|
Kaupang
Kaupang was a Norse term for ''market-place'' composed of kaup- (buy) and angr (fjord, harbor), hence "buy fjord" or "buy harbor" (similar to the literal translation of Copenhagen). Today, it is generally used as a name of the first town-like market-place in Norway, the '' Kaupang in Skiringssal'', which is located in Tjølling near Larvik in Vestfold. Kaupang was an important merchant and craft center during the Viking period and as yet the first known Norwegian trading outpost. Kaupang is home to remains for the oldest Nordic town yet discovered. At Kaupang lie remains of one of Scandinavia’s earliest urban sites, established in year 800 A.D. Kaupang was abandoned in the mid-10th century. It has been described as Norway’s most important monument from the Viking Age. History Kaupang was founded in the 780s and abandoned for unknown reasons in the early 10th century. It was situated on a beach by Viksfjord in Larvik municipality. Documentary sources indicate that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjølling
Tjølling is a former municipality in Vestfold county, Norway. Tjølling was established as a municipality January 1, 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt). Together with Brunlanes, Stavern and Hedrum, it was merged into Larvik on January 1, 1988. Tjølling had 7,878 residents at one point, as well as an area of 70km². Tjøllingvollen is currently a village and a town that was the municipal center in the then Tjølling municipality. Geography and demography Tjølling includes the 69,5 km² area between Numedalslågen and Sandefjordsfjorden, south of E18. There's some agriculture and numerous quarries excavating of larvikite in Tjølling. The biggest quarry is Klåstad, which extracts a type of larvikite called Mørk Labrador (English: Dark Labrador). Tjølling has a long coastline with many fine beaches and coves. Tjølling is also known as a popular cottage area, as well as a popular holiday area. The most popular ports are Ula and Kjerringvik. Viksfjord is an idyllic side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestfold
Vestfold is a traditional region, a former county and a current electoral district in Eastern Norway. In 2020 the county became part of the much larger county of Vestfold og Telemark. Located on the western shore of the Oslofjord, it bordered the previous Buskerud and Telemark counties. The county administration was located in Tønsberg, Norway's oldest city, and the largest city is Sandefjord. With the exception of the city-county of Oslo, Vestfold was the smallest county in Norway by area. Vestfold was the only county in which all municipalities had declared Bokmål to be their sole official written form of the Norwegian language. Vestfold is located west of the Oslofjord, as the name indicates. It includes many smaller, but well-known towns in Norway, such as Larvik, Sandefjord, Tønsberg and Horten; these towns run from Oslo in an almost constant belt of urban areas along the coast, ending in Grenland in neighbouring region Telemark. The river Numedalslågen runs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolay Nicolaysen
Nicolay Nicolaysen (14 January 1817 - 22 January 1911) was a Norwegian archaeologist and Norway's first state employed antiquarian. He is perhaps best known for his excavations of the ship burial at Gokstad in 1880. Nicolay Nicolaysen ''Norsk biografisk leksikon'' Biography Nicolay Nicolaysen was born in Bergen to merchant and bank administrator Lyder Wentzel Nicolaysen (1794–1876) and Sophia Susanna Siewers (1797–1826). He was the half-brother of professor of medicine (1831–1909). Nicolaysen graduated from the University of Christiania now (University of O ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Blindheim
Charlotte Blindheim (née Undset, 6 July 1917 – 5 March 2005) was a Norwegian archaeologist. She was the first female member of the scientific staff at the University of Oslo to be permanently employed when she hired as the museum curator in 1946. Biography She was born in Kristiania (now Oslo), Norway. She was the daughter of Sigge Pantzerhielm Thomas (1886-1944) and Signe Dorothea Undset (1887-1973). Her father was a classical philologist and lecturer at the University of Oslo. She completed a master's degree in archaeology in 1946 at the University of Oslo, writing her thesis on Viking costume and jewellery. She was subsequently hired as a curator at the University as the museum's first permanently employed female member of scientific staff. As an archaeologist, Blindheim became particularly known for her work with the excavations at Kaupang in Skiringssal in the former municipality of Tjølling (now Larvik in Vestfold). Excavations were started systematically in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köping
''Köping'' was a Swedish denomination for a market town since the Middle Ages, derived from the Old Norse word '' kaupang''. The designation was officially abolished with the municipal reform of 1971, when Sweden was subdivided into the Municipalities of Sweden (currently amounting to 290). As present-day Finland was once a part of Sweden, the Finnish word ''kauppala'' has the same meaning. In modern Finnish, the word ''kaupunki'', borrowed from the Old Norse word ''kaupang'', is the main word for town and city. Swedish ''köping'' and the English toponym ''chipping'' are also cognates as is the Norwegian word '' kjøpstad'' and the Danish toponymical suffix '' -købing''. Sweden History In 1863 the first local government acts were implemented in Sweden. There were two acts, one for cities and one for rural areas. Of the around 2,500 municipalities, 89 had city rights and thus had the right to call themselves ''stad'' (city). Under the "rural" act there were also e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
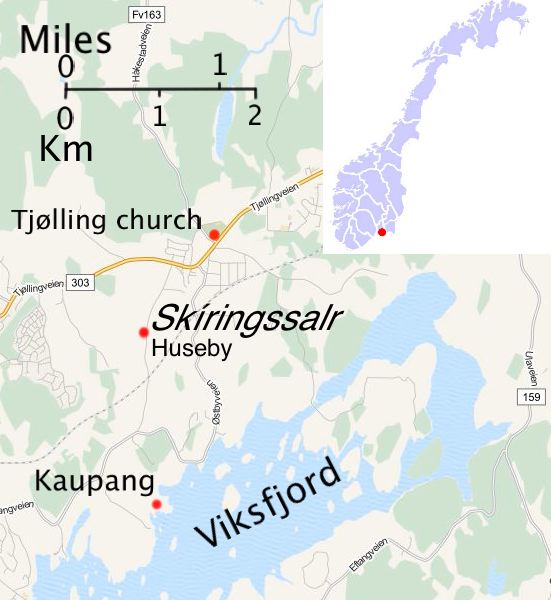
Skiringssal Map
Skiringssal (Old Norse ''Skíringssalr'') was the name of a Viking Age hall which stood at a site now known as Huseby, about 0.73 miles (1.2 km) south-west of Tjølling, a settlement a little over east of Larvik, in the south of the Norwegian county of Vestfold. By extension the name also referred to the local ''bygd'', or settlement area, and in the 15th century it was probably used synonymously for the ecclesiastical parish of Tjølling. Skiringssal is mentioned in several early medieval sources, including the ''Ynglinga saga'', the ''Fagrskinna'' and the ''Sögubrot af nokkrum fornkonungum''. The name last occurs in 1445, in the form "Skirisall", in a hospital register from Tønsberg. This and other documents from earlier in the 15th century associate Skiringssal with locations in the parish of Tjølling. Archaeological excavations at Huseby have shown that a large hall was built there in the mid-8th century and went out of use by about 900. Excavations at Kaupa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skiringssal
Skiringssal (Old Norse ''Skíringssalr'') was the name of a Viking Age hall which stood at a site now known as Huseby, about 0.73 miles (1.2 km) south-west of Tjølling, a settlement a little over east of Larvik, in the south of the Norwegian county of Vestfold. By extension the name also referred to the local ''bygd'', or settlement area, and in the 15th century it was probably used synonymously for the ecclesiastical parish of Tjølling. Skiringssal is mentioned in several early medieval sources, including the ''Ynglinga saga'', the ''Fagrskinna'' and the ''Sögubrot af nokkrum fornkonungum''. The name last occurs in 1445, in the form "Skirisall", in a hospital register from Tønsberg. This and other documents from earlier in the 15th century associate Skiringssal with locations in the parish of Tjølling. Archaeological excavations at Huseby have shown that a large hall was built there in the mid-8th century and went out of use by about 900. Excavations at Kaupa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohthere Of Hålogaland
Ohthere of Hålogaland ( no, Ottar fra Hålogaland) was a Viking Age Norwegian seafarer known only from an account of his travels that he gave to King Alfred (r. 871–99) of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex in about 890 AD. His account was incorporated into an Old English adaptation of a Latin historical book written early in the fifth century by Paulus Orosius, called ''Historiarum Adversum Paganos Libri VII'', or ''Seven Books of History Against the Pagans''. The Old English version of this book is believed to have been written in Wessex in King Alfred's lifetime or soon after his death, and the earliest surviving copy is attributed to the same place and time. In his account, Ohthere said that his home was in "Halgoland", or Hålogaland, where he lived "north-most of all Norwegians … inceno-one ivedto the north of him". Ohthere spoke of his travels north to the White Sea, and south to Denmark, describing both journeys in some detail. He also spoke of '' Sweoland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorestad
Dorestad (''Dorestat, Duristat'') was an early medieval emporium, located in the southeast of the province of Utrecht in the Netherlands, close to the modern-day town of Wijk bij Duurstede. It flourished during the 8th to early 9th centuries, as an important port on the northeastern shipping routes due to its proximity to the fork in the Rhine, with access to Germany via the Nederrijn (the northernmost branch of the Rhine), to the southern Netherlands, northern France, and England (via the Lek), and to the northern Netherlands, northern Germany, and Scandinavia (via the Kromme Rijn). History The township was established at the base of the former Roman fortress of ''Levefanum'' in the 7th century. The Frankish Carolingian Empire and the Frisians fought for control of the territory, until the Franks gained control of the Frisian Coast in 719. Dorestad flourished between the 7th century and the mid-9th century. The settlement was well known for minting coins under the control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top universities in the world and as one of the leading universities of Northern Europe; the Academic Ranking of World Universities ranked it the 58th best university in the world and the third best in the Nordic countries. In 2016, the Times Higher Education World University Rankings listed the university at 63rd, making it the highest ranked Norwegian university. Originally named the Royal Frederick University, the university was established in 1811 as the de facto Norwegian continuation of Denmark-Norway's common university, the University of Copenhagen, with which it shares many traditions. It was named for King Frederick VI of Denmark and Norway, and received its current name in 1939. The university was commonly nicknamed "The Royal Freder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Købstad
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural towns with a hinterland of villages are still commonly called market towns, as sometimes reflected in their names (e.g. Downham Market, Market Rasen, or Market Drayton). Modern markets are often in special halls, but this is a recent development, and the rise of permanent retail establishments has reduced the need for periodic markets. Historically the markets were open-air, held in what is usually called (regardless of its actual shape) the market square (or "Market Place" etc), and centred on a market cross ( mercat cross in Scotland). They were and are typically open one or two days a week. History The primary purpose of a market town is the provision of goods and services to the surrounding locality. Although market towns were kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kjøpstad
A (historically: ''kjøbstad'', ''kjöbstad'', or ''kaupstad'') is an old Scandinavian term for a "market town" that was used in the Kingdom of Denmark-Norway for several hundred years. The name comes from the on, kaupstaðr. Kjøpstads were places of trade and exporting materials (e.g. timber, flour, iron and other common goods). Towns were given the "dignity" or rank of being referred to as a ''kjøpstad'' when they reached a certain population and had established means of industry and other notable items such as dock yards, steam mills, iron works, churches, grammar schools. The citizens of a kjøpstad were able to buy and sell goods and conduct other economic activities. Ladested Norway also had a subordinate category to the market town, which was the "small seaport" ( no, ladested) or . These were a port or harbour with a monopoly to import and export goods and materials in both the port and a surrounding outlying district. These places were usually subordinate to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |