|
Khin Nyunt
General Khin Nyunt (; ; born 23 October 1939) is a Burmese military officer and politician. He held the office of Chief of Intelligence and was Prime Minister of Myanmar from 25 August 2003 until 18 October 2004. Early life and education Khin Nyunt was born on 23 October 1939 in Kyauktan Township, near Rangoon (now Yangon). He is of Burmese Chinese descent; his parents are Hakkas with ancestry from Meixian, Meizhou, Guangdong, China. Khin Nyunt graduated from the 25th batch of the Officer's Training School in 1960, after dropping out of Yankin College in the late 1950s. Political career After his career in the military, he was ordered back to Rangoon in 1984 after an attack on a visiting South Korean delegation. Twenty-one people, including three South Korean cabinet ministers, died during the attack, which occurred on 9 October 1983 and was perpetrated by terrorists sent from North Korea. Khin Nyunt was then appointed Chief of Intelligence. From the mid-1980s to the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Myanmar
The prime minister of Myanmar is the head of government of Myanmar. The post was re-established in 2021 by the State Administration Council, the country's ruling military junta, to lead its nominally-civilian provisional government. The provisional government is subject to the decision-making of the SAC; additionally, there is a significant overlap in the membership of both bodies. There is no provision for a prime minister in the 2008 Constitution of Myanmar, with the president being the constitutional head of government. The current prime minister is Min Aung Hlaing, who is also the leader of the junta and the commander-in-chief of defence services. The post had been used by previous military governments, as recently as 2011. History of the office The position of Prime Minister was created in 1948, with the adoption of the Burmese Declaration of Independence from the United Kingdom. Since then, eleven people have held the office (with two of them doing so on multiple occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
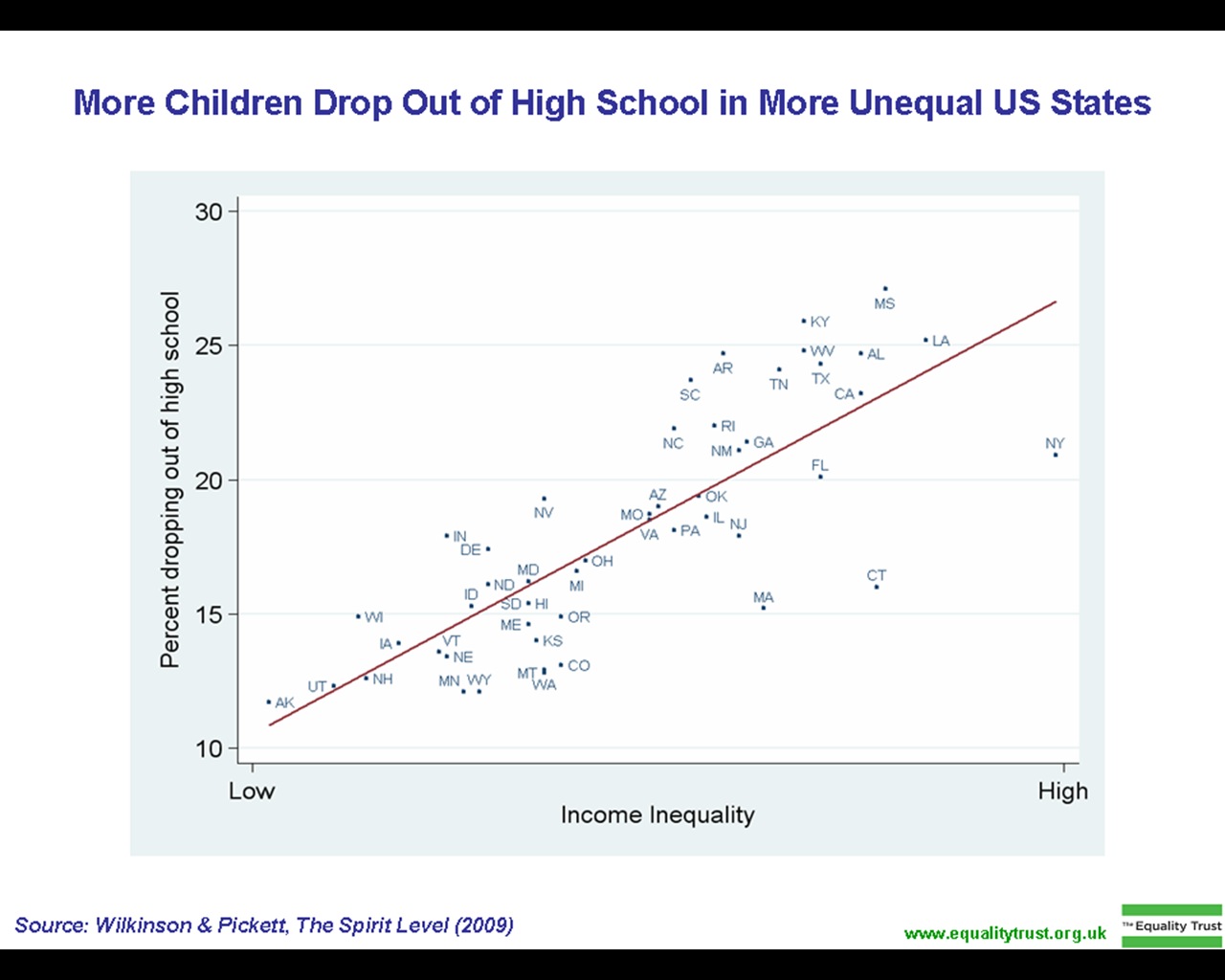
Dropping Out
Dropping out refers to leaving high school, college, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves. Canada In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey. The LFS is the official survey used to collect unemployment data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma (Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese Armed Forces
Tatmadaw (, , ) is the official name of the armed forces of Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is administered by the Ministry of Defence and composed of the Myanmar Army, the Myanmar Navy and the Myanmar Air Force. Auxiliary services include the Myanmar Police Force, the Border Guard Forces, the Myanmar Coast Guard, and the People's Militia Units. Since independence, the Tatmadaw has faced significant ethnic insurgencies, especially in Kachin, Kayin, Kayah, and Shan states. General Ne Win took control of the country in a 1962 coup d'état, attempting to build an autarkic society called the Burmese Way to Socialism. Following the violent repression of nationwide protests in 1988, the military agreed to free elections in 1990, but ignored the resulting victory of the National League for Democracy and imprisoned its leader Aung San Suu Kyi. The 1990s also saw the escalation of the conflict between Buddhists and Rohingya Muslims in Rakhine State due to RSO attacks on Tatmadaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myanmar Police Force
The Myanmar Police Force ( my, မြန်မာနိုင်ငံ ရဲတပ်ဖွဲ့), formerly the People's Police Force (), is the law enforcement agency of Myanmar. It was established in 1964 as an independent department under the Ministry of Home Affairs. History The Police Force in Myanmar have an extensive history; the police force also includes local police and regional police in different jurisdictions. British rule in Myanmar The ''Indian Imperial Police'' was the primary law enforcement in Burma until 1937, when it was split from British India. In 1872 the third mayor of Mergui District, Sir Ashly Din (1870–1875) assigned the first police officer to be stationed at Maliwan, a village 24 miles north of current Victoria Point. Perhaps the most famous policeman in Burma from this period is the author George Orwell, who in 1922 joined the Indian Imperial Police in Burma. Post-independence (1948–present) On 16 March 1988 following the killing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Show Trial
A show trial is a public trial in which the judicial authorities have already determined the guilt or innocence of the defendant. The actual trial has as its only goal the presentation of both the accusation and the verdict to the public so they will serve as both an impressive example and a warning to other would-be dissidents or transgressors. Show trials tend to be retributive rather than corrective and they are also conducted for propagandistic purposes. When aimed at individuals on the basis of protected classes or characteristics, such trials are examples of political persecution. The term was first recorded in 1928. China During the Land Reform Movement, between 1 and 2 million landlords were executed as counterrevolutionaries during the early years of Communist China. After the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989, show trials were given to "rioters and counter-revolutionaries" involved in the protests and the subsequent military massacre. Chinese Nobel Peace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maung Aye
Vice Senior General Maung Aye ( my, မောင်အေး ; born 25 December 1937) is a Burmese military official who was Vice Chairman of the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC), the ruling military junta of Myanmar, from July 1993 to March 2011. Maung Aye was the second highest-ranking member of the SPDC. Career Maung Aye graduated from the Defence Services Academy in Pyin U Lwin with a Bachelor of Science degree in 1960. In 1968, he became commander of the Northeast Region. In 1988, he became commander of the Eastern Region. Two years later he was promoted to major-general. In 1992, he was made Army Chief. In 1993, he was named Lieutenant General and the Deputy Commander in Chief of Defense Services. In 1994, he was appointed Deputy Chairman of SLORC, and subsequently held the same position in the SPDC. Vice Senior General Maung Aye and Senior General Than Shwe, along with six other top military officers, were reported to have resigned their military posts on 27 Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 Myanmar Constitutional Referendum
A constitutional referendum was held in Myanmar on 10 May 2008 (24 May 2008 in some townships) according to an announcement by the State Peace and Development Council in February 2008. According to the military government, the new Constitution of Myanmar will ensure the creation of a "discipline-flourishing democracy". Multi-party elections followed in 2010. The constitutional referendum law was enacted and a referendum commission was set up on 26 February 2008. Reportedly, the law ensures the secret casting of votes and requires a public count of the ballots to prove it is fair. The draft constitution was published and the date of the referendum finally announced on 9 April 2008. Among the changes that the referendum sought to make are: * One quarter of all parliamentary seats would be reserved for military officers. * The Ministry of Home Affairs would fall exclusively under military control. * Anyone married to a person who was not a citizen of Myanmar would be barred from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roadmap To Democracy
Myanmar's roadmap to democracy ( my, ဒီမိုကရေစီလမ်းပြမြေပုံ ၇ ချက်; officially the Roadmap to Discipline-flourishing Democracy), announced by General Khin Nyunt on 30 August 2003 in state media, provided a seven-step process in restoring democracy in the country. Endorsed by the State Peace and Development Council, it essentially describes the reassembly of the National Convention () in Nyaunghnapin, Hmawbi Township, Yangon Division to write a constitution, hold a national referendum to approve the constitution, hold a general election to elect members to the Hluttaw (legislative body), and finally hold parliamentary sessions. Phases This road map has been variously translated into English as: # First Phase – To reassemble the National Convention, which had been suspended since 1996. # Second Phase – To implement step by step the requisite tasks for the founding of a democratic system when the National Convention has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8888 Uprising
The 8888 Uprising ( my, ၈၈၈၈ အရေးအခင်း), also known as the People Power UprisingYawnghwe (1995), pp. 170 and the 1988 Uprising, was a series of nationwide protests, marches, and riots in Burma (present-day Myanmar) that peaked in August 1988. Key events occurred on 8 August 1988 and therefore it is commonly known as the "8888 Uprising". The protests began as a student movement and were organised largely by university students at the Rangoon Arts and Sciences University and the Rangoon Institute of Technology (RIT). Since 1962, the Burma Socialist Programme Party had ruled the country as a totalitarian one-party state, headed by General Ne Win. Under the government agenda, called the Burmese Way to Socialism, which involved economic isolation and the strengthening of the military, Burma became one of the world's most impoverished countries.Burma Watcher (1989)Woodsome, Kate. (7 October 2007)'Burmese Way to Socialism' Drives Country into Poverty Voic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ne Win
Ne Win ( my, နေဝင်း ; 10 July 1910, or 14 or 24 May 1911 – 5 December 2002) was a Burmese politician and military commander who served as Prime Minister of Burma from 1958 to 1960 and 1962 to 1974, and also President of Burma from 1962 to 1981. Ne Win was Burma's military dictator during the Socialist Burma period of 1962 to 1988. Ne Win founded the Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP) and overthrew the democratic Union Parliament of U Nu in the 1962 Burmese coup d'état, establishing Burma as a one-party socialist state under the Burmese Way to Socialism ideology. Ne Win was Burma's ''de facto'' leader as chairman of the BSPP, serving in various official titles as part of his military government, and was known by his supporters as U Ne Win. His rule was characterized by a non-aligned foreign policy, isolationism, one-party rule, economic stagnation and superstition. Ne Win resigned in July 1988 in response to the 8888 Uprising that overthrew the BSPP, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) and Tumen River, Tumen rivers, and South Korea to the south at the Korean Demilitarized Zone. North Korea's border with South Korea is a disputed border as both countries claim the entirety of the Korean Peninsula. The country's western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. North Korea, like South Korea, its southern counterpart, claims to be the legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of North Korea, adjacent islands. Pyongyang is the capital and largest city. In 1910, Korean Empire, Korea was Korea under Japanese rule, annexed by the Empire of Japan. In 1945, after the Surrender of Japan, Japanese surrender at the End of World War II in Asia, end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangoon Bombing
The Rangoon bombing of 9 October 1983, was an assassination attempt against Chun Doo-hwan, the fifth president of South Korea, in Rangoon, Burma (present-day Yangon, Myanmar). The attempt was orchestrated by North Korea. Although Chun survived, 21 people died in the attack and 46 were injured. One suspect was later killed, and the two other suspected bombers were captured, one of whom confessed to being a North Korean military officer. Bombing On 9 October 1983, President Chun Doo-hwan flew to Rangoon on an official visit to the capital of Burma. During the visit he planned to lay a wreath at the Martyrs' Mausoleum to commemorate Aung San, one of the founders of independent Burma who was assassinated in 1947. As some of the president's staff began assembling at the mausoleum, one of three bombs concealed in the roof exploded. The huge blast ripped through the crowd below, killing 21 people and wounding 46 others. Four senior South Korean politicians were killed: foreign mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.gif)

