|
Kenneth Boulding's Evolutionary Perspective
Kenneth E. Boulding's evolutionary perspective is an approach to economics (see also evolutionary economics) put forward most completely in his ''Ecodynamics'' (1978) and ''Evolutionary Economics'' (1981) had roots in his 1934 work on population theory and the age structure of capital as well as his ''Reconstruction'' (1950) with chapter titles like "An Ecological Introduction" and "The Theory of the Economic Organism." Perspectives One of the first major perspectives of Boulding's evolutionary perspective was his emphasis on know-how or, to use the term of Vladimir Vernadsky (1926) and Teilhard de Chardin (1959), which Boulding used as well, the "Noosphere." This is the counterpart in social and economic evolution to the role of genetic information and DNA in biological evolution. Just as DNA provides the genetic know-how to produce a chicken from an egg, automotive engineers and their recording devices contain the know-how to produce an automobile. One of the first major n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth E
Kenneth is an English given name and surname. The name is an Anglicised form of two entirely different Gaelic personal names: ''Cainnech'' and '' Cináed''. The modern Gaelic form of ''Cainnech'' is ''Coinneach''; the name was derived from a byname meaning "handsome", "comely". A short form of ''Kenneth'' is '' Ken''. Etymology The second part of the name ''Cinaed'' is derived either from the Celtic ''*aidhu'', meaning "fire", or else Brittonic ''jʉ:ð'' meaning "lord". People :''(see also Ken (name) and Kenny)'' Places In the United States: * Kenneth, Indiana * Kenneth, Minnesota * Kenneth City, Florida In Scotland: * Inch Kenneth, an island off the west coast of the Isle of Mull Other * "What's the Frequency, Kenneth?", a song by R.E.M. * Hurricane Kenneth * Cyclone Kenneth Intense Tropical Cyclone Kenneth was the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mozambique since modern records began. The cyclone also caused significant damage in the Comoro Islands an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Economics
Evolutionary economics is part of mainstream economics as well as a heterodox school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Much like mainstream economics, it stresses complex interdependencies, competition, growth, structural change, and resource constraints but differs in the approaches which are used to analyze these phenomena. Some scholars prefer to call their evolutionary theory by a different names. Samuel Bowles named it "evolutionary social science" and Joachim Rennstich called it "evolutionary systems theory". Evolutionary economics deals with the study of processes that transform economy for firms, institutions, industries, employment, production, trade and growth within, through the actions of diverse agents from experience and interactions, using evolutionary methodology. Evolutionary economics analyzes the unleashing of a process of technological and institutional innovation by generating and testing a diversity of ideas which discover and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky
Vladimir Ivanovich Vernadsky (russian: link=no, Влади́мир Ива́нович Верна́дский) or Volodymyr Ivanovych Vernadsky ( uk, Володи́мир Іва́нович Верна́дський; – 6 January 1945) was a Russian Empire, Russian, Ukrainian and Soviet mineralogist and geochemist who is considered one of the founders of geochemistry, biogeochemistry, and radiogeology. He was one of the founders and the first president of the Ukrainian Academy of Sciences (now National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine). Vladimir Vernadsky is most noted for his 1926 book ''The Biosphere'' in which he inadvertently worked to popularize Eduard Suess' 1885 term biosphere, by hypothesizing that life is the geological force that shapes the earth. In 1943 he was awarded the USSR State Prize, Stalin Prize. Vernadsky's portrait is depicted on the Ukrainian ₴1,000 hryvnia banknote. Early life Vernadsky was born in Saint Petersburg, Russian Empire, on in the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teilhard De Chardin
Pierre Teilhard de Chardin ( (); 1 May 1881 – 10 April 1955) was a French Jesuit priest, scientist, paleontologist Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ..., Theology, theologian, philosopher and teacher. He was Charles Darwin, Darwinian in outlook and the author of several influential theological and philosophical books. He took part in the discovery of Peking Man. He conceived the vitalism, vitalist idea of the Omega Point. With Vladimir Vernadsky he developed the concept of the noosphere. In 1962, the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith condemned several of Teilhard's works based on their alleged ambiguities and doctrinal errors. Some eminent Catholic figures, including Pope Benedict XVI and Pope Francis, have made positive comments on some of his ideas sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noosphere
The noosphere (alternate spelling noösphere) is a philosophical concept developed and popularized by the Russian-Ukrainian Soviet biogeochemist Vladimir Vernadsky, and the French philosopher and Jesuit priest Pierre Teilhard de Chardin. Vernadsky defined the noosphere as the new state of the biosphere and described as the planetary "sphere of reason". The noosphere represents the highest stage of biospheric development, its defining factor being the development of humankind's rational activities. The word is derived from the Greek νόος ("mind", "reason") and σφαῖρα ("sphere"), in lexical analogy to "atmosphere" and "biosphere". The concept, however, cannot be accredited to a single author. The founding authors Vernadsky and de Chardin developed two related but starkly different concepts, the former being grounded in the geological sciences, and the latter in theology. Both conceptions of the noosphere share the common thesis that together human reason and the scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgescu-Roegen
Nicholas Georgescu-Roegen (born Nicolae Georgescu, 4 February 1906 – 30 October 1994) was a Romanian mathematician, statistician and economist. He is best known today for his 1971 ''The Entropy Law and the Economic Process'', in which he argued that all natural resources are irreversibly degraded when put to use in economic activity. A progenitor and a paradigm founder in economics, Georgescu-Roegen's work was decisive for the establishing of ecological economics as an independent academic sub-discipline in economics. Several economists have hailed Georgescu-Roegen as a man who lived well ahead of his time, and some historians of economic thought have proclaimed the ingenuity of his work. In spite of such appreciation, Georgescu-Roegen was never awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics, although benefactors from his native Romania were lobbying for it on his behalf. After Georgescu-Roegen's death, his work was praised by a surviving friend of the highest rank: Prominent Keynes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
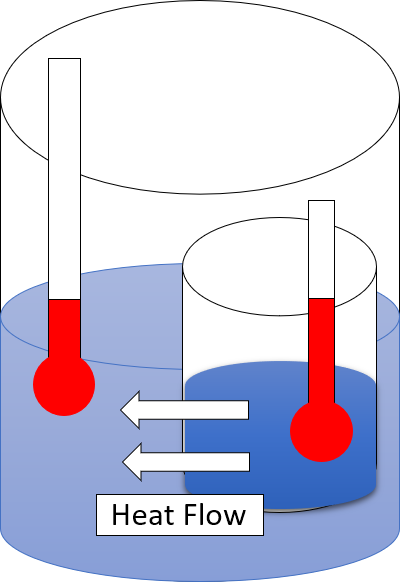
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm () is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field. Etymology ''Paradigm'' comes from Greek παράδειγμα (''paradeigma''), "pattern, example, sample" from the verb παραδείκνυμι (''paradeiknumi''), "exhibit, represent, expose" and that from παρά (''para''), "beside, beyond" and δείκνυμι (''deiknumi''), "to show, to point out". In classical (Greek-based) rhetoric, a paradeigma aims to provide an audience with an illustration of a similar occurrence. This illustration is not meant to take the audience to a conclusion, however it is used to help guide them get there. One way of how a ''paradeigma'' is meant to guide an audience would be exemplified by the role of a personal accountant. It is not the job of a personal accountant to tell a client exactly what (and what not) to spend money on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English cleric, scholar and influential economist in the fields of political economy and demography. In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Malthus observed that an increase in a nation's food production improved the well-being of the population, but the improvement was temporary because it led to population growth, which in turn restored the original per capita production level. In other words, humans had a propensity to utilize abundance for population growth rather than for maintaining a high standard of living, a view that has become known as the "Malthusian trap" or the "Malthusian spectre". Populations had a tendency to grow until the lower class suffered hardship, want and greater susceptibility to war famine and disease, a pessimistic view that is sometimes referred to as a Malthusian catastrophe. Malthus wrote in opposition to the popular view in 18th-century Europe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaigner Émile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress in Glasgow in 1901. A related term is '' ahimsa'' (to do no harm), which is a core philosophy in Indian Religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. While modern connotations are recent, having been explicated since the 19th century, ancient references abound. In modern times, interest was revived by Leo Tolstoy in his late works, particularly in '' The Kingdom of God Is Within You''. Mahatma Gandhi propounded the practice of steadfast nonviolent opposition which he called " satyagraha", instrumental in its role in the Indian Independence Movement. Its effectiveness served as inspiration to Martin Luther King Jr., James Lawson, Mary and Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. The main organization ceased operations on 20 April 1946 but many of its components were relocated into the new United Nations. The League's primary goals were stated in its Covenant. They included preventing wars through collective security and disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Its other concerns included labour conditions, just treatment of native inhabitants, human and drug trafficking, the arms trade, global health, prisoners of war, and protection of minorities in Europe. The Covenant of the League of Nations was signed on 28 June 1919 as Part I of the Treaty of Versailles, and it became effective together with the rest of the Treaty on 10 January 1920. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Wellcome_M0001113.jpg)