|
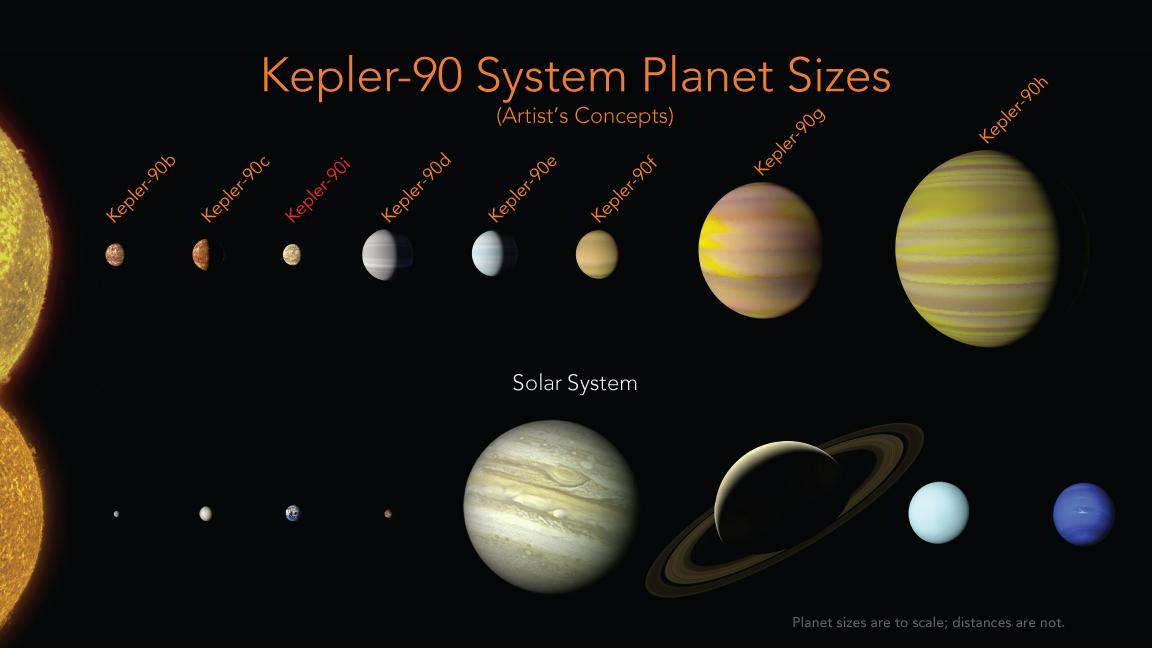
Kepler-90
Kepler-90, also designated 2MASS J18574403+4918185, is an F-type star located about from Earth in the constellation of Draco (constellation), Draco. It is notable for possessing a planetary system that has the same number of observed planets as the Solar System. On 14 December 2017, NASA and Google announced the discovery of an eighth exoplanet, Kepler-90i, in the Kepler-90 system. The discovery was made using a new machine learning method developed by Google. Nomenclature and history Prior to Kepler observation, Kepler-90 had the 2MASS catalogue number 2MASS J18574403+4918185. It has the designation of KIC 11442793 in the Kepler Input Catalog, and given the Kepler object of interest number of KOI-351 when it was found to have a transiting planet candidate. The star's planetary system was discovered by NASA's Kepler Mission, a mission tasked with discovering planets in transit method, transit around their stars. The transit method that Kepler uses involves detecting dip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90h
Kepler-90h (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation ''KOI-351.01'') is an exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of the early G-type main sequence star Kepler-90, the outermost of eight such planets Discovery (observation), discovered by NASA's Kepler (spacecraft), Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 2,840 light-years (870 parsecs), from Earth in the constellation Draco (constellation), Draco. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. Characteristics Physical characteristics Kepler-90h is a gas giant with no solid surface. Its equilibrium temperature is . It is around 1.2 times as massive and around 1.01 times as large as Jupiter. This makes it very similar to Jupiter, in terms of mass and radius. Orbit Kepler-90h orbits its host star about every 331.6 days at a distance of 1.01 astronomical units, very similar to Earth's orbital distance from the Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90i
Kepler-90i (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation KOI-351.08) is a super-Earth exoplanet with a radius 1.32 times that of Earth, orbiting the early G-type main sequence star Kepler-90 every 14.45 days, discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft. It is located about 2,840 light-years (870 parsecs, or nearly km) from Earth in the constellation Draco. The exoplanet is the eighth in the star's multiplanetary system. As of December 2017, Kepler-90 is the star hosting the most exoplanets found. Kepler-90i was found with the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured, and by a newly utilized computer tool, deep learning, a class of machine learning algorithms. Characteristics Mass, radius and temperature Kepler-90i is a super-Earth exoplanet with a radius of 1.32 , indicating that it is small enough to be rocky. With an Earth-like composition, Kepler-90i would have a mass of about 2.3 , since its volum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90g
Kepler-90g (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation ''KOI-351.02'') is a super-puff exoplanet orbiting the early G-type main sequence star Kepler-90, one of eight planets around this star discovered using NASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...'s Kepler space telescope. It is located about from Earth, in the constellation Draco (constellation), Draco. The exoplanet was found by using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. It orbits its parent star about every 210.5 days at a distance of 0.71 astronomical units. Kepler-90g's orbital period changes by 25.7 hours between two consecutive transits, caused by gravitational perturbations from other planets in the system. Addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90f
Kepler-90f is an exoplanet orbiting the star Kepler-90, located in the constellation Draco. It was discovered by the ''Kepler Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...'' telescope in October 2013. It orbits its parent star at only 0.48 astronomical units away, and at its distance it completes an orbit once every 124.91 days. References Hot Neptunes Transiting exoplanets Draco (constellation) Exoplanets discovered by the Kepler space telescope Exoplanets discovered in 2013 {{Extrasolar-planet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90e
Kepler-90e is an exoplanet orbiting the star Kepler-90, located in the constellation Draco. It was discovered by the ''Kepler Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws o ...'' telescope in October 2013. It orbits its parent star at only 0.42 astronomical units away, and at its distance it completes an orbit once every 91.94 days. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Kepler-90e Transiting exoplanets Exoplanets discovered by the Kepler space telescope Draco (constellation) Exoplanets discovered in 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin Scale
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90d
Kepler-9 is a sunlike star in the constellation Lyra. Its planetary system, discovered by the Kepler Mission in 2010 was the first detected with the transit method found to contain multiple planets. Nomenclature and history Kepler-9 was named for the Kepler Mission, a project headed by NASA that was designed to search for Earth-like planets. In June 2010, some 43 days after Kepler came online, its operating scientists submitted a list of over 700 exoplanet candidates for review. Of those, five were originally suspected to have more than one planet. Kepler-9 was one of the multiplanetary systems; it was identified as such when scientists noticed significant variations in the time intervals at which Kepler-9 was transited. Kepler-9 holds the first multiplanetary system discovered using the transit method. It is also the first planetary system where transiting planets were confirmed through transit timing variations method, allowing to calculate the masses of planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90c
Kepler-9 is a sunlike star in the constellation Lyra. Its planetary system, discovered by the Kepler Mission in 2010 was the first detected with the transit method found to contain multiple planets. Nomenclature and history Kepler-9 was named for the Kepler Mission, a project headed by NASA that was designed to search for Earth-like planets. In June 2010, some 43 days after Kepler came online, its operating scientists submitted a list of over 700 exoplanet candidates for review. Of those, five were originally suspected to have more than one planet. Kepler-9 was one of the multiplanetary systems; it was identified as such when scientists noticed significant variations in the time intervals at which Kepler-9 was transited. Kepler-9 holds the first multiplanetary system discovered using the transit method. It is also the first planetary system where transiting planets were confirmed through transit timing variations method, allowing to calculate the masses of planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler-90b
Kepler-9 is a sunlike star in the constellation Lyra. Its planetary system, discovered by the Kepler Mission in 2010 was the first detected with the transit method found to contain multiple planets. Nomenclature and history Kepler-9 was named for the Kepler Mission, a project headed by NASA that was designed to search for Earth-like planets. In June 2010, some 43 days after Kepler came online, its operating scientists submitted a list of over 700 exoplanet candidates for review. Of those, five were originally suspected to have more than one planet. Kepler-9 was one of the multiplanetary systems; it was identified as such when scientists noticed significant variations in the time intervals at which Kepler-9 was transited. Kepler-9 holds the first multiplanetary system discovered using the transit method. It is also the first planetary system where transiting planets were confirmed through transit timing variations method, allowing to calculate the masses of planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puffy Planet
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to their stars and high surface-atmosphere temperatures resulted in their informal name "hot Jupiters". Hot Jupiters are the easiest extrasolar planets to detect via the radial-velocity method, because the oscillations they induce in their parent stars' motion are relatively large and rapid compared to those of other known types of planets. One of the best-known hot Jupiters is . Discovered in 1995, it was the first extrasolar planet found orbiting a Sun-like star. has an orbital period of about 4 days. General characteristics Though there is diversity among hot Jupiters, they do share some common properties. * Their defining characteristics are their large masses and short orbital periods, spanning 0.36–11.8 Jupiter masses and 1.3–111 Earth days. The mass c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Sphere
The Hill sphere of an astronomical body is the region in which it dominates the attraction of satellites. To be retained by a planet, a moon must have an orbit that lies within the planet's Hill sphere. That moon would, in turn, have a Hill sphere of its own. Any object within that distance would tend to become a satellite of the moon, rather than of the planet itself. One simple view of the extent of the Solar System is the Hill sphere of the Sun with respect to local stars and the galactic nucleus. In more precise terms, the Hill sphere approximates the gravitational sphere of influence of a smaller body in the face of perturbations from a more massive body. It was defined by the American astronomer George William Hill, based on the work of the French astronomer Édouard Roche. In the example to the right, the Earth's Hill sphere extends between the Lagrange points and , which lie along the line of centers of the two bodies. The region of influence of the smaller body is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit-timing Variation
Transit-timing variation is a method for detecting exoplanets by observing variations in the timing of a transit. This provides an extremely sensitive method capable of detecting additional planets in the system with masses potentially as small as that of Earth. In tightly packed planetary systems, the gravitational pull of the planets among themselves causes one planet to accelerate and another planet to decelerate along its orbit. The acceleration causes the orbital period of each planet to change. Detecting this effect by measuring the change is known as transit-timing variations. "Timing variation" asks whether the transit occurs with strict periodicity or if there's a variation. The first significant detection of a non-transiting planet using transit-timing variations was carried out with NASA's Kepler telescope. The transiting planet Kepler-19b shows transit-timing variation with an amplitude of 5 minutes and a period of about 300 days, indicating the presence of a second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |