|
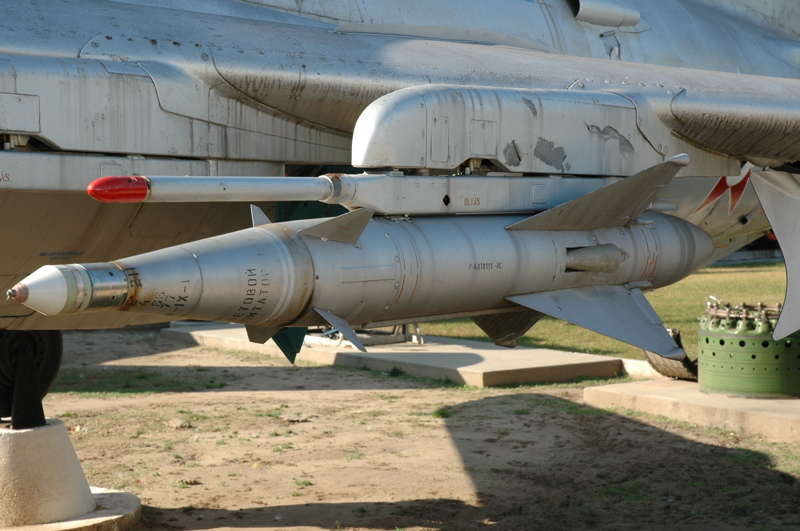
Kh-23 Grom
The Zvezda Kh-66 and Kh-23 ''Grom'' (russian: Kha (Cyrillic), Х-23 Гром 'Thunder'; NATO reporting name, NATO: AS-7 'Kerry') are a family of early Soviet Union, Soviet tactical air-to-surface missiles with a range of 10 km. They were intended for use against small ground or naval targets. The Kh-66 was effectively a heavy-warhead, beam-riding version of the K-8 (missile), K-8 (AA-3 'Anab') air-to-air missile rushed into service in Vietnam in 1968. The Kh-23 was an improved Kh-66 with command-guidance, similar to the AGM-12 Bullpup. Development Work on air-to-air missiles had started at the Kaliningrad Engineering Plant (then known as Plant #455, and later merged into Zvezda-Strela) in 1955. This had resulted in the Kaliningrad K-5 (AA-1 'Alkali') family of beam-guided missiles, including the K-51 (RS-2-US) carried by the Su-9 'Fishpot'. OKB-4 Molniya (later Vympel NPO) under Matus Bisnovat would go on to produce missiles such as the R-40 (missile), AA-6 Acrid. Meanwhile, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NATO Reporting Name
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manner in place of the original designations, which either may have been unknown to the Western world at the time or easily confused codes. For example, the Russian bomber jet Tupolev Tu-160 is simply called "Blackjack". NATO maintains lists of the names. The assignment of the names for the Russian and Chinese aircraft was once managed by the five-nation Air Standardization Coordinating Committee (ASCC), but that is no longer the case. American variations The United States Department of Defense (DOD) expands on the NATO reporting names in some cases. NATO refers to surface-to-air missile systems mounted on ships or submarines with the same names as the corresponding land-based systems, but the US DoD assigns a different series of numbers with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vympel NPO
Vympel NPO is a Russian research and production company based near Moscow, mostly known for their air-to-air missiles. Other projects include SAM and ABM defenses. It was started in the Soviet era as an OKB (experimental design bureau). History Vympel started out after World War II as OKB-134, with leading the team. The first product they designed was the K-7 missile. Their first missile built in serial production was the K-13 (R-13) in 1958. Toropov moved to Tushino Aviation Facility in 1961 and was replaced by . Somewhere between 1966 and 1968 the OKB got renamed to Vympel. In 1977 Matus Bisnovat of OKB-4 Molniya died, and all missile related work was passed to Vympel. G. Khokhlov led the team until 1981, when Genadiy A. Sokolovski succeeded him. In 1992 the GosMKB Vympel got started on the basis of the OKB and in 1994 Sokolovski became the director of development at the company. In May 2004 the Tactical Missiles Corporation was formed and Vympel became a part of it, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AS-20
The AS-20 (Type 5110) was a French air-to-surface missile developed during the late 1950s. It was similar to the U.S. AGM-12 Bullpup missile. Development The AS-20 was based on an earlier Nord Aviation air-to-air missile the AA.20 (designated Type 5103). Only minor changes were required to make it an air-to-surface missile, the size of the warhead was increased as a result of replacing the large proximity fuze with a simple impact fuze. Design The AS-20 had four steeply swept-back fins, cruciform in cross-section around the midsection of its body. It used a dual-thrust solid rocket motor, which exhausted through two large nozzles during the boost stage, and a single center line nozzle during the sustain stage. The AS-20 uses a simple MCLOS guidance with the pilot aligning the flares on the missile's rear with the target and controlling the missile in flight after launch with a small joystick sending steering commands to the missile via a radio link. The steering commands steer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGM-65 Maverick
The AGM-65 Maverick is an air-to-ground missile (AGM) designed for close air support. It is the most widely produced precision-guided missile in the Western world, and is effective against a wide range of tactical targets, including armor, air defenses, ships, ground transportation and fuel storage facilities. Development began in 1966 at Hughes Aircraft Company as the first missile to use an electronic contrast seeker. It entered service with the United States Air Force in August 1972. Since then, it has been exported to more than 30 countries and is certified on 25 aircraft. The Maverick served during the Vietnam, Yom Kippur, Iran–Iraq, and Persian Gulf Wars, along with other smaller conflicts, destroying enemy forces and installations with varying degrees of success. Since its introduction into service, numerous Maverick versions had been designed and produced using electro-optical, laser, and imaging infrared guidance systems. The AGM-65 has two types of warhead: one has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grom (missile)
The Grom (meaning "thunder" in Polish) is a man-portable air-defense system produced in Poland and based on the Soviet man-portable infrared homing surface-to-air missile (SAM) 9K38 Igla. It consists of a 72 mm anti-aircraft missile set with a flight speed of 650 m/s, as well as a single-use launcher, re-usable gripstock and thermal battery coolant assembly electric unit. The full name of the system is PZR Grom, PZR standing for ''Przeciwlotniczy Zestaw Rakietowy'' (literally anti-air rocket-propelled set). It is designed to target low-flying helicopters and aeroplanes. As such, the Grom missile is used by other surface-to-air defence systems of Polish design, including ZSU-23-4MP Biała, ZUR-23-2 kg and Poprad self-propelled artillery system. It should not to be confused with versions of the Zvezda Kh-23 air-to-surface missile built under licence in Yugoslavia/Serbia as the Grom-A and Grom-B. History Initially at least since the 1970s the MESKO metal works in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-25
The Kh-25/Kh-25M (russian: Х-25; NATO: AS-10 'Karen) is a family of Soviet lightweight air-to-ground missiles with a modular range of guidance systems and a range of 10 km. The anti-radar variant (Kh-25MP) is known to NATO as the AS-12 ' Kegler and has a range up to 40 km. Designed by Zvezda-Strela, the Kh-25 is derived from the laser-guided version of the Kh-23 Grom (AS-7 'Kerry'). The Kh-25 remains in widespread use despite the apparent development of a successor, the Kh-38. Development Based on an air-to-air missile, the beam-riding Kh-66 had been the Soviet Union's first air-to-ground missile for tactical aircraft, entering service in 1968. However it proved difficult to use in practice as the launch aircraft had to dive towards the target. A version with radio-command guidance, the Kh-23, was first tested in 1968 but problems with the guidance system meant that it would not enter service for another five years. So in 1971 work began on a version with a semi-act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Su-17M3 2008 G10
The JSC Sukhoi Company (russian: ПАО «Компания „Сухой“», ) is a Russian aircraft manufacturer (formerly Soviet), headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, that designs both civilian and military aircraft. It was founded in the Soviet Union by Pavel Sukhoi in 1939 as the Sukhoi Design Bureau (OKB-51, design office prefix Su). During February 2006, the Russian government merged Sukhoi with Mikoyan, Ilyushin, Irkut, Tupolev, and Yakovlev as a new company named United Aircraft Corporation.Russian Aircraft Industry Seeks Revival Through Merger ." '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.png)