|
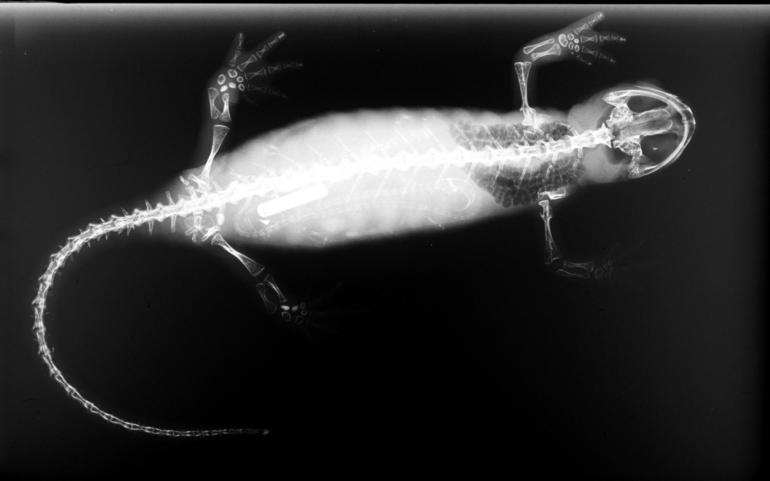
Keraterpeton
''Keraterpeton'' is an extinct genus of lepospondyl amphibian, previously included within the monotypic Keraterpedontidae family, from the Carboniferous period of Europe (Czech Republic, England and Ireland)Brownrigg, W. B. (1865). Notes on part of the Leinster Coalfield, with a record of some fossils found therein. ''Dublin Quarterly Journal of Science'' 6, 195–196.Google Scholar and North America (United States); it is the oldest known member of the family Diplocaulidae. The type species is ''Keraterpeton galvani'', named in 1866 as ''Ceraterpeton'' by Robert Etheridge and later amended to ''Keraterpeton'' in 1868 by Thomas Henry Huxley and Edward Percival Wright; three years earlier (in November 1865), they were authorised by William Bookey Brownrigg to describe some fossil vertebrates in his collection, and among them was NHMING F 14735, the holotype of ''Keraterpeton galvani'', which was discovered in the Jarrow Colliery in County Kilkenny, Ireland. Wyse Jackson, P. N., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocaulids
The Diplocaulidae ("double cauls") is an extinct family of lepospondyl amphibians that arose during the Late Carboniferous and died out in the Late Permian. They are distinguished from other amphibians, extinct and extant, by the presence of strange, horn-like protrusions jutting out from the rear of their skulls; in some genera said protrusions gave their heads an almost boomerang-like outline. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... modified from Germain (2010): References Diplocaulids Pennsylvanian first appearances Lopingian extinctions {{Lepospondyli-stub es:Keraterpetontidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocaulidae
The Diplocaulidae ("double cauls") is an extinct family of lepospondyl amphibians that arose during the Late Carboniferous and died out in the Late Permian. They are distinguished from other amphibians, extinct and extant, by the presence of strange, horn-like protrusions jutting out from the rear of their skulls; in some genera said protrusions gave their heads an almost boomerang-like outline. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... modified from Germain (2010): References Diplocaulids Pennsylvanian first appearances Lopingian extinctions {{Lepospondyli-stub es:Keraterpetontidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diceratosaurus
''Diceratosaurus'' is an extinct genus of nectridean lepospondyl within the family Keraterpetontidae. Fossils of ''Diceratosaurus'' were first described by Edward Drinker Cope in 1874. The species ''D. brevirostris'' is well known from Jefferson County, Ohio, with approximately 50 specimens having been collected from the Ohio Diamond Coal Mine. The mine was situated in the village of Linton, which became obscure soon after operations were completed and the mine closed in 1921. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Carboniferous amphibians of North America Diplocaulids Carboniferous amphibians Fossil taxa described in 1903 {{Lepospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepospondyli
Lepospondyli is a diverse taxon of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco (''Diplocaulus minumus''), lepospondyls lived from the Early Carboniferous ( Mississippian) to the Early Permian and were geographically restricted to what is now Europe and North America. Five major groups of lepospondyls are known: Adelospondyli; Aïstopoda; Lysorophia; Microsauria; and Nectridea. Lepospondyls have a diverse range of body forms and include species with newt-like, eel- or snake-like, and lizard-like forms. Various species were aquatic, semiaquatic, or terrestrial. None were large (the biggest genus, the diplocaulid ''Diplocaulus'', reached a meter in length, but most were much smaller), and they are assumed to have lived in specialized ecological niches not taken by the more numerous temnospondyl amphibians that coexisted with them in the Paleozoic. Lepospondyli was named in 1888 by Karl Alfred von Zittel, who coined the name t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobu Tamura
Nobumichi Tamura, often shortened to Nobu Tamura, is a France, French-born Japanese Americans, Japanese American paleoartist and physicist.Ronson, Jacqueline.Meet Nobu Tamura, the Artist and Physicist Determined to Draw All the Dinosaurs, Inverse, March 9, 2016. He currently lives in California, United States. Biography Tamura became a physicist with Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) and is an artist specializing in the field of paleoart. Tamura was a student at Grenoble Institute of Technology from 1986-1989 for electrochemistry, and then from 1989-1993 for his PhD in Materials Science. He worked at Oak Ridge National Laboratory from May 1998 to August 1999, and then moved to LBNL. He has worked there ever since as the project leader for the development of the Advanced Light Source, ALS X-Ray microdiffraction beamline. He is a Senior Scientist in Diffraction and Imaging, and Photon Science Operations. He has published over 300 articles, including in publications suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Amphibians Of Europe
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Amphibians
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)