|
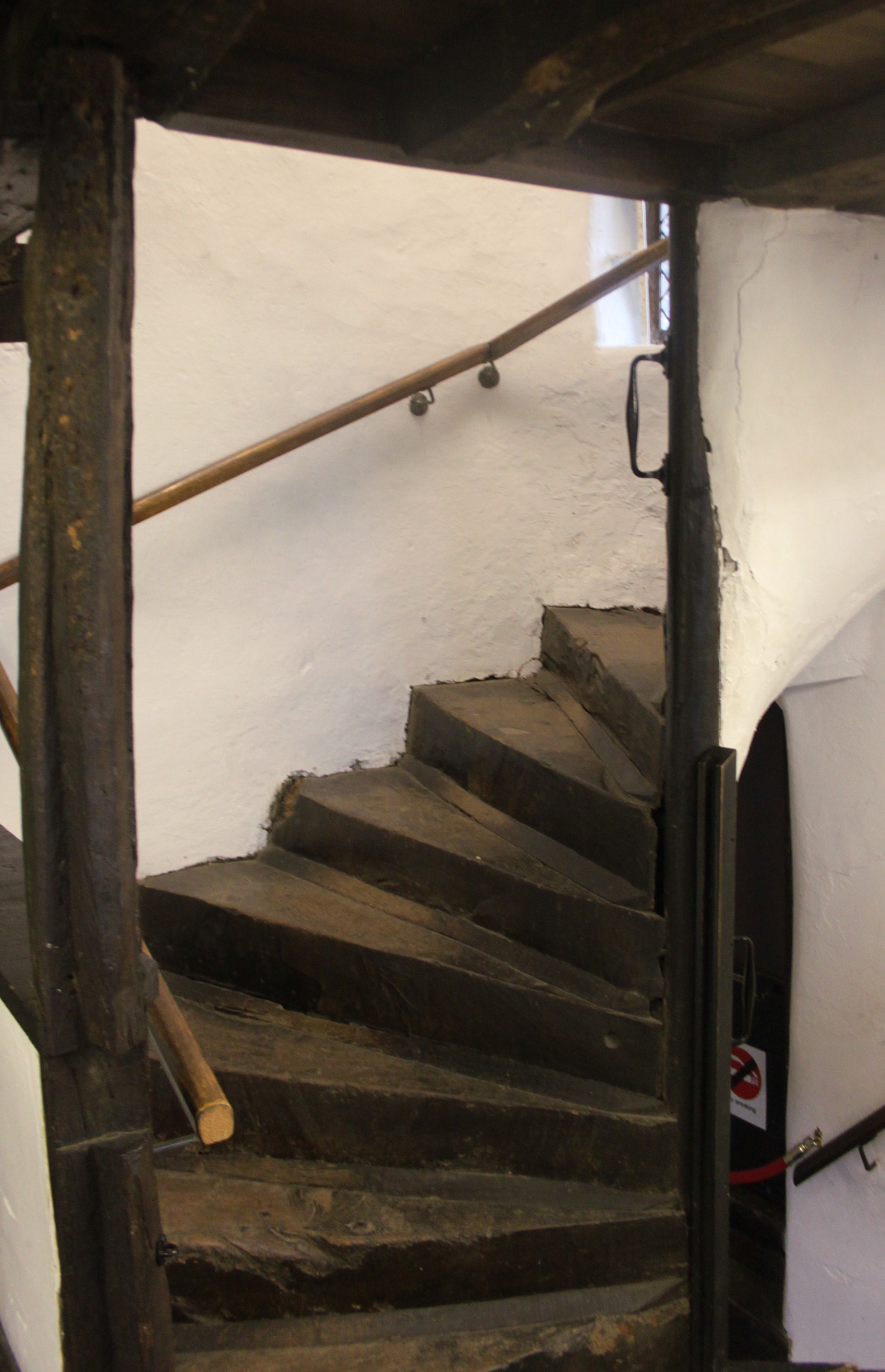
King John's Hunting Lodge, Axbridge
King John's Hunting Lodge is a wool-merchant's house built , long after the death of King John of England, King John in 1216, in Axbridge, a town in the English county of Somerset. It is a Jettying, jettied timber framing, timber-frame building of three storeys, occupying a corner plot on the town square. The building has served a variety of purposes with shops on the ground floor and workshops and living quarters on the first and second floors. At one time part of the building was occupied by the King's Head Inn; a sculpture of a king's head, which acted as a sign for the pub, is preserved within and a replica is attached to the outside. The lodge was bequeathed to the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust in 1971, and repairs were undertaken to reverse significant deterioration to the building. The house is leased by the National Trust to Axbridge and District Museum Trust, who operate it as a local museum which includes exhibits rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tollard Royal
Tollard Royal is a village and civil parish on Cranborne Chase, Wiltshire, England. The parish is on Wiltshire's southern boundary with Dorset and the village is southeast of the Dorset town of Shaftesbury, on the B3081 road between Shaftesbury and Sixpenny Handley. History Evidence of prehistoric occupation in the area includes a bowl barrow, reduced by ploughing, in the west of the parish on Woodley Down. Nearby is a linear earthwork straddling the county border, which is truncated by the Roman road from Badbury to Bath; a separate 480m section of the road survives as earthworks, with the flint road surface visible in places. On Berwick Down in the north of the parish a late Iron Age farmstead was replaced by a Romano-British settlement. Domesday Book in 1086 recorded 31 households at ''Tollard''. Much of the land was owned by Aiulf, whose other estates included Farnham in Dorset, immediately to the south. This was later reflected in the shape of the ancient parish, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John, King Of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empire and contributing to the subsequent growth in power of the French Capetian dynasty during the 13th century. The baronial revolt at the end of John's reign led to the sealing of , a document considered an early step in the evolution of the constitution of the United Kingdom. John was the youngest of the four surviving sons of King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine. He was nicknamed John Lackland because he was not expected to inherit significant lands. He became Henry's favourite child following the failed revolt of 1173–1174 by his brothers Henry the Young King, Richard I of England, Richard, and Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany, Geoffrey against the King. John was appointed Lord of Ireland in 1177 and given lands in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendip Hills
The Mendip Hills (commonly called the Mendips) is a range of limestone hills to the south of Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. Running from Weston-super-Mare and the Bristol Channel in the west to the Frome valley in the east, the hills overlook the Somerset Levels to the south and the Chew Valley and other tributaries of the Avon to the north. The hills give their name to the local government district of Mendip, which administers most of the area. The higher, western part of the hills, covering has been designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), which gives it a level of protection comparable to a national park. The hills are largely formed from Carboniferous Limestone, which is quarried at several sites. Ash–maple woodland, calcareous grassland and mesotrophic grassland which can be found across the Mendip Hills provide nationally important semi-natural habitats. With their temperate climate these support a range of flora and fauna including birds, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses In Somerset
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II* Listed Buildings In Sedgemoor
Sedgemoor is a local government district in the English county of Somerset. In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural significance; Grade II* structures are those considered to be "particularly significant buildings of more than local interest". Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning Act 1947. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. In England, the authority for listing under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 rests with Historic England, a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport; local authorities have a responsibility to regulate and enforce the planning regulations. Sedgemoor is a low-lying area of land close to sea level between the Quantock and Mendip hills, histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National Trust Properties In Somerset
The National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty (informally known as the National Trust) owns or manages a range of properties in the ceremonial county of Somerset, England. These range from sites of Iron and Bronze Age occupations including Brean Down, Cadbury Camp and Cheddar Gorge to Elizabethan and Victorian era mansions, which include examples such as Montacute House and Tyntesfield. Some of the smaller properties include Coleridge Cottage and Stembridge Mill, the last remaining thatched windmill in England. Somerset consists of a non-metropolitan county, administered by Somerset County Council, which is divided into five districts, and two unitary authorities. The districts of Somerset are West Somerset, South Somerset, Taunton Deane, Mendip and Sedgemoor. North Somerset and Bath and North East Somerset historically came under Somerset County Council. In 1974 they became part of county of Avon, and in 1996 they became administratively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
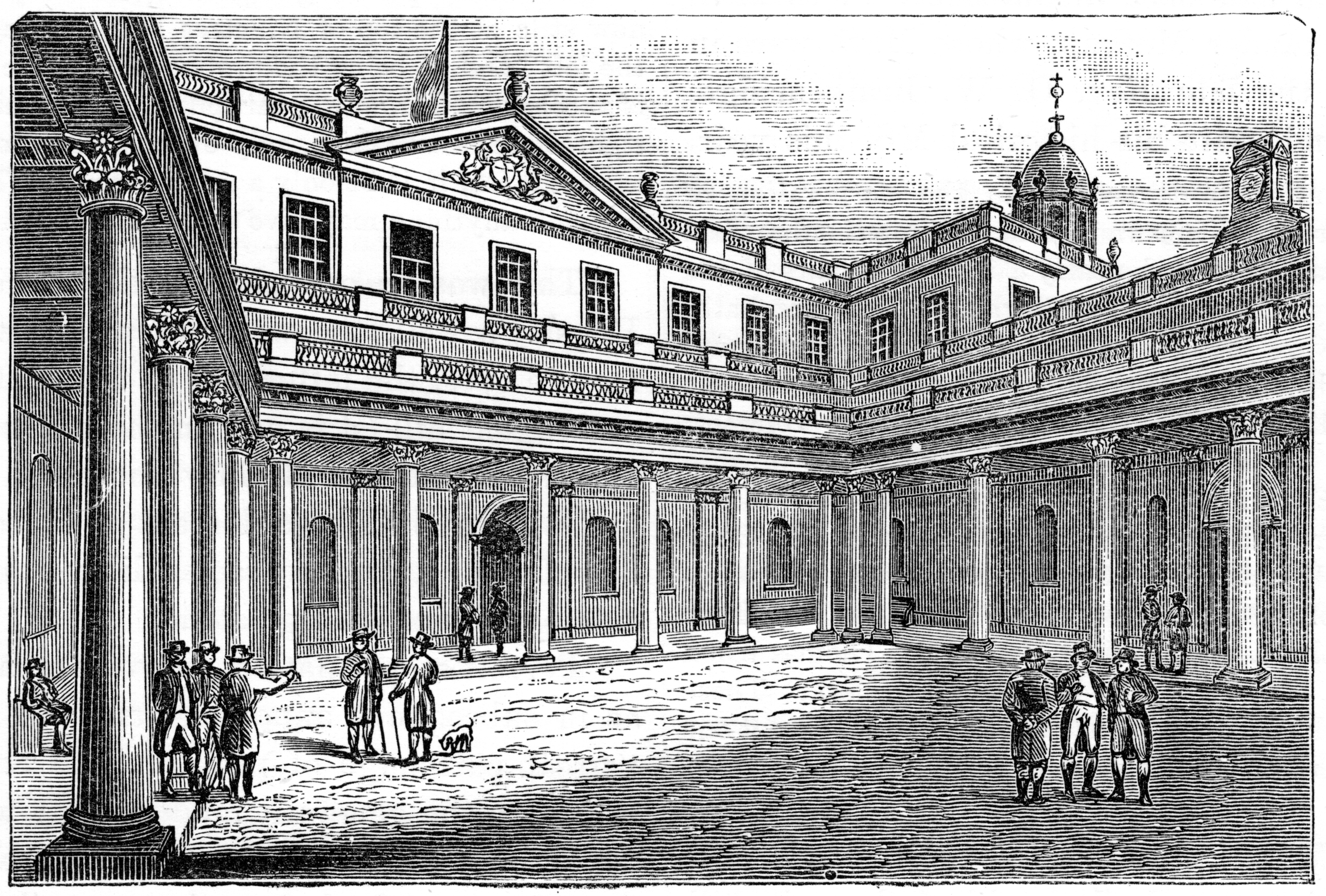
The Exchange, Bristol
The Exchange is a Grade I listed building built in 1741–43 by John Wood the Elder, on Corn Street, near the junction with Broad Street in Bristol, England. It was previously used as a corn and general trade exchange but is now used as offices and St Nicholas Market. The Exchange underwent major building work in 1872, including roofing over the courtyard, and again in the early 1900s when the City Valuer's Department moved to the building. Since World War II the external clock tower has been removed and the roof lowered. Outside the building are four bronze tables dating from the 16th and 17th centuries, known as "nails," at which merchants carried out their business. At the front of the building is a clock showing both Greenwich Mean Time and "local time". History The Exchange was built in 1741–43 by John Wood the Elder, with carvings by Thomas Paty. Wood was also the architect of the Liverpool Exchange, which was completed in 1754 and gutted by fire in 1795. The Lond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilbie Family
The Bilbie family were bell founders and clockmakers based initially in Chew Stoke, Somerset and later at Cullompton, Devon in south-west England from the late 17th century to the early 19th century. Their importance to the local economy and in local history is commemorated by Bilbie Road in Chew Stoke and in the village sign. Bell making The Bilbie family produced more than 1,350 bells, which are hung in churches all over the West Country. The oldest bell, cast in 1698, is still giving good service in St Andrew's Church, Chew Stoke. Supplies of the tin and copper used to make bell metal were probably obtained from brass foundries in Kelston and Bristol. The metal was melted in a wood-burning furnace to over and then poured into a mould made from loam, or foundry mud, from the River Chew. Legend suggests the Bilbies were wild-looking men with long hair who could scarcely read or write, who would never cast a bell except when it was a full moon, midnight, and conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebbor Gorge
Ebbor Gorge is a limestone gorge in Somerset, England, designated and notified in 1952 as a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in the Mendip Hills. It was donated to the National Trust in 1967 and is now managed by Natural England as a national nature reserve. The gorge was cut mostly into the Clifton Down Limestone, part of the Lower Carboniferous Pembroke Group, by water. The site was occupied by humans in the Neolithic Era and their tools and flint arrow heads have been discovered, along with pottery from the Bronze Age. There are also fossils of small mammals from the Late Devensian. The nature reserve provides a habitat for a variety of flora and fauna, including flowers, butterflies and bats. Geology Ebbor Gorge lies on the southwest-facing slope of the Mendip Hills and consists of a steep-sided ravine cut into 350-million-year-old Carboniferous Limestone of the Dinantian. The gorge was cut into Clifton Down Limestone by meltwater in the Pleistocene Ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winscombe
Winscombe is a large village in the North Somerset unitary district of Somerset, South West England, close to the settlements of Axbridge and Cheddar, on the western edge of the Mendip Hills, southeast of Weston-super-Mare and southwest of Bristol. The Parish of Winscombe and Sandford, centred on the Parish Church of Church of St James the Great, includes the villages/hamlets of Barton, Hale, Oakridge, Nye, Sidcot and Woodborough. Winscombe has a few shops and businesses focused in the centre of the village, along Woodborough Road and Sandford Road. There is a doctor's surgery in the village, a vet and two dentists. West of the village is the Max Bog biological Site of Special Scientific Interest. History It has been suggested that the name means a valley belonging to a Saxon named Wine. The parish was part of the Winterstoke Hundred. Winscombe was the subject of a historical and archaeological study led by Professor Mick Aston, published in the ''Proceedings of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark, Somerset
Mark is a village and civil parish which lies approximately from Bridgwater, from Axbridge, and from Highbridge in the Sedgemoor district of the county of Somerset, England. It includes the hamlets of Yarrow and Southwick. The Mark Yeo river has its source near the village. Mark is home to two pubs, a village hall, a village stores and post office, the Ki-Aikido Federation of Great Britain and many clubs and societies, including a Youth Theatre group. History The origin of the name is believed to mean ''A boundary of property'' from the Old English ''mærc''. The estate was given to the Bishop of Wells by Edith of Wessex and with Wedmore was used to endow the deanery of Wells Cathedral by 1157 and continued until 1547. Mark was part of the hundred of Bempstone. Governance The parish council has responsibility for local issues, including setting an annual precept (local rate) to cover the council's operating costs and producing annual accounts for public scruti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
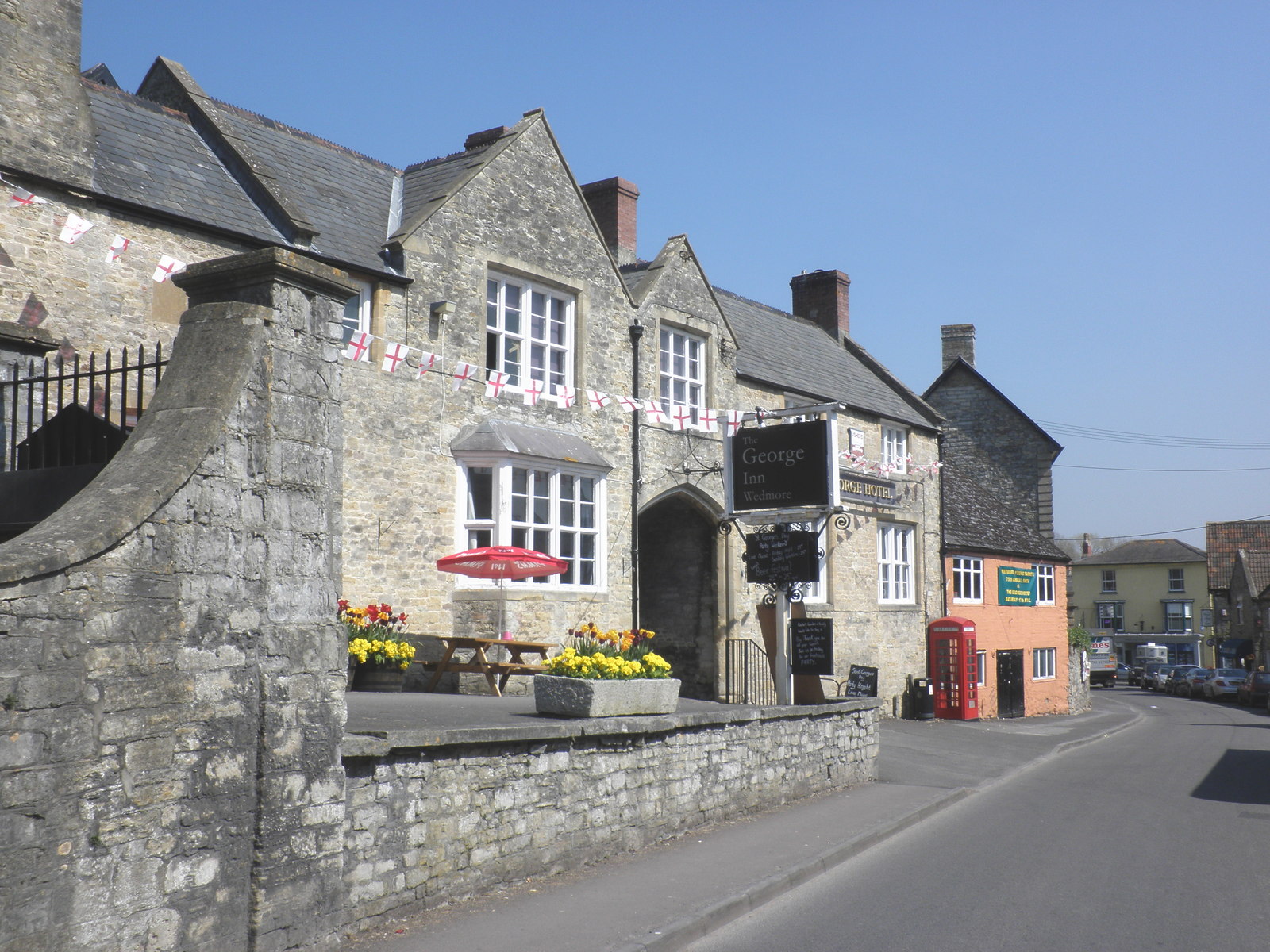
Wedmore
Wedmore is a large village and civil parish in the county of Somerset, England. It is situated on raised ground, in the Somerset Levels between the River Axe and River Brue, often called the Isle of Wedmore. It forms part of Sedgemoor district. The parish consists of three main villages: Wedmore, Blackford and Theale, with the 17 hamlets of Bagley, Blakeway, Clewer, Crickham, Cocklake, Heath House, Latcham, Little Ireland, Middle Stoughton, Mudgley, Panborough, Sand, Stoughton Cross, Washbrook, West End, West Ham and West Stoughton. The parish of Wedmore has a population of 3,318 according to the 2011 census. Its facilities include a medical and dental practice, pharmacy, butcher's, a village store with off licence, three pubs, restaurant, café and several other local shops. It is south of Cheddar, west of the city of Wells and north west of Glastonbury. Etymology The name ''Wedmore'' in Old English is thought to mean "hunting lodge" or "hunting moor"; there was a Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |