|
Kheraskov
Mikhail Matveyevich Kheraskov (russian: Михаи́л Матве́евич Хера́сков; – ) was Russian poet and playwright. A leading figure of the Russian Enlightenment, Kheraskov was regarded as the most important Russian poet by Catherine the Great and her contemporaries. Kheraskov's father was a Wallachian boyar who settled in Ukraine. Patronized by his Freemason friends, Mikhail furthered his education abroad and was appointed dean of the Moscow University in 1763 at the age of 30. In 1771–1779, he wrote the ''Rossiad'' (russian: Россиада, ''Rossiada''), the first Russian epic in the tradition of Homer and Virgil, about Ivan the Terrible's taking of Kazan in 1552. The ''Rossiads only rival for the title of the longest poem in the Russian language is Kheraskov's ''Vladimir Reborn'' (1785), concerned with the baptism of Kievan Rus. Somewhat more popular is his oriental tale ''Bakhariana'' (1803). Kheraskov also wrote 20 plays but, like the rest o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grebnevo, Moscow Oblast
Grebnevo (russian: Гребнево) is a rural locality (a village) in Shchyolkovsky District of Moscow Oblast, Russia, located about east of Moscow, on the outskirt of the town of Fryazino, on the bank of the Lyuboseyevka River. History Best known for its historical manor, Grebnevo served as a country seat of the Galitzine, Trubetskoy, and Bibikov noble families. Among the early owners were Bogdan Belsky and Dmitry Troubetskoy. The last Russian boyar, Ivan Trubetskoy, gave the property to his daughter Anastasia, the wife of Prince Dimitrie Cantemir, whose daughter Catherine further expanded the estate. Mikhail Kheraskov, the foremost poet of Catherine the Great's time, was the next owner. It was in Grebnevo that he completed the '' Rossiad'', arguably the longest Russian poem. In the late 19th-century, the estate was owned by a merchant family which built several small factories on the grounds. Fyodor Grinevsky, one of Moscow's most popular physicians, bought Grebnevo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikita Trubetskoy
Prince Nikita Yurievich Trubetskoy ( Russian: ''Никита Юрьевич Трубецкой'') (26 May 1699 – 16 October 1767) was a Russian statesman and Field Marshal (1756), minister of defense of Russia 1760. His parents were general-poruchik and senator Prince Yuri Yurievich Troubetzkoy (20 April 1668 – 8 September 1739), who was governor of Belgorod, and Princess Elena Grigorievna Tcherkassky (b. before 1696). In 1715-1717, Nikita Trubetskoy was educated abroad. He started his military career as the batman of Peter I. In 1722 he joined the Preobrazhensky Regiment in the rank of sergeant and promoted to ensign in 1722.Journal of Kammer-junker Cercholz 11, 190 In 1730, Trubetskoy was one of staunch opponents of the Supreme Privy Council and supported the empress Anna Ivanovna. He had taken part in all of the Russian wars until 1740, then he presided the Voiennaia Kolleguia (ministere of army). He was appointed General-Prosecutor of the Governing Senate. Trubetsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taking Of Kazan
The Russo-Kazan Wars was a series of wars fought between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Khanate of Kazan from 1439, until Kazan was finally conquered by the Tsardom of Russia under Ivan the Terrible in 1552. General Before it separated from the Golden Horde, the Kazan region was part of Volga Bulgaria (c. 630–1240) and then the Bulgar Ulus of the Golden Horde (c. 1240–1438). They adopted Islam in 921, 67 years before Russia became Christian. The boundary between Muscovy and Kazan was near Nizhny Novgorod, about half way between the two cities. The land east of Nizhny Novgorod was fairly difficult. When the Tatars attacked they would first hit Nizhny Novgorod and then move on Murom, Ryazan, and other places, only twice approaching Moscow. When the Russians attacked they would usually send two armies, one down the Volga and one over land. As Muscovy grew stronger, fighting shifted eastward. Before 1552 the Russians made no attempt to conquer Kazan and contented themselves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow University
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU; russian: Московский государственный университет имени М. В. Ломоносова) is a public research university in Moscow, Russia and the most prestigious university in the country. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches (including five foreign ones in the Commonwealth of Independent States countries). Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner had been affiliated with the university. The university was ranked 18th by '' The Three University Missions Ranking'' in 2022, and 76th by the ''QS World University Rankings'' in 2022, #293 in the world by the global '' Times Higher World University Rankings'', and #326 by '' U.S. News & World Report'' in 2022. It was the highest-ranking Russian educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Enlightenment
The Russian Age of Enlightenment was a period in the 18th century in which the government began to actively encourage the proliferation of arts and sciences, which had a profound impact on Russian culture. During this time, the first Russian university was founded, a library, a theatre, a public museum, as well as relatively independent press. Like other enlightened despots, Catherine the Great played a key role in fostering the arts, sciences, and education. The national Enlightenment in the Russian Empire differed from its Western European counterpart in that it promoted further modernization of all aspects of Russian life and was concerned with abolishing the institution of serfdom in Russia. Pugachev's Rebellion and the French Revolution may have shattered the illusions of rapid political change, but the intellectual climate in Russia was altered irrevocably. Russia's place in the world was debated by Denis Fonvizin, Mikhail Shcherbatov, Andrey Bolotov, Alexander Radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izium
Izium or Izyum ( uk, Ізюм, ; russian: Изюм) is a city on the Donets River in Kharkiv Oblast (province) of eastern Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Izium Raion (district). Izium hosts the administration of Izium urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. It is about southeast of the oblast capital, Kharkiv. Izium had a population of History In 1681, a Cossack fortress was built within a small settlement, which marks the foundation date of Izium.Изюм // Украинская Советская Энциклопедия. том 4. Киев, «Украинская Советская энциклопедия», 1980. стр.231 It grew to be an important defense against Tatar invasions of the region. In 1684 the five-domed Baroque cathedral of the Saviour's Transfiguration was built. The cathedral was renovated in 1902 and restored in 1955. In 1765, Izium became a city, and in 1780 became an administrative center of Izyumsky Uyezd, one of the subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine ( uk, Лівобережна Україна, translit=Livoberezhna Ukrayina; russian: Левобережная Украина, translit=Levoberezhnaya Ukraina; pl, Lewobrzeżna Ukraina) is a historic name of the part of Ukraine on the left (east) bank of the Dnieper River, comprising the modern-day oblasts of Chernihiv, Poltava and Sumy as well as the eastern parts of Kyiv and Cherkasy. History The term appeared in 1663 with the election of Ivan Bryukhovetsky as the hetman of Ukraine in opposition to Pavlo Teteria. Bryukhovetsky was the first known "left-bank Ukraine" hetman over the area that was under the Russian influence. Up until the mid-17th century, the area had belonged to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Treaty of Pereyaslav of 1654 saw the region tentatively come under Russian control, when local Cossack leaders swore allegiance to the Russian monarchy in exchange for military protection. Russian sovereignty over the area was later reaffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later autonomous state, it existed from the 14th century to 1859, when it united with Wallachia () as the basis of the modern Romanian state; at various times, Moldavia included the regions of Bessarabia (with the Budjak), all of Bukovina and Hertsa region, Hertsa. The region of Pokuttya was also part of it for a period of time. The Moldavia (region of Romania), western half of Moldavia is now part of Romania, the eastern side belongs to the Moldova, Republic of Moldova, and the Chernivtsi Oblast, northern and Budjak, southeastern parts are territories of Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Trubetskaya
Anna may refer to: People Surname and given name * Anna (name) Mononym * Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke * Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773) * Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century) * Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) * Anna of Poland, Countess of Celje (1366–1425) * Anna of Cilli (1386–1416) * Anna, Grand Duchess of Lithuania (died 1418) * Anne of Austria, Landgravine of Thuringia (1432–1462) * Anna of Nassau-Dillenburg (died 1514) * Anna, Duchess of Prussia (1576–1625) * Anna of Russia (1693–1740) * Anna, Lady Miller (1741–1781) * Anna Russell, Duchess of Bedford (1783–1857) * Anna, Lady Barlow (1873–1965) * Anna (feral child) (1932–1942) * Anna (singer) (born 1987) Places Australia * Hundred of Anna, a cadastral district in South Australia Iran * Anna, Fars, a village in Fars Province * Anna, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, a village in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Province Russia * Anna, Voronezh Oblast, an urban locality in Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
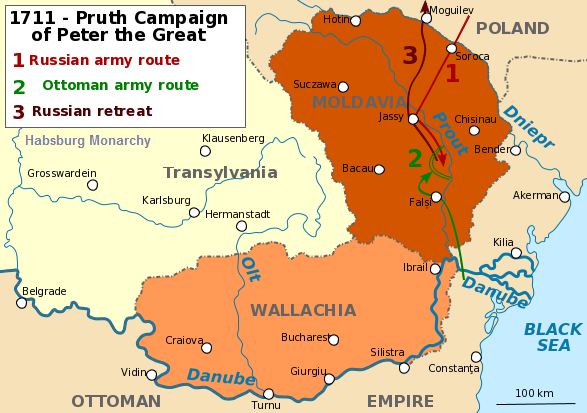
Pruth River Campaign
The Russo-Ottoman War of 1710—1711, also known as the Pruth River Campaign, was a brief military conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire. The main battle took place during 18-22 July 1711 in the basin of the Pruth river near Stănilești (Stanilesti) after Tsar Peter I entered the Ottoman vassal Principality of Moldavia, following the Ottoman Empire’s declaration of war on Russia. The ill-prepared 38,000 Russians with 5,000 Moldavians, found themselves surrounded by 200,000 Turks under Grand Vizier Baltaci Mehmet Pasha. After three days of fighting and heavy casualties the Tsar and his armies were allowed to withdraw after agreeing to abandon the fortress of Azov and its surrounding territory. The Ottoman victory led to the Treaty of the Pruth which was confirmed by the Treaty of Adrianople. Background The Russo-Ottoman War of 1710-1711 broke out as a result of the Great Northern War, which pitted the Swedish Empire of King Charles XII of Sweden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |