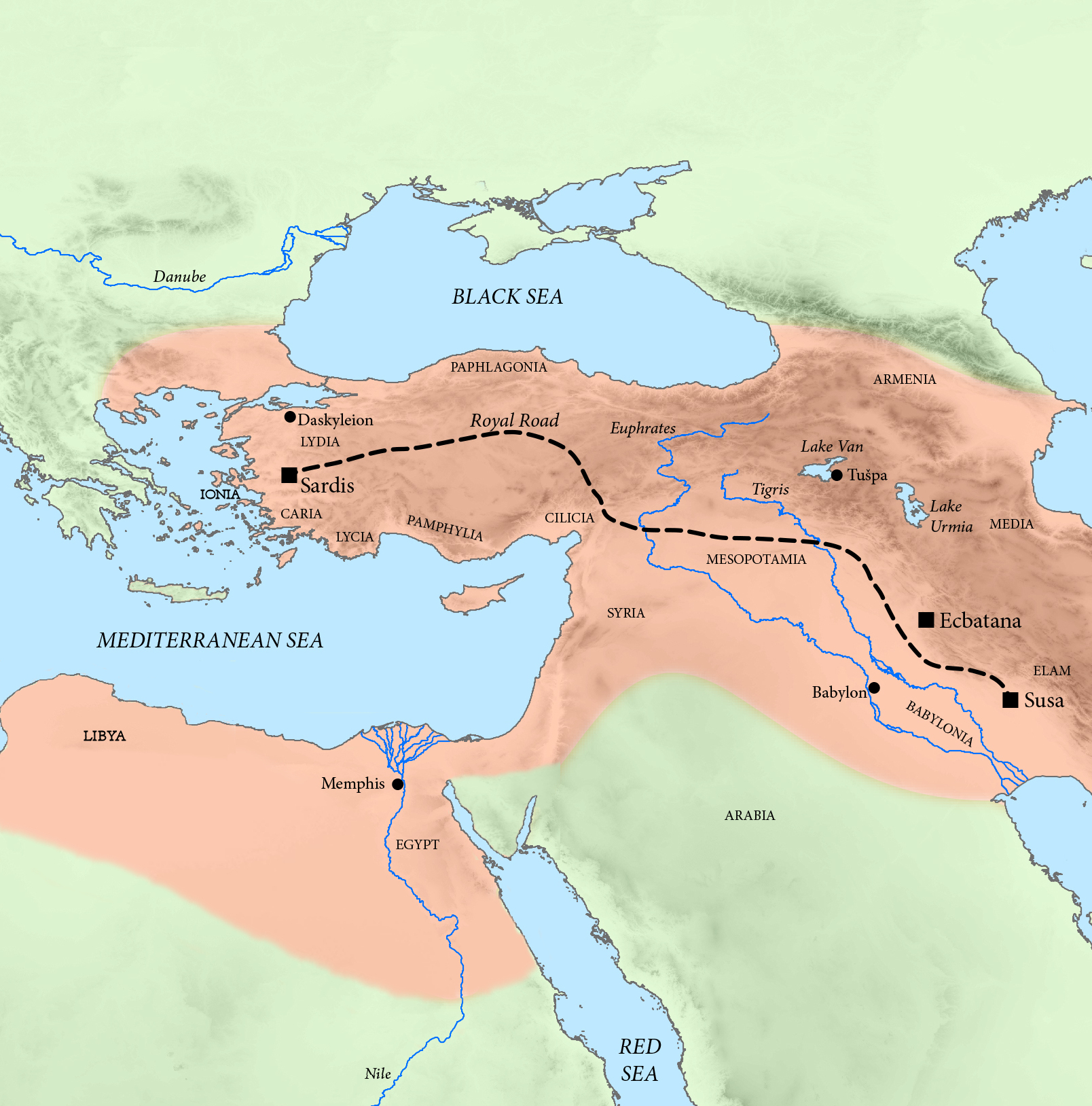
Former Countries In Western Asia
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilicia plain. The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye, along with parts of Hatay and Antalya. Geography Cilicia is extended along the Mediterranean coast east from Pamphylia to the Nur Mountains, which separates it from Syria. North and east of Cilicia lie the rugged Taurus Mountains that separate it from the high central plateau of Anatolia, which are pierced by a narrow gorge called in antiquity the Cilician Gates. Ancient Cilicia was naturally divided into Cilicia Trachea and Cilicia Pedias by the Limonlu River. Salamis, the city on the east coast of Cyprus, was included in its administrative jurisdiction. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan civilization, Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syennesis II
Syennesis ( grc, Συέννεσις) was the name of a number of men in classical antiquity. In particular it seems to have been a common name of the native kings of Cilicia. * Syennesis (5th century), a figure in the conflict of Artaxerxes II of Persia and Cyrus the Younger * Syennesis of Cyprus, an ancient Greek physician in the 4th century BCE *Syennesis, a contemporary with Achaemenid Empire king Darius I, to whom he was tributary *Syennesis, a king of Cilicia, who joined with Labynetus (Nebuchadnezzar) in mediating between Cyaxares and Alyattes of Lydia Alyattes (Lydian language: ; grc, wikt:Ἀλυάττης, Ἀλυάττης ; reigned c. 635-585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the List of kings of Lydia#Mermnadae, Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyatt ..., the kings respectively of Media and Lydia {{given name 5th-century BC rulers People from ancient Cilicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syennesis I
Syennesis ( grc, Συέννεσις) was the name of a number of men in classical antiquity. In particular it seems to have been a common name of the native kings of Cilicia. * Syennesis (5th century), a figure in the conflict of Artaxerxes II of Persia and Cyrus the Younger * Syennesis of Cyprus, an ancient Greek physician in the 4th century BCE *Syennesis, a contemporary with Achaemenid Empire king Darius I, to whom he was tributary *Syennesis, a king of Cilicia, who joined with Labynetus (Nebuchadnezzar) in mediating between Cyaxares and Alyattes of Lydia Alyattes (Lydian language: ; grc, wikt:Ἀλυάττης, Ἀλυάττης ; reigned c. 635-585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the List of kings of Lydia#Mermnadae, Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyatt ..., the kings respectively of Media and Lydia {{given name 5th-century BC rulers People from ancient Cilicia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talent (measurement)
The talent was a unit of weight that was introduced in Mesopotamia at the end of the 4th millennium BC, and was normalized at the end of the 3rd millennium during the Akkadian-Sumer phase, divided into 60 minas or 3,600 shekels. In classical antiquity, the talent ( la, talentum, from Ancient Greek: , ''talanton'' "scale, balance, sum") was the heaviest of common weight units for commercial transactions. An Attic weight talent was approximately John William Humphrey, John Peter Oleson, Andrew Neil Sherwood, ''Greek and Roman technology'', p. 487. (approximately the mass of water of an amphora), and a Babylonian talent was .Herodotus, Robin Waterfield and Carolyn Dewald, ''The Histories'' (1998), p. 593. Ancient Israel adopted the Babylonian weight talent, but later revised it.III. Measures of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis. Soon after his accession, Artaxerxes II faced opposition from his younger brother Cyrus the Younger, who assembled an army composing of troops from his Lydian and Ionian satrapies as well as Greek mercenaries in his bid for the throne. The forces of the brothers clashed at Cunaxa in 401 BC, which resulted in the defeat and death of Cyrus. Following this, Artaxerxes II had to contend with several other revolts; a revolt by Evagoras I () in Cyprus between 391–380 BC, by the Phoenicians in , and most importantly, the revolts by the western satraps (known as the Great Satraps' Revolt) in the 360s and 350s BC, led by distinguished figures such as Datames, Ariobarzanes, and Autophradat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrus The Younger
Cyrus the Younger ( peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ''Kūruš''; grc-gre, Κῦρος ; died 401 BC) was an Achaemenid prince and general. He ruled as satrap of Lydia and Ionia from 408 to 401 BC. Son of Darius II and Parysatis, he died in 401 BC in battle during a failed attempt to oust his elder brother, Artaxerxes II, from the Persian throne. The history of Cyrus and of the retreat of his Greek mercenaries is told by Xenophon in his ''Anabasis''. Another account, probably from Sophaenetus of Stymphalus, was used by Ephorus. Further information is contained in the excerpts from Artaxerxes II's physician, Ctesias, by Photius; ''Plutarch’s Lives'' of Artaxerxes II and Lysander; and Thucydides' ''History of Peloponnesian War''. These are the only early sources of information on Cyrus the Younger. Biography According to Xenophon, Cyrus the Younger was born after the accession of his father in 424 BC. He had an elder brother, Arsicas (whose name changed to Artaxerxes II when he a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilicia (satrapy)
Cilicia was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, with its capital being Tarsus. It was conquered sometime in the 540's BC by Cyrus the Great. Cilicia was a vassal, and although it had a vassal king it had to pay a tribute of 360 horses and 500 talents of silver, according to Herodotus. The fertile Cilician plains were the most important part of the satrapy. There were several sanctuaries that remained more or less independent from Persian rule. Some of these included Castabala, Mazaca, and Mallus. The last vassal king of Cilicia became involved in the civil war between Artaxerxes II and Cyrus the Younger. Having sided with Cyrus the Younger, who was defeated, the king was dethroned and Cilicia became an ordinary satrapy. The second to last satrap (governor) of Cilicia was the Babylonian Mazaios. Shortly afterwards, his successor was expelled by Alexander the Great. The region was later incorporated by the Roman Empire. See also *Cilicia * Çukurova *Adana *Cilician Gates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrus The Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced all of the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Western Asia and much of Central Asia. Spanning from the Mediterranean Sea and Hellespont in the west to the Indus River in the east, the empire created by Cyrus was the largest the world had yet seen. At its maximum extent under his successors, the Achaemenid Empire stretched from parts of the Balkans ( Eastern Bulgaria– Paeonia and Thrace– Macedonia) and Southeast Europe proper in the west to the Indus Valley in the east. The reign of Cyrus lasted about thirty years; his empire took root with his conquest of the Median Empire followed by the Lydian Empire and eventually the Neo-Babylonian Empire. He also led an expedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)