|
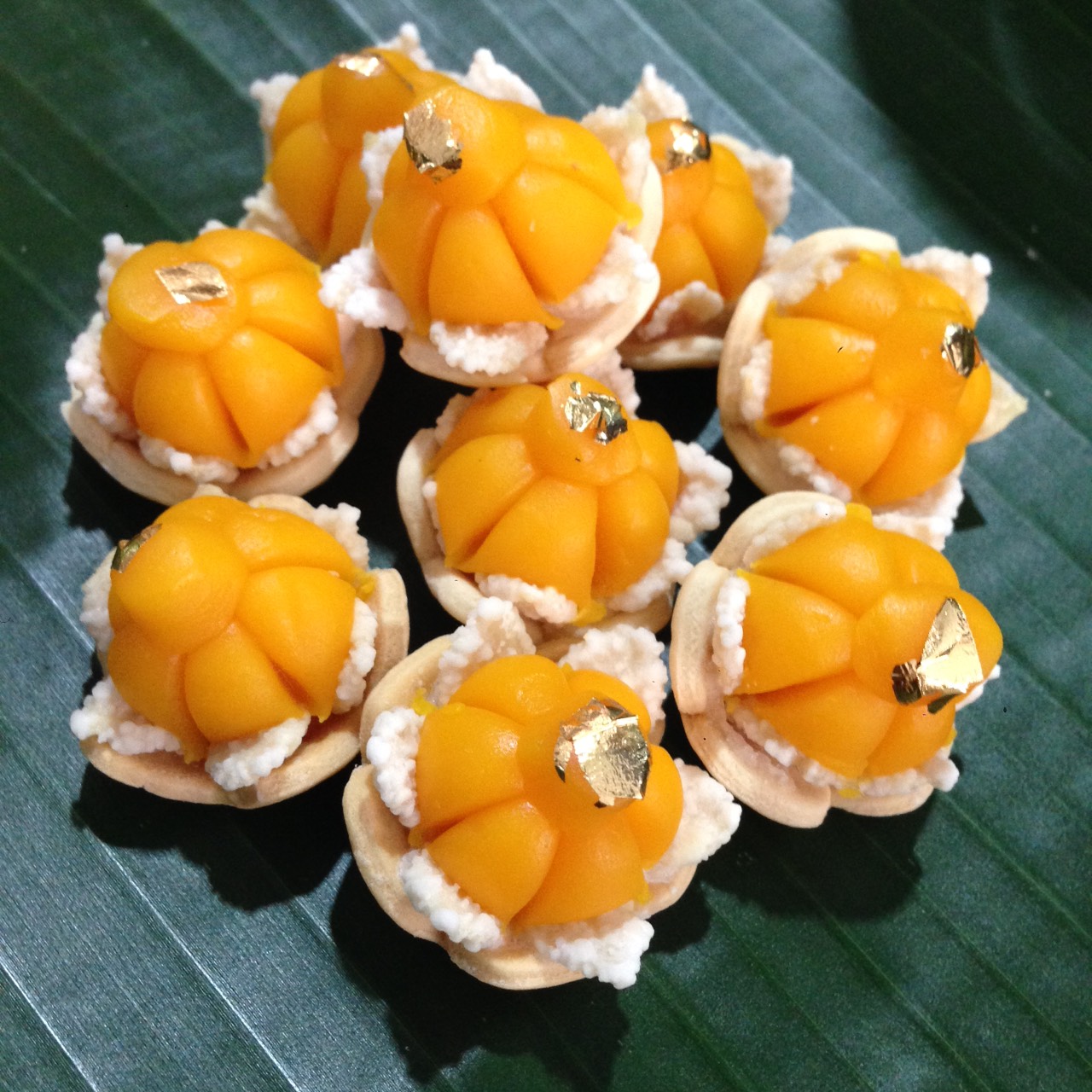
Khanom Tan
Khanom tan ( th, ขนมตาล; ) is a popular Thai dessert consisting of small steamed cakes flavoured with toddy palm sugar and coconut milk, wrapped in banana leaves, and topped with grated coconut. It is most often found in the provinces where sugar palm is grown, such as Phetchaburi, Nakhon Pathom and Suphanburi. History Khanom Tan is one of many popular Thai desserts that dates from the Sukhothai period. During that time, the main ingredients used in preparing desserts were rice flour, sugar and coconut, in contrast to desserts from the later Ayutthaya period, which are based on a mixture of eggs and sugar. Today, Khanom Tan is not well known among younger generations due to its disappearance from street markets, but it is still a popular Thai dessert outside of the Bangkok area. Preparation Khanom tan is made using a similar technique to the steamed dessert khanom kluay, the key difference being that khanom tan requires the batter to be fermented to achieve a spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the extremity of Myanmar. Thailand also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast, and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the nation's capital and largest city. Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 11th century. Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon, Khmer Empire and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of Ngoenyang, Sukhothai, Lan Na and Ayutthaya, which also rivalled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayutthaya Kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom (; th, อยุธยา, , IAST: or , ), the Empire of Ayutthaya (1569–1767), or the Ayutthaya Empire, was a Siamese kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. European travellers in the early 16th century called Ayutthaya one of the three great powers of Asia (alongside Vijayanagar and China). The Ayutthaya Kingdom is considered to be the precursor of modern Thailand, and its developments are an important part of the history of Thailand. The Ayutthaya Kingdom emerged from the mandala/merger of three maritime city-states on the Lower Chao Phraya Valley in the late 13th and 14th centuries (Lopburi, Suphanburi, and Ayutthaya). The early kingdom was a maritime confederation, oriented to post-Srivijaya Maritime Southeast Asia, conducting raids and tribute from these maritime states. After two centuries of political organization from the Northern Cities and a transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thai Dishes
Below is a list of dishes found in Thai cuisine. Individual dishes Note: The Thai script column is linked to how it is pronounced when available. Rice dishes }) where the omelette is topped with a minced pork and vegetable stir-fry. , - , Khao khluk kapi , ข้าวคลุกกะปิ , Fried rice with shrimp paste , , , Rice is fried with shrimp paste and served with sweet pork, sour mango, fried shrimp, chili peppers, and shallots. , - , Khao mok gai , ข้าวหมกไก่ , Thai chicken biryani , , , The Thai version of a "chicken biryani". The name literally means "rice covered chicken" and this Thai-Muslim dish is made by cooking rice together with the chicken curry. , - , Khao mok nuea , ข้าวหมกเนื้อ , Thai beef biryani , , , The Thai version of a "beef biryani". , - , Khao man gai , ข้าวมันไก่ , Chicken rice , , , Rice steamed with garlic served with sliced chicken, chicken broth, and a spicy dippin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thai Desserts
This is a list of Thai khanom, comprising snacks and desserts that are a part of Thai cuisine. Some of these dishes are also a part of other cuisines. The word "khanom" ( th, ขนม), refers to snack or dessert, presumably being a compound between two words, "khao" (ข้าว), "rice" and "khnom" (หนม), "sweet". The word "khanom" in the Thai sense is snack or sweet food made from flour. Thai khanom * ''Bua Loy, rice flour rolled into small balls and then cooked in coconut milk.'' * '' Bulan dan mek'' * '' Lot chong'' * '' Cha mongkut'' * '' Fakthong kaeng buat'' * '' Foi thong'' * Fresh fruit * ''Grass jelly'' * ''Khanom babin'' * ''Khanom bueang'' – known as Thai crêpes * ''Khanom chan'' – means layer dessert * '' Khanom keson lamchiak'' * '' Khanom khai pla'' * ''Khanom khrok'' * '' Khanom khuai ling'' * '' Khanom mo kaeng'' * '' Khanom namdokmai'' * '' Khanom phing'' * '' Khanom piakpun'' * '' Khanom sane chan'' * ''Khanom sot sai'' * ''Khanom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Cuisine
Thai cuisine ( th, อาหารไทย, , ) is the national cuisine of Thailand. Thai cooking places emphasis on lightly prepared dishes with strong Odor, aromatic components and a spicy edge. Australian chef David Thompson (chef), David Thompson, an expert on Thai food, observes that unlike many other cuisines, Thai cooking is "about the juggling of disparate elements to create a harmonious finish. Like a complex musical chord it's got to have a smooth surface but it doesn't matter what's happening underneath. Simplicity isn't the dictum here, at all." Traditional Thai cuisine loosely falls into four categories: ''tom'' (boiled dishes), ''yam'' (spicy salads), ''tam'' (pounded foods), and ''kaeng'' (curries). Deep-fries, stir-fries, and steamed dishes derive from Chinese cuisine. In 2017, seven Thai dishes appeared on a list of the "World's 50 Best Foods", an online poll of 35,000 people worldwide by ''CNN Travel''. Thailand had more dishes on the list than any other co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
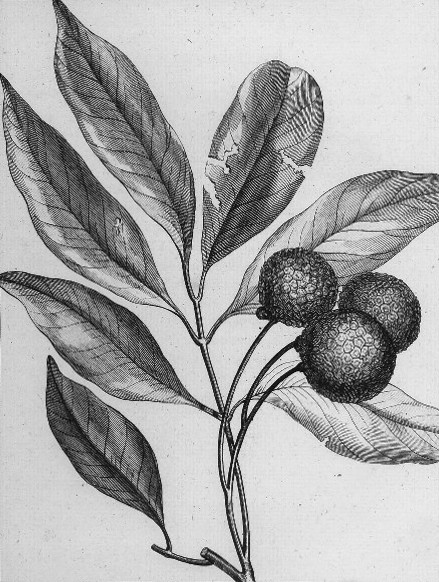
Lychee
Lychee (US: ; UK: ; ''Litchi chinensis''; ) is a Monotypic taxon, monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus ''Litchi'' in the Sapindus, soapberry family, ''Sapindaceae''. It is a tropical tree native to Southeast and Southwest China (the Guangdong, Fujian, Yunnan and Hainan provinces), Assam, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaya, Java, Jawa, Borneo, Philippines and New Guinea. The tree is introduced into Cambodia, Andaman Islands, Bangladesh, East Himalaya, India, Mauritius and Réunion. The cultivation in China is documented from the 11th century. China is the main producer of lychees, followed by Vietnam, India, other countries in Southeast Asia, the Indian Subcontinent, Madagascar and South Africa. A tall evergreen tree, the lychee bears small fleshy Drupe, fruits. The outside of the fruit is pink-red, roughly textured, and inedible, covering sweet flesh eaten in many different dessert dishes. Lychee seeds contain Methylene cyclopropyl acetic acid, methylene cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raising Agent
In cooking, a leavening agent () or raising agent, also called a leaven () or leavener, is any one of a number of substances used in doughs and batters that cause a foaming action (gas bubbles) that lightens and softens the mixture. An alternative or supplement to leavening agents is mechanical action by which air is incorporated (i.e. kneading). Leavening agents can be biological or synthetic chemical compounds. The gas produced is often carbon dioxide, or occasionally hydrogen. When a dough or batter is mixed, the starch in the flour and the water in the dough form a matrix (often supported further by proteins like gluten or polysaccharides, such as pentosans or xanthan gum). The starch then gelatinizes and sets, leaving gas bubbles that remain. Biological leavening agents * ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' producing carbon dioxide found in: ** baker's yeast ** Beer barm (unpasteurised—live yeast) ** ginger beer ** kefir ** sourdough starter * ''Clostridium perfringens'' pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Flour
Rice flour (also rice powder) is a form of flour made from finely milled rice. It is distinct from rice starch, which is usually produced by steeping rice in lye. Rice flour is a common substitute for wheat flour. It is also used as a thickening agent in recipes that are refrigerated or frozen since it inhibits liquid separation. Rice flour may be made from either white rice or brown rice. To make the flour, the husk of rice or paddy is removed and raw rice is obtained, which is then ground to flour. Types and names By rice Rice flour can be made from indica, japonica, and wild rice varieties. Usually, rice flour ( zh, c=米粉, p=mǐfěn, ja, 米粉, komeko, ko, 쌀가루, ssal-garu, vi, bột gạo, th, แป้งข้าวเจ้า, paeng khao chao, lo, ແປ້ງເຂົ້າຈ້າວ, pèng khao chao, km, ម្សៅអង្ករ, msau ângkâ, my, ဆန်မှုန့်, hcan hmun, ms, tepung beras, tr, pirinç) refers to flour made f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut Milk
Coconut milk is an opaque, milky-white liquid extracted from the grated pulp of mature coconuts. The opacity and rich taste of coconut milk are due to its high oil content, most of which is saturated fat. Coconut milk is a traditional food ingredient used in Southeast Asia, Oceania, South Asia, and East Africa. It is also used for cooking in the Caribbean, tropical Latin America, and West Africa, where coconuts were introduced during the colonial era. Coconut milk is differentiated into subtypes based on fat content. They can be generalized into coconut cream (or thick coconut milk) with the highest amount of fat; coconut milk (or thin coconut milk) with a maximum of around 20% fat; and coconut skim milk with negligible amounts of fat. This terminology is not always followed in commercial coconut milk sold in western countries. Coconut milk can also be used to produce milk substitutes (differentiated as "coconut milk beverages"). These products are not the same as regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanom Kluay
Khanom may refer to: *'' Khanum'', a female royal and aristocratic title *''Khanom'' (), the Thai word for dessert or snack. See Thai cuisine * Khanom District, Thailand () * Places in Iran ( fa, خانم): ** Khanom Kan ** Khanom Sheykhan Khanom Sheykhan ( fa, خانم شيخان, also Romanized as Khānom Sheykhān, Khānam-i-Shaikhan, and Khānom-e Sheykhān) is a village in Khav and Mirabad Rural District, Khav and Mirabad District, Marivan County, Kurdistan Province, Iran. At t ... See also * Khanam, a surname {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangkok
Bangkok, officially known in Thai language, Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon and colloquially as Krung Thep, is the capital and most populous city of Thailand. The city occupies in the Chao Phraya River delta in central Thailand and has an estimated population of 10.539 million as of 2020, 15.3 percent of the country's population. Over 14 million people (22.2 percent) lived within the surrounding Bangkok Metropolitan Region at the 2010 census, making Bangkok an extreme primate city, dwarfing Thailand's other urban centres in both size and importance to the national economy. Bangkok traces its roots to a small trading post during the Ayutthaya Kingdom in the 15th century, which eventually grew and became the site of two capital cities, Thonburi Kingdom, Thonburi in 1768 and Rattanakosin Kingdom (1782–1932), Rattanakosin in 1782. Bangkok was at the heart of the modernization of Siam, later renamed Thailand, during the late-19th century, as the country faced pressures from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom ( th, สุโขทัย, , IAST: , ) or the Northern Cities was a post-classical Thai kingdom (mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Si Inthrathit in 1238 and existed as an independent polity until 1438, when it fell under the influence of the neighboring Ayutthaya after the death of Borommapan (Maha Thammaracha IV). Sukhothai was originally a trade center in Lavo—itself under the suzerainty of the Khmer Empire—when Central Thai people led by Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, a local leader, revolted and gained their independence. Bang Klang Hao took the regnal name of Si Inthrathit and became the first monarch of the Phra Ruang dynasty. The kingdom was centralized and expanded to its greatest extent during the reign of Ram Khamhaeng the Great (1279–1298), who some historians considered to have introduced Theravada Buddhism and the initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)
