|
Kibblesworth
Kibblesworth is a village west of Birtley, Tyne and Wear, England. Kibblesworth was a mainly rural community until the development of the pit and brickworks and the resulting increase in population. Following the closure of the pit in 1974, few of the residents now work in the village. Historically in County Durham, it was transferred into the newly created county of Tyne and Wear in 1974. After being predominantly a council estate project consisting of prefabricated homes built in the 1950s, Kibblesworth has seen a massive change in recent times with the 'pre-fabs' being demolished and the new 'Ridings Estate' homes built by Keepmoat replacing them all, providing a much needed facelift and more providing more homes to buy. There are plans to build around 220 new homes by Taylor Wimpey on the surrounding outskirts of the village, with previous green belt land being downgraded to brown belt by the Government, with planning permission at an advanced stage, although this has had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibblesworth Academy
Kibblesworth is a village west of Birtley, Tyne and Wear, England. Kibblesworth was a mainly rural community until the development of the pit and brickworks and the resulting increase in population. Following the closure of the pit in 1974, few of the residents now work in the village. Historically in County Durham, it was transferred into the newly created county of Tyne and Wear in 1974. After being predominantly a council estate project consisting of prefabricated homes built in the 1950s, Kibblesworth has seen a massive change in recent times with the 'pre-fabs' being demolished and the new 'Ridings Estate' homes built by Keepmoat replacing them all, providing a much needed facelift and more providing more homes to buy. There are plans to build around 220 new homes by Taylor Wimpey on the surrounding outskirts of the village, with previous green belt land being downgraded to brown belt by the Government, with planning permission at an advanced stage, although this has had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowes Railway
The Bowes Railway, built by George Stephenson in 1826, is the world's only operational preserved standard gauge cable railway system. It was built to transport coal from pits in Durham to boats on the River Tyne. The site is a scheduled monument. The railway is open every week on Thursday, Friday and Saturday (Easter til October) as well as on a number of event days throughout the year. History Background The ''Grand Allies'', a partnership of businessmen including John Bowes, opened a colliery at Springwell in Durham. A railway was needed to transport the coal to the River Tyne. The plan was to build inclined planes and use a combination of steam power and gravity to move the coal wagons. The railway was designed by George Stephenson, who built the Hetton colliery railway completed in 1822. Construction The railway was built between Mount Moor and Jarrow via Springwell village. The first section, between Springwell and Jarrow, opened on 17 January 1826. Mount Moor follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Si King
Simon James King (born 20 October 1966) is an English television presenter, best known as one half of the Hairy Bikers with Dave Myers. Together they have presented a number of television cookery series for BBC television and have since launched an online weight loss programme, 'The Hairy Bikers Diet Club'. Early life King was born in Kibblesworth, County Durham. An alumnus of St Robert of Newminster Catholic School in Washington, he once stated that he "went through a phase of wanting to be a priest when I was about 13, but soon discovered girls and music were way more interesting." King's father served in the Royal Navy during World War II on the Arctic convoys and was then employed as a motorcycle despatch rider. Aged 16 Si worked laying paving stones for a construction firm.Si King Guardian money inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamesley
Lamesley is a village and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, England. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 3,742. The village is on the southern outskirts of Gateshead, near to Birtley. The parish includes Kibblesworth, Lamesley village, Eighton Banks and Northside, Birtley which is predominantly private housing in neighbourhoods named The Hollys, Long Bank, Northdene and Crathie. The ruined Ravensworth Castle is also in Lamesley. A hilltop contemporary sculpture in the parish is the Angel of the North by Anthony Gormley on a minor hilltop which is lower than the adjoining Low Fell and High Fell outside the parish. Demography Combined, this area has a population of 3,928 people as at the 2001 census and unlike the small rise in the overall region saw a decrease to 3,742 at the following census. The Gateshead MBC ward of Lamesley had a population of 8,662 at the 2011 Census. Both the ward and civil parish are very homo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent ceremonial counties of England, counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it List of metro systems, one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateshead
Gateshead () is a large town in northern England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank, opposite Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle to which it is joined by seven bridges. The town contains the Gateshead Millennium Bridge, Millennium Bridge, Sage Gateshead, The Sage, and the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, and has on its outskirts the twenty metre tall Angel of the North sculpture. Historic counties of England, Historically part of County Durham, under the Local Government Act 1888 the town was made a county borough, meaning it was administered independently of the county council. Since 1974, the town has been administered as part of the Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead within Tyne and Wear. In the 2011 Census, town had a population 120,046 while the wider borough had 200,214. Toponymy Gateshead is first mentioned in Latin translation in Bede, Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' as ''ad caput caprae'' ("at the goat's head"). This interpretation is consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Railway
The Metropolitan Railway (also known as the Met) was a passenger and goods railway that served London from 1863 to 1933, its main line heading north-west from the capital's financial heart in the City to what were to become the Middlesex suburbs. Its first line connected the main-line railway termini at , , and King's Cross to the City. The first section was built beneath the New Road using cut-and-cover between Paddington and King's Cross and in tunnel and cuttings beside Farringdon Road from King's Cross to near Smithfield, near the City. It opened to the public on 10 January 1863 with gas-lit wooden carriages hauled by steam locomotives, the world's first passenger-carrying designated underground railway. The line was soon extended from both ends, and northwards via a branch from Baker Street. Southern branches, directly served, reached Hammersmith in 1864, Richmond in 1877 and the original completed the '' Inner Circle'' in 1884. The most important route was northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-acting Incline
A gravity railroad (American English) or gravity railway (British English) is a railroad on a slope that allows cars carrying minerals or passengers to coast down the slope by the force of gravity alone. The speed of the cars is controlled by a braking mechanism on one or more cars on the train. The cars are then hauled back up the slope using animal power, a locomotive or a stationary engine and a cable, a chain or one or more wide, flat iron bands. A much later example in California used steam engines to pull gravity cars back to the summit of Mt. Tamalpais. The typical amusement park roller coaster is designed from gravity railroad technology based on the looping track incorporated into the second railroad of the United States, the Mauch Chunk & Summit Hill Railroad, which remained in operation for decades as a tourist ride after it was withdrawn from freight service hauling coal. Types of gravity railroad Some gravity railroads were designed to allow the weight of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
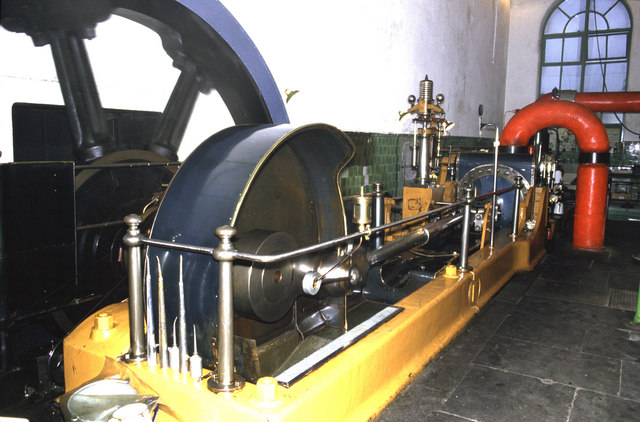
Stationary Steam Engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam cars (and other motor vehicles), agricultural engines used for ploughing or threshing, marine engines, and the steam turbines used as the mechanism of power generation for most nuclear power plants. They were introduced during the 18th century and widely made for the whole of the 19th century and most of the first half of the 20th century, only declining as electricity supply and the internal combustion engine became more widespread. Types of stationary steam engine There are different patterns of stationary steam engines, distinguished by the layout of the cylinders and crankshaft: * Beam engines have a rocking beam providing the connection between the vertical cylinder and crankshaft. *Table engines have the crosshead above the vert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight (see CargoSprinter). Traditionally, locomotives pulled trains from the front. However, Push-pull train, push-pull operation has become common, where the train may have a locomotive (or locomotives) at the front, at the rear, or at each end. Most recently railroads have begun adopting DPU or distributed power. The front may have one or two locomotives followed by a mid-train locomotive that is controlled remotely from the lead unit. __TOC__ Etymology The word ''locomotive'' originates from the Latin language, Latin 'from a place', Ablative case, ablative of 'place', and the Medieval Latin 'causing mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |