|
Kennington Common
Kennington Common was a swathe of common land mainly within the London Borough of Lambeth. It was one of the earliest venues for cricket around London, with matches played between 1724 and 1785.G B Buckley, ''Fresh Light on 18th Century Cricket'', Cotterell, 1935H T Waghorn, ''The Dawn of Cricket'', Electric Press, 1906 The common was also used for public executions, fairs and public gatherings. Important orators spoke there, addressing crowds numbering tens of thousands. Early history In 1600, the common was bounded on the south west by Vauxhall Creek. The common extended over marshy land to the south west of the Roman road called Stane Street, now Kennington Park Road. There is a 1660 record of a common keeper being paid for grazing. In 1661, the Vauxhall Pleasure Gardens were laid out nearby (its location is noted as the Vauxhall End at The Oval). The large open space was often used for a variety of purposes by people living on the south bank of the River Thames. Cricket venu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
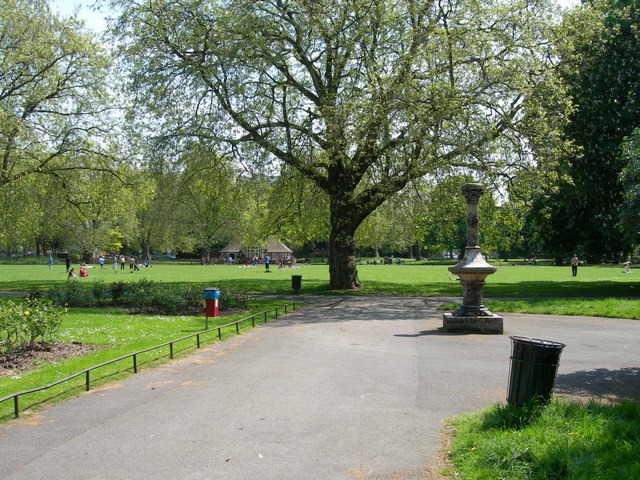
Kennington Park
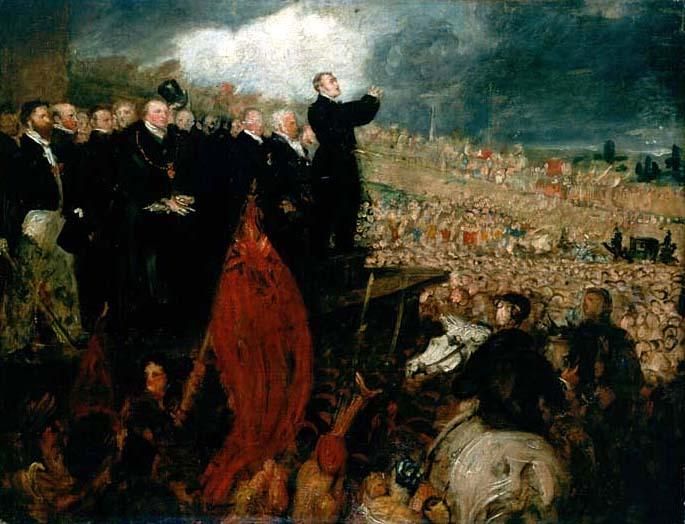
Kennington Park is a public park in Kennington, south London and lies between Kennington Park Road and St. Agnes Place. It was opened in 1854 on the site of what had been Kennington Common, where the Chartists gathered for their biggest "monster rally" on 10 April 1848. Soon after this demonstration the common was enclosed and, sponsored by the royal family, made into a public park. Kennington Common was a site of public executions until 1800 as well as being an area for public speaking. Some of the most illustrious orators to speak here were Methodist founders George Whitefield and John Wesley who is reputed to have attracted a crowd of 30,000. The common was one of the earliest London cricket venues and is known to have been used for top-class matches in 1724. G. B. Buckley, ''Fresh Light on 18th Century Cricket'', Cotterell, 1935. Kennington Park hosts the first inner London community cricket ground, sponsored by Surrey County Cricket Club whose home, The Oval, is close to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartford Cricket Club
Dartford Cricket Club is one of the oldest cricket clubs in England with origins which date from the early 18th century, perhaps earlier. The earliest known match involving a team from Dartford took place in 1722, against London, but the club's own website says it was formally established in 1727. Dartford Cricket Club. Retrieved 2017-11-28. The club is still in existence and now plays in the . History Dartford players were reckoned by |
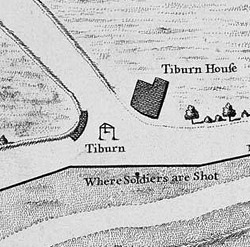
Tyburn
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street), the junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For this reason, for many centuries, the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment, it having been the principal place for execution of London criminals and convicted traitors, including many religious martyrs. It was also known as 'God's Tribunal', in the 18th century. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream',Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. but Tyburn Brook should not be confused wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oval Tube Station
Oval is a London Underground station in the London Borough of Lambeth. It is on the Northern line between Kennington and Stockwell stations and is in Travelcard Zone 2. It opened on 18 December 1890 as part of the City and South London Railway and is named after The Oval cricket ground, which it serves. Location The station is located at the junction of Kennington Park Road (heading north-east), Camberwell New Road (south-east), Clapham Road (south west) and Harleyford Street (north west) and is about 500 yards from The Oval cricket ground. Also close by are Kennington Park and the imposing St Mark's Church. History The City and South London Railway opened to passengers between Stockwell and King William Street on 18 December 1890, and was both the first standard gauge tube and the first railway to employ electric traction in London. To avoid disturbance of surface buildings the construction of the tube was shield-driven at deep level, and much of the work was done via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mark's Church, Kennington
St Mark's Church, Kennington, is an Anglican church on Kennington Park Road in Kennington, London, United Kingdom, near Oval tube station. The church is a Commissioners' church, receiving a grant from the Church Building Commission towards its cost. Authorised by the Church Building Act 1824 (5 Geo 4 Cap CIII), it was built on the site of the old gallows corner on Kennington Common. The architect was David R. Roper, possibly with A.B. Clayton, and was opened in 1824. The total cost of the church, including the land and other expenses, was £22,720. This was paid partly by the local parishioners and partly by Parliament through a grant known as "The Million Fund". Clergy The first incumbent was William Otter (1824-1832), subsequently Bishop of Chichester. His son, William Bruère Otter, subsequently Archdeacon of Lewes, was another early Stipendiary Curate. He was followed by the Rev Charlton Lane (1832-1865), whose son, also the Rev Charlton Lane, would go on to play cric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Plan
The National Land Company was founded as the Chartist Cooperative Land Company in 1845 by the chartist Feargus O'Connor to help working-class people satisfy the landholding requirement to gain a vote in county seats in Great Britain. It was wound up by Act of Parliament by 1851. Chartism The Reform Act of 1832 extended the franchise. In county constituencies in addition to forty shilling freeholders franchise rights were extended to owners of land in copyhold worth £10 and holders of long-term leases (more than sixty years) on land worth £10 and holders of medium-term leases (between twenty and sixty years) on land worth £50 and to tenants-at-will paying an annual rent of £50. The chartists had, as one of their objectives, the enfranchisement of the working man. O'Connor focussed his energies on enabling working-class people to satisfy the landholding requirement to gain a vote in county seats. In his single minded pursuit of this objective he diverged from the mainstrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feargus O'Connor
Feargus Edward O'Connor (18 July 1796 – 30 August 1855) was an Irish Chartist leader and advocate of the Land Plan, which sought to provide smallholdings for the labouring classes. A highly charismatic figure, O'Connor was admired for his energy and oratory, but was criticised for alleged egotism. His newspaper '' Northern Star'' (1837–1852) was widely read among workers (and read aloud in taverns), becoming the voice of the Chartist movement. After the failure of his Land Plan, O'Connor's behaviour became increasingly erratic, culminating in an assault on three MPs and a mental breakdown, from which he did not recover. After his death three years later at the age of 59, 40,000 people witnessed the funeral procession. Early life Feargus O'Connor was born on 18 July 1796 in Connorville house, near Castletown-Kinneigh in west County Cork, into a prominent Irish Protestant family. He was originally christened Edward Bowen O'Connor, but his father chose to call him Feargu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartism
Chartism was a working-class movement for political reform in the United Kingdom that erupted from 1838 to 1857 and was strongest in 1839, 1842 and 1848. It took its name from the People's Charter of 1838 and was a national protest movement, with particular strongholds of support in Northern England, the East Midlands, the Staffordshire Potteries, the Black Country, and the South Wales Valleys. The movement was fiercely opposed by government authorities who finally suppressed it. Support for the movement was at its highest when petitions signed by millions of working people were presented to the House of Commons. The strategy employed was to use the scale of support which these petitions and the accompanying mass meetings demonstrated to put pressure on politicians to concede manhood suffrage. Chartism thus relied on constitutional methods to secure its aims, though some became involved in insurrectionary activities, notably in South Wales and in Yorkshire. The People's Chart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Whitefield
George Whitefield (; 30 September 1770), also known as George Whitfield, was an Anglican cleric and evangelist who was one of the founders of Methodism and the evangelical movement. Born in Gloucester, he matriculated at Pembroke College at the University of Oxford in 1732. There he joined the "Holy Club" and was introduced to the Wesley brothers, John and Charles, with whom he would work closely in his later ministry. Whitefield was ordained after receiving his Bachelor of Arts degree. He immediately began preaching, but he did not settle as the minister of any parish. Rather he became an itinerant preacher and evangelist. In 1740, Whitefield traveled to North America, where he preached a series of revivals that became part of the " Great Awakening". His methods were controversial and he engaged in numerous debates and disputes with other clergymen. Whitefield received widespread recognition during his ministry; he preached at least 18,000 times to perhaps 10 million listeners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Methodist movement that continues to this day. Educated at Charterhouse School, Charterhouse and Christ Church, Oxford, Wesley was elected a fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford, in 1726 and ordination, ordained as an Anglican priest two years later. At Oxford, he led the "Holy Club", a society formed for the purpose of the study and the pursuit of a devout Christian life; it had been founded by his brother Charles Wesley, Charles and counted George Whitefield among its members. After an unsuccessful ministry of two years, serving at Christ Church (Savannah, Georgia), Christ Church, in the Georgia colony of Savannah, Georgia, Savannah, he returned to London and joined a religious so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chartist Meeting On Kennington Common By William Edward Kilburn 1848 - Restoration1 , a member of Portuguese political movement which arose in the 1820s (sometimes rendered as "Chartist" in English)
{{disambig ...
Chartist may refer to: * Chartist (occupation), a person who uses charts for technical analysis * ''Chartist'' (magazine), a British democratic socialist periodical *An adherent of Chartism, a 19th-century political and social reform movement in the UK *Cartista Cartista was a Portuguese form of Chartism which arose after the Portuguese Liberal Revolution of 1820. Members supported the Constitutional Charter of 1826 granted by Peter IV of Portugal, which was an attempt to reduce the conflicts created by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowls
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which the objective is to roll biased balls so that they stop close to a smaller ball called a "jack" or "kitty". It is played on a bowling green, which may be flat (for "flat-green bowls") or convex or uneven (for "crown green bowls"). It is normally played outdoors (although there are many indoor venues) and the outdoor surface is either natural grass, artificial turf or cotula (in New Zealand). History Bowls is a variant of the ''boules'' games (Italian ''Bocce''), which, in their general form, are of ancient or prehistoric origin. Ancient Greek variants are recorded that involved throwing light objects (such as flat stones, coins, or later also stone balls) as far as possible. The aspect of tossing the balls to approach a target as closely as possible is recorded in ancient Rome. This game was spread to Roman Gaul by soldiers or sailors. A Roman sepulchre in Florence shows people playing this game, stooping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |