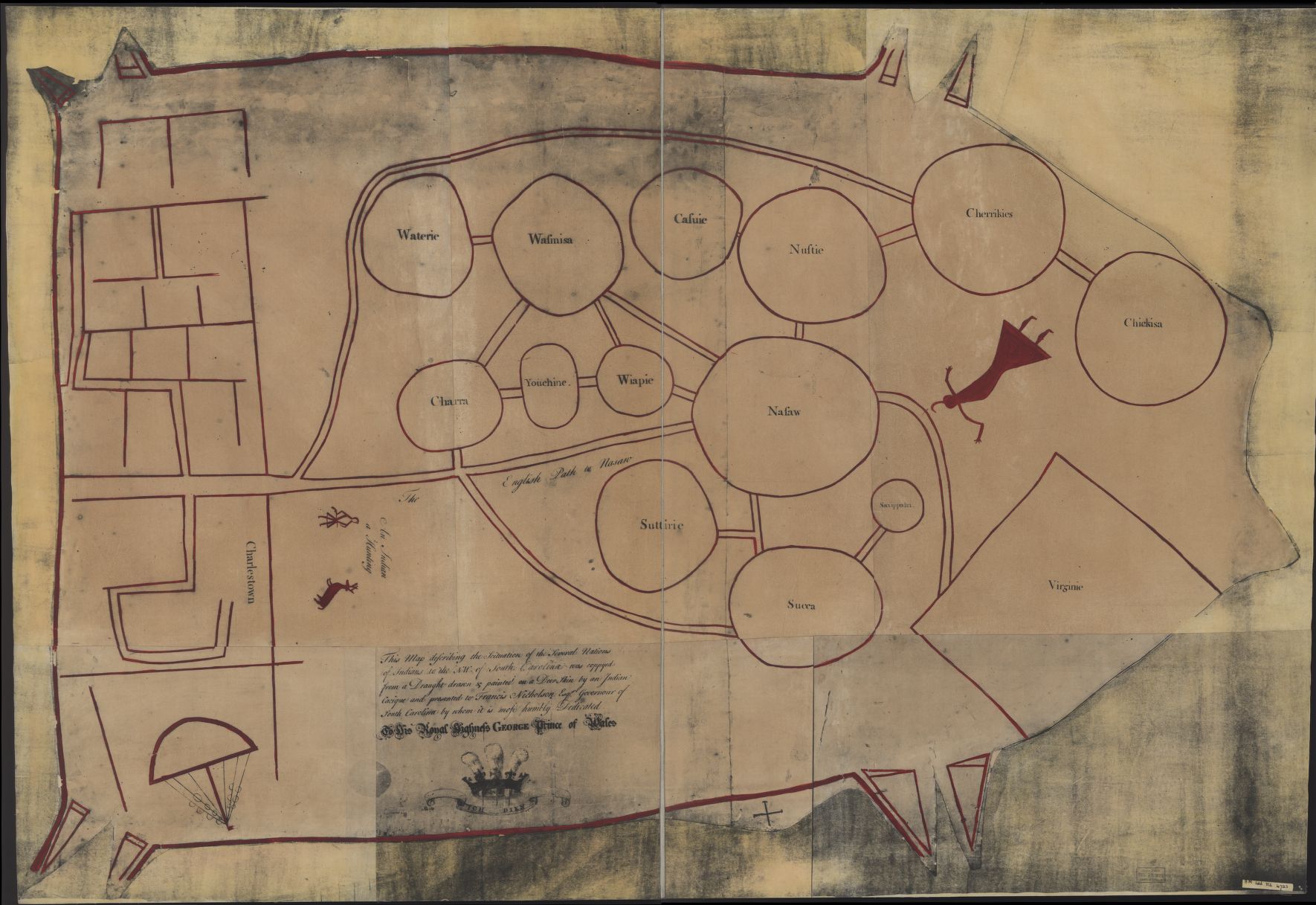
|
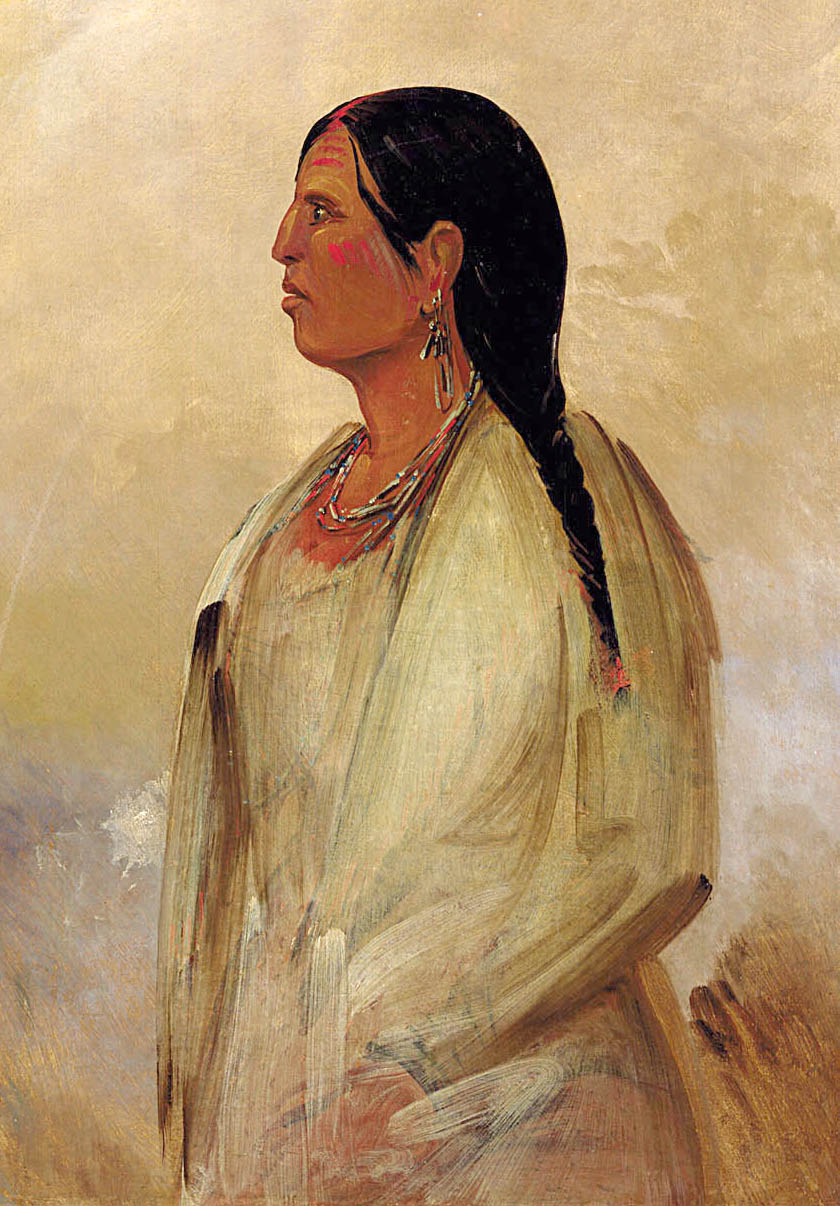
King Yanabe Yalangway
King Yanabe Yalangway was the ''eractasswa'' (chief) of the Catawba (tribe), Catawba Indian Nation, sometime around the 1740s. Not much is known about him other than the fact that he preceded King Hagler as chief. His training was evidently under "king" Whitmannetaughehee's leadership. As a warrior he served during a longstanding state of warfare with northern tribes, particularly the Iroquois Seneca nation, Seneca, and the Lenape (aka Delaware), an Algonquian peoples, Algonquian-speaking people who had occupied coastal areas and had become vassals of the Iroquois after migrating to Ohio Valley. The Catawba chased their raiding parties back to the north in the 1720s and 1730s, going across the Potomac River. At one point, a party of Catawba is said to have followed a party of Lenape who attacked them, and to have overtaken them near Leesburg, Virginia. There they fought a pitched battle. Similar encounters in this tireless warfare were reported to have occurred at present-day Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Hagler
King Hagler (also spelled Haiglar) or Nopkehee (c. 1700–1763) was a chief of the Catawba Native American tribe from 1754 to 1763. Hagler is known as the "Patron Saint of Camden, South Carolina." He was the first Native American to be inducted into the South Carolina Hall of Fame. He is known for opposing the sale of alcohol to Catawbas and other Native Americans, and encouraged the Catawba people to abstain from alcohol.Thomas J. Blumer, Robert P. Smith, E. Fred Sanders. ''Catawba Nation: Treasures in History,'' American Heritage, Arcadia Publishing, 2007. He worked to negotiate fair |
Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in northeast North America/Turtle Island (Native American folklore), Turtle Island. They were known during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English people, English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk people, Mohawk, Oneida people, Oneida, Onondaga people, Onondaga, Cayuga people, Cayuga, and Seneca people, Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by The Great Peacem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winyaw
The Winyaw were a Native American tribe living near Winyah Bay, Black River, and the lower course of the Pee Dee River in South Carolina. The Winyaw people disappeared as a distinct entity after 1720 and are thought to have merged with the Waccamaw. Name The meaning of the name ''Winyaw'' is unknown. Winyaw has also been written as Winyah, Weenee, and Wineaw. History The Winyaw might have been the Yenyohol mentioned in 1521 by Francisco de Chicora, a Native American captive held by the Spanish. If so, they may have been carried away during Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón's expedition during that same year. The Winyaw were first mentioned by colonists of South Carolina after 1670. The tribe at first allied with the English colonists who settled in Charles Town, but this friendship soon was shattered when European slave dealers instigated a war against them in 1683 as an excuse to capture slaves. During the Tuscarora War of 1711, John Barnwell brought 24 "Wineaws" on his expedition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waccamaw
The Waccamaw people were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, who lived in villages along the Waccamaw and Pee Dee rivers in North and South Carolina in the 18th century.Lerch 328 Language Very little remains of the Waccamaw's ancestral Woccon language today, it was one of the two Catawban branches of the Siouan language family. The language was lost due to devastating population losses and social disruptions during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. It is attested today in a vocabulary of 143 words, printed in 1709. History While the Waccamaw were never populous, the arrival of settlers and their diseases in the 16th century resulted in devastating population loss and dispersal. In 1600, anthropologist James Mooney estimated the population of the "Waccamaw, Winyaw, Hook, &c" at 900 people, while the 1715 census registers only one remaining Waccamaw village with a total population of 106 people, 36 of them men. According to the early 20th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santee Tribe
The Santee tribe were a historical tribe of Siouan-language speakers from South Carolina. Historically the Santee were a small tribe (est. at a population of 3,000 around AD 1600), and centered in the area of the present town of Santee, South Carolina. Their settlement was along the Santee River, since dammed and called Lake Marion. History Historically, the great majority of various Siouan-speaking tribes were found in the Great Plains states, where they had migrated and settled before European contact. Some Siouan-speaking tribes also inhabited territory in present-day Virginia, Maryland and North Carolina. The Santee had Lower Town connections to the Lower Town Cherokee and the Creek people, due to the westward movement of such American Indian groups during the Colonial Conquest era. An earthwork mound believed to have been constructed by the Mississippian culture (1000-1500 AD) stands on the shore of Lake Marion. This structure was likely built by prehistoric indigeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugeree
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an Ethnography, ethnographic classification for Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common culture, cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Frank Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions.Jackson and Fogelson 3 Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco tribe, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa people, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congaree (tribe)
The Congaree (also spelled Conagree) were a group of Native Americans who lived in what is now central South Carolina of the United States, along the Congaree River. They spoke a dialect distinct from, and not intelligible by, Siouan language speakers; it is considered unclassified. This was the primary language family of Native Americans in the Piedmont, such as the Catawba. Some linguists, however, believe that the language was related to Catawban Siouan. Unclassified language Early European observers and later American scholars thought the Congaree were likely part of the Siouan language family, given their geographic location and characteristics of neighboring tribes. The Catawba and other tribes in this area spoke Siouan languages. The Cherokee, located to the west, spoke an Iroquoian language, associated more with tribes around the Great Lakes to the north. Since the late 20th century, scholars more widely agree that the Congaree people were not a Siouan people. Their lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wateree People
The Wateree were a Native American tribe in the interior of the present-day Carolinas. They probably belonged to the Siouan-Catawba language family. First encountered by the Spanish in 1567 in Western North Carolina, they migrated to the southeast and what developed as South Carolina by 1700, where English colonists noted them. There they had settled along the Wateree River, near the site of what developed as present-day Camden, South Carolina. Originally a large tribe, they suffered high mortality during the Yamasee War of 1715 and became extinct as a tribe by the end of the century. Language and name The name ''Wateree'' may come from Catawban ''wateran'', "to float on the water" or from ''yeh is-WAH h'reh'', meaning "people of the atereeriver". 16th- and 17th-century history This people were recorded in 1567 by Spanish captain Juan Pardo's scribe Juan de la Bandera during their expedition through the interior of the Carolinas. Bandera called them the ''Guatari'' in his j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxhaw Tribe
The Waxhaw people (also referred to as Wisacky, the Gueça and possibly Wastana and Weesock) were a tribe native to what are now the counties of Lancaster, in South Carolina; and Union and Mecklenburg in North Carolina, around the area of present-day Charlotte. The Waxhaw were related to other nearby Southeastern peoples, such as the Catawba people and the Sugeree. It is speculated that they were culturally influenced by the Mississippian culture. Some scholars suggest the Waxhaw may have been a band of the Catawba rather than a distinctly separate people, given the similarity in what is known of their language and customs. A distinctive custom which they shared was flattening the forehead of individuals as infants; the only other people group to do so in the southeastern United States is the Choctaw. Flattening of the head gave the Waxhaw a distinctive look, with wide eyes and sloping foreheads. They started the process at birth by binding the infant to a flat board. The wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians (excluding Massanutten Mountain), to the north by the Potomac River and to the south by the James River. The cultural region covers a larger area that includes all of the valley plus the Virginia highlands to the west, and the Roanoke Valley to the south. It is physiographically located within the Ridge and Valley province and is a portion of the Great Appalachian Valley. Geography Named for the river that stretches much of its length, the Shenandoah Valley encompasses eight counties in Virginia and two counties in West Virginia. * Augusta County, Virginia *Clarke County, Virginia *Frederick County, Virginia *Page County, Virginia *Rockbridge County, Virginia *Rockingham County, Virginia * Shenandoah County, Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |