|
Kimberley (Western Australia)
The Kimberley is the northernmost of the nine regions of Western Australia. It is bordered on the west by the Indian Ocean, on the north by the Timor Sea, on the south by the Great Sandy and Tanami deserts in the region of the Pilbara, and on the east by the Northern Territory. The region was named in 1879 by government surveyor Alexander Forrest after Secretary of State for the Colonies John Wodehouse, 1st Earl of Kimberley. History The Kimberley was one of the earliest settled parts of Australia, with the first humans landing about 65,000 years ago. They created a complex culture that developed over thousands of years. Yam ('' Dioscorea hastifolia'') agriculture was developed, and rock art suggests that this was where some of the earliest boomerangs were invented. The worship of Wandjina deities was most common in this region, and a complex theology dealing with the transmigration of souls was part of the local people's religious philosophy. During the 18th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shire Of Broome
The Shire of Broome is one of the four local government areas in the Kimberley region of northern Western Australia, covering an area of , most of which is sparsely populated. The Shire's estimated population as at the was 16,222 most of whom reside in the town of Broome. Many Aboriginal communities are within the Shire, notably Beagle Bay and Bardi (One Arm Point). The Shire of Broome includes the Rowley Shoals to the west. History The Shire of Broome was first established as the second Broome Road District on 20 December 1918, when it was separated from the West Kimberley Road District. The area had been previously represented by an earlier Broome Road District (1901-1908) and the Municipality of Broome (1904-1918) but both had merged back into the West Kimberley district. It was declared a shire with effect from 1 July 1961 following the passage of the ''Local Government Act 1960'', which reformed all remaining road districts into shires. Elected council The Shire i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioscorea Hastifolia
''Dioscorea hastifolia'', the Adjigo (ˈadʒɪɡəʊ) yam, also known as the Warram, is a yam with long, white, edible tubers that is native to South Western Australia. It is a climbing vine with hastate, spearheaded, leaves and bears green triangular fruit. The tubers are used by Australian Aboriginals as a source of carbohydrates, whom cultivated the plant extensively. After the yellow flowers have seeded the plant is dug up in winter and roasted. References hastifolia {{Australia-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
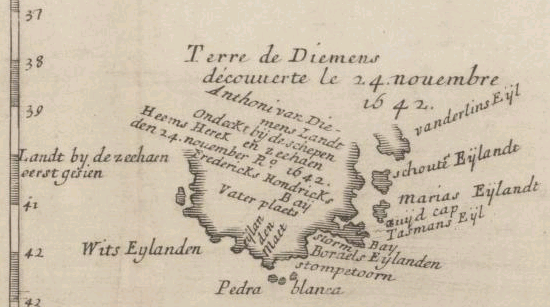
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Van Diemen
Anthony van Diemen (also ''Antonie'', ''Antonio'', ''Anton'', ''Antonius'') (1593 – 19 April 1645) was a Dutch colonial governor. Early life He was born in Culemborg in the Netherlands, the son of Meeus Anthonisz van Diemen and Christina Hoevenaar. In 1616, he moved to Amsterdam, in hope of improving his fortune as a merchant; in this he failed and was declared bankrupt. After a year he became a servant of the Dutch East India Company and sailed to Batavia, Dutch East Indies (Jakarta), capital of the Dutch East Indies. On the voyage out, the East Indiaman ''Mauritius'' inadvertently put in on unknown coast of Australia. Career Governor Jan Pieterszoon Coen found van Diemen to be a talented official and by 1626 he was Director-General of Commerce and member of the Council for the Indies. In 1630, he married Maria van Aelst. A year later he returned to the Netherlands as Admiral on the ship ''Deventer''. While on route to the Indies in 1633, Van Diemen sighted and named Amst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor-general Of The Dutch East Indies
The governor-general of the Dutch East Indies ( nl, gouverneur-generaal van Nederlands Indië) represented Dutch rule in the Dutch East Indies between 1610 and Dutch recognition of the independence of Indonesia in 1949. Occupied by Japanese forces between 1942 and 1945, followed by the Indonesian National Revolution until 1949. Indonesia proclaimed its independence on 17 August 1945. History The first governors-general were appointed by the Dutch East India Company (VOC). After the VOC was formally dissolved in 1800, the territorial possessions of the VOC were nationalised under the Dutch government as the Dutch East Indies, a colony of the Netherlands. Governors-general were now appointed by either the Dutch monarch or the Dutch government. During the Dutch East Indies era most governors-general were expatriate Dutchmen, while during the earlier VOC era most governors-general became settlers who stayed and died in the East Indies. Under the period of British control (1811 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock company in the world, granting it a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be bought by any resident of the United Provinces and then subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). It is sometimes considered to have been the first multinational corporation. It was a powerful company, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike its own coins, and establish colonies. They are also known for their international slave trade. Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Macfarquhar
Colin Macfarquhar (1744 or 1745? – 2 April 1793 or May 1793, Edinburgh?, Scotland) was a Scottish bookseller and printer who is most known for co-founding ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' with Andrew Bell, first published in December 1768. The dates of his birth and death remain uncertain, even to Britannica itself. Biography Macfarquhar was born in Edinburgh to his father James Macfarquhar who was a wigmaker and his mother Margaret. His formal education ended when he was apprenticed to a printing firm and achieved the status of a master printer in 1767. On 13 December 1767 Macfarquhar married Jane whose father, James Scruton, was an accountant in Glasgow. Macfarquhar and Jane had one son and four daughters. Macfarquhar opened a printing shop in Edinburgh Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin, Northern Territory
Darwin ( ; Larrakia: ) is the capital city of the Northern Territory, Australia. With an estimated population of 147,255 as of 2019, the city contains the majority of the residents of the sparsely populated Northern Territory. It is the smallest, wettest, and most northerly of the Australian capital cities and serves as the Top End's regional centre. Darwin's proximity to Southeast Asia makes the city's location a key link between Australia and countries such as Indonesia and East Timor. The Stuart Highway begins in Darwin, extends southerly across central Australia through Tennant Creek and Alice Springs, concluding in Port Augusta, South Australia. The city is built upon a low bluff overlooking Darwin Harbour. Darwin's suburbs begin at Lee Point in the north and stretch to Berrimah in the east. The Stuart Highway extends to Darwin's eastern satellite city of Palmerston and its suburbs. The Darwin region, like much of the Top End, experiences a tropical climate with a wet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Exploration Of Australia
The maritime European exploration of Australia consisted of several waves of European seafarers who sailed the edges of the Australian continent. Dutch navigators were the first Europeans known to have explored and mapped the Australian coastline. The first documented encounter was that of Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon, in 1606. Dutch seafarers also visited the west and north coasts of the continent, as did French explorers. The most famous expedition was that of Royal Navy Lieutenant (later Captain) James Cook 164 years after Janszoon's sighting. After an assignment to make observations of the 1769 Transit of Venus, Cook followed Admiralty instructions to explore the south Pacific for the reported ''Terra Australis'' and on 19 April 1770 sighted the south-eastern coast of Australia and became the first recorded European to explore the eastern coastline. Explorers by land and sea continued to survey the continent for some years after settlement. Pro-Iberian hypotheses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Hoorn.jpg)
.jpg)
