|
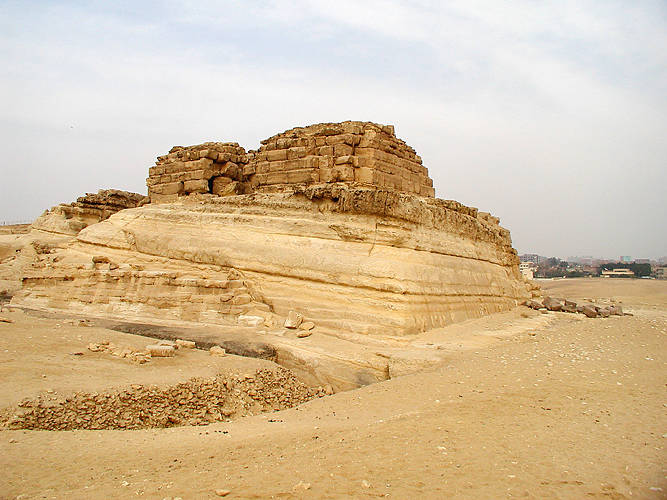
Khentkaus I
Khentkaus I, also referred to as Khentkawes, was a royal woman who lived in ancient Egypt during both the Fourth Dynasty and the Fifth Dynasty. She may have been a daughter of king Menkaure, the wife of both king Shepseskaf and king Userkaf (the founder of the Fifth Dynasty), the mother of king Sahure.Michael Rice: ''Who is who in Ancient Egypt'', Routledge London & New York 1999, , see p. 96 Some suggest that she was the regent for one of her sons. Perhaps, in her own right, she may have been the king of Upper and Lower Egypt, which aspects of her burial suggest. Her mastaba at Giza – tomb LG100 – is located very close to Menkaure's pyramid complex. This close connection may point to a family relationship. Although the relationship is not clear, the proximity of the pyramid complex of Khentkaus to that of king Menkaure has led to the conjecture that she may have been his daughter. Life Khentkaus's burial complex confirms her royal status. Some of her titles are ambiguous and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khentkaus II
Khentkaus II ( 2475 BC – 2445 BC) was a royal woman who lived in Ancient Egypt. She was a wife of Egyptian king Neferirkare Kakai of the Fifth Dynasty. She was the mother of two kings, Neferefre and Nyuserre Ini.Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, Thames & Hudson (2004), p.66 Biography Khentkaus II was the wife of Neferirkare Kakai. Her pyramid complex was started during the reign of her husband, when her title was still that of king's wife (''hmt nswt''). The construction of her tomb was halted, possibly when her husband died, and later was resumed during the reign of her son. After the building was resumed her title was ''king's mother'' (''mwt nswt'').M. Verner, Abusir III: The Pyramid Complex of Khentkaus, Czech Institute of Egyptology, Praha, 1995 Khentkaues II is shown on a block with her husband Neferirkare and a son named Ranefer B (The future Pharaoh Neferefre). A limestone fragment was found in the pyramid complex mentioning a ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartwig Altenmüller
Hartwig Altenmüller Hamburg University biography (in German) (born 1938, in Saulgau, Württemberg, Germany) is a German Egyptologist. He became professor at the Archaeological Institute of the University of Hamburg in 1971. He worked as an archaeologist in Saqqara from 1969 to 1982, and then the Valley of the Kings (where he worked on KV13, KV14 and KV47 Tomb KV47, located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt, was used for the burial of Pharaoh Siptah of the Nineteenth Dynasty. It was discovered on December 18, 1905 by Edward R. Ayrton, excavating on behalf of Theodore M. Davis; Siptah's mummy had ...) from 1984 to 1998, retiring in 2003. Publications * ''Zwei Annalenfragmente aus dem frühen Mittleren Reich'', Hamburg 2015, * "Lederbänder und Lederanhänger von der Mumie des Chonsu-maacheru" and "Die Mumienbinden des Chonsu-maacheru " in Alt-Ägypten 30 (2000), pp. 73–76, 88–89, 102–114* "Zwei Ostraka und ein Baubefund: Zum Tod des Schatzkanzlers Bay im 3 Regierun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other countries is documented. The Fourth Dynasty heralded the height of the pyramid-building age. The relative peace of the Third Dynasty allowed the Dynasty IV rulers the leisure to explore more artistic and cultural pursuits. King Sneferu's building experiments led to the evolution from the mastaba-styled step pyramids to the smooth sided “true” pyramids, such as those on the Giza Plateau. No other period in Egypt's history equaled Dynasty IV's architectural accomplishments.Egypt: Land and Lives of the Pharaohs Revealed, (2005), pp. 80–90, Global Book Publishing: Australia Each of the rulers of this dynasty (except for Shepseskaf, the last) commissioned at least one pyramid to serve as a tomb or cenotaph. The Fourth Dynasty was the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
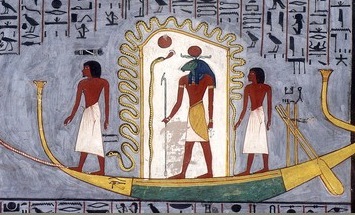
Solar Barge
Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet ( egy, mꜥnḏt) or the Boat of Millions of Years ( egy, wjꜣ-n-ḥḥw), and the vessel he used during the night was known as the Mesektet ( egy, msktt). Ra was said to travel through the sky on the barge, providing light to the world. Each twelfth of his journey formed one of the twelve Egyptian hours of the day, each overseen by a protective deity. Ra then rode the barque through the underworld, with each hour of the night considered a gate overseen by twelve more protective deities. Passing through all of these while fending off various destructive monsters, Ra reappeared each day on the eastern horizon. He was said to travel across the sky in the Mandjet Barque through the hours of the day, and then switch to the Mesektet Barque to descend into the underworld for the hours of the night. The progress of Ra upon the Mandjet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqara lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tura, Egypt
Tura ( arz, طرة ' , , ) was the primary quarry for limestone in ancient Egypt. The site, which was known by the ancient Egyptians as ''Troyu'' or ''Royu'', is located about halfway between modern-day Cairo and Helwan. Its ancient Egyptian name was misinterpreted by the ancient Greek geographer Strabo, who thought it meant it was inhabited by Trojans, thus the Hellenistic city was named Troia. The site is located by the modern town of ''Tora'' in the Cairo Governorate. Ancient mining town The limestone from Tura was the finest and whitest of all the Egyptian quarries, so it was used for facing stones for the richest tombs, as well as for the floors and ceilings of mastabas, which were otherwise made of mudbrick. It was used during the Old Kingdom and was the source of the limestone used for the "Rhomboidal Pyramid" or Bent Pyramid of Sneferu, the Great Pyramid of Khufu, the sarcophagi of many Old Kingdom nobles, the pyramids of the Middle Kingdom, and certain temples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |