|
Kasula Purushottama Kavi
Kasula Purushottama Kavi was a Telugu language, Telugu poet who lived during the late 18th century (). His parents were Kasula Appalaraju and Ramanamma. He hailed from the Diviseema area of Krishna District, Andhra Pradesh. He was a court poet of the then-Yarlagadda Sivarama Prasad, Raja of Challapalli, Yarlagadda Ankineedu Prasad I (r. 1792–1819) of the Challapalli, Challapalli ''Samasthanam'' and possibly of his father as well. Purushottama Kavi is recognized for composing literary works in Telugu consisting of one hundred poetic stanzas, known as Satakam, satakams. Works Kasula Purushottama Kavi is known for composing the ''Andhra Nayaka Satakam'' on Srikakula Andhra Mahavishnu, apparently when the temple was occupied by raiding Muslim soldiers. The prominent Andhra Maha Vishnu Temple, to whose presiding deity Purushottama Kavi dedicated his ''satakam'' to, is where Vijayanagara Emperor Krishnadevaraya had a dream compelling him to write the Telugu text ''Amuktamalyada''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu Language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken by Telugu people predominantly living in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. It is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language family and one of the twenty-two scheduled languages of the Republic of India. It is one of the few languages that has primary official status in more than one Indian state, alongside Hindi and Bengali. Telugu is one of six languages designated as a classical language (of India) by the Government of India. Telugu is also a linguistic minority in the states of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, West Bengal, and the union territories of Puducherry and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by members of the Telugu diaspora spread across countries like United States, Australia, United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand in the Anglosphere; Myanmar, Malaysia, South Africa, Mauritius; and the Arabian Gulf count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diviseema
Diviseema is a small and deltaic island in Krishna District of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It comprises three Mandals - Avanigadda, Koduru and Nagayalanka. Etymology The word Diviseema translates as the ''abode of the divine''. Diviseema is obtained from the two words Deevi meaning 'island' and seema meaning 'country' or 'region' in telugu... Diviseema (pronounced as Deeviseema) means 'Region of the Island'... Geography Diviseema is located in the delta area formed at Puligadda (Avanigadda), where the Krishna River is divided into two before merging into the Bay of Bengal. One merges in Bay of Bengal at Hamsaladeevi ( Koduru mandal) and the other near to Gullalamoda (Nagayalanka mandal Nagayalanka mandal is one of the 25 mandals in Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is under the administration of Machilipatnam revenue division and has its headquarters at Nagayalanka. The mandal is bounded by Avanigad ...). It is a fertile low lying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
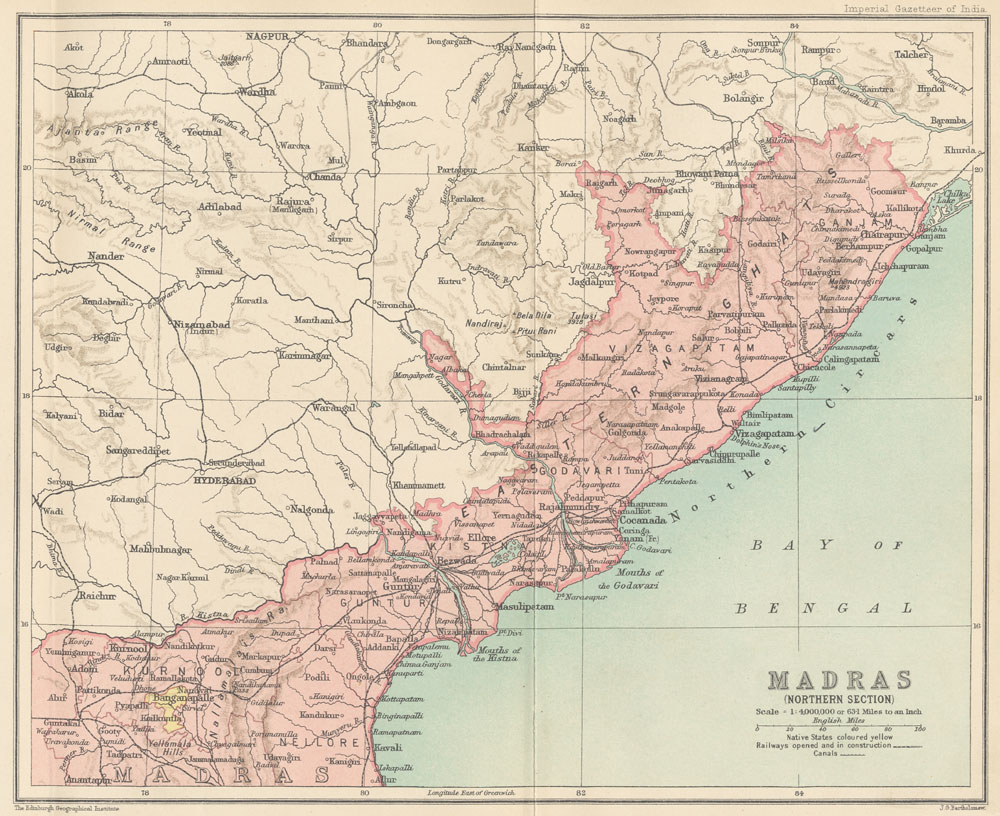
Krishna District
Krishna district is district in the coastal Andhra Region in Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, with Machilipatnam as its administrative headquarters. It is the coastal district of Andhra Pradesh. Machilipatnam is the most populated city in the district. It is surrounded on the east by Bay of Bengal, west by Guntur and north by Eluru and NTR districts and south again by Bay of Bengal. In 2022 Krishna district was divided into Krishna and NTR districts. Etymology Krishna district, with its district headquarters at Machilipatnam was formerly called Machilipatnam district. Later it was renamed as Krishna district, by adding certain Taluks of the abolished Guntur District in 1859 with Machilipatnam with its head. It was named after the Krishna River, the third longest river in India. The river flows through the state of Andhra Pradesh before it empties itself into Bay of Bengal, near Hamsaladevi village of Krishna district. History This history of this region dates back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the north-west, Chhattisgarh to the north, Odisha to the north-east, Tamil Nadu to the south, Karnataka to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. It has the second longest coastline in India after Gujarat, of about . Andhra State was the first state to be formed on a linguistic basis in India on 1 October 1953. On 1 November 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu-speaking areas (ten districts) of the Hyderabad State to form United Andhra Pradesh. ln 2014 these merged areas of Hyderabad State are bifurcated from United Andhra Pradesh to form new state Telangana . Present form of Andhra similar to Andhra state.but some mandalas like Bhadrachalam still with Telangana. Visakhapatnam, Guntur, Kurnool is People Capital of And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarlagadda Sivarama Prasad
Yarlagadda Sivarama Prasad (3 April 1903 - 1976), also known as Challapalli Raja, was an Indian aristocrat, industrialist, politician, film producer, and film studio owner. He was the last hereditary zamindar of the Challapalli Samasthanam (estate)''.'' In politics, Sivarama Prasad was affiliated with the Indian National Congress. He served as the Minister of Health for Andhra Pradesh during the 1960s and was elected as an MLA from Krishna District. He established the Andhra Scientific Company. It manufactured precise scientific instruments and was later acquired by Bharat Electronics in 1982. He also financed new sugar mills and factories in Vuyyuru and in Rayagada, Orissa. Sivarama Prasad financed Pattabhi Sitaramayya's Andhra Bank. He set up the production company Sarathi Studios#Sarathi Films, Sarathi Films in 1938, which produced successful films like ''Mayalokam'' (1945) and ''Rojulu Marayi'' (1955). He also established the film studio complex Sarathi Studios in Hyderabad i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Challapalli
Challapalli (officially known as Challapalle) is a village in the Krishna district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in the Challapalli mandal, Machilipatnam revenue division. Geography Challapalli is located at . It has an average elevation of . It is located from the district headquarters, Machilipatnam, and lies on the border of the Krishna District and the Guntur District near Repalle, in the South Guntur District. Demographics According to the 2011 Census of India, Challapalli had a population of 17,069 inhabitants: 8,183 males and 8,884 females. It has an average gender ratio of 1,086 females per 1,000 males, which is higher than the national average of 940 per 1,000. The average literacy rate stands at 83.28%, significantly higher than the national average of 73.00%. History In the early 18th century, the Raja of Challapalli, Yaralagadda Ankineedu Prasad built Challapalli. The village of Challapalli developed around the palace and became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satakam
Sathakam is a Telugu literary piece of art. The name derives from ''Sata'', which means a ''hundred'' in Sanskrit. Sathakam usually comprises a hundred poems (give or take). Hence, a Sathakam is a volume (book) of hundred poems.It is one of the most important forms of poetry in Telugu Literature. Since the creation of Satakams have been around for centuries, they were passed down by transcribers of the bygone eras. Sometime some of the poems are lost to time. At other times the transcribers insert new ones mistakenly or deliberately. However, by doing a comparative study of the same literary work from multiple branches scholars establish which parts are authentic and original. Purpose of Sathakam Satakams are usually devotional, philosophical or convey morals. Some sathakams such as the Sumathi Satakam are popular because of their simplicity and their usefulness in conveying morals which can be taught to school aged children. Structure and Composition Satakams are written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Nayaka Satakam
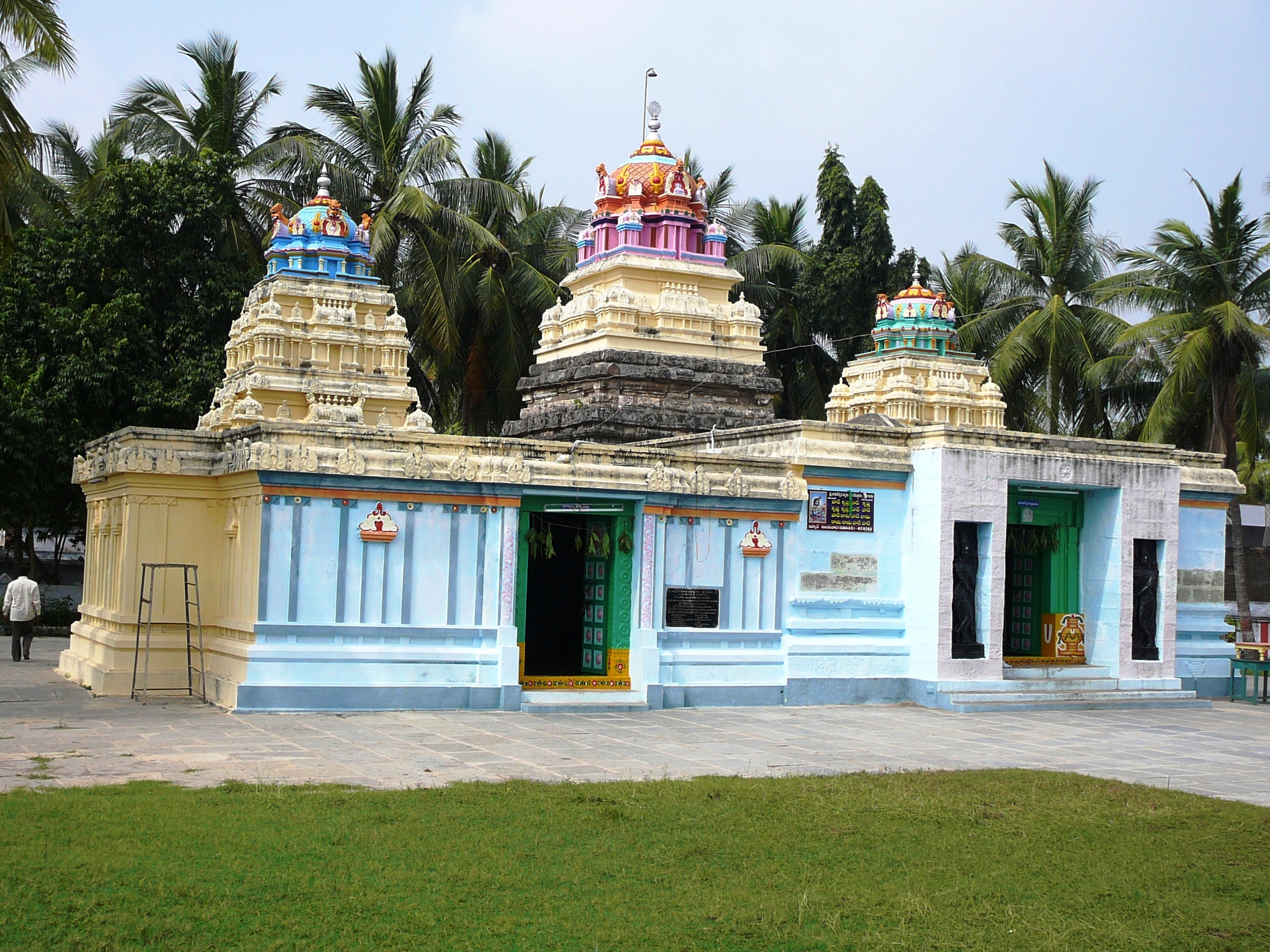
Andhra Vishnu, better known as Srikakula Mahavishnu statue, was set up in Andhra in a pre-existing older temple. The previous deistic form worshiped in the temple is unknown. Āndhra Vishnu temple The deity of the temple is known as ''Andhra Maha Vishnu ''or ''Srikakulandhra Maha Vishnu''. The main sanctum of the temple survived at least since the time of the Satavahana emperors. The deity for whom the Satavahanas built the temple is unknown. The temple was also repaired and worshipped restored by the Rajas of Challapalli after a period of decline due to Muslim raids. This temple has many attractions and historical links. As many as 32 inscriptions, including those issued by Krishnadevaraya, appear on the walls of the temple. The presiding deity has some striking peculiarities. The deity holds a sankha in right hand and a chakra in left hand as against usual practice of vice versa.The inscriptions on Avatars were added after 1010 reconstruction. The oldest version had no re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishnadevaraya
Krishnadevaraya (17 January 1471 – 17 October 1529) was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Empire, reigning from 1509 to 1529. He was the third monarch of the Tuluva dynasty, and is considered to be one of the greatest rulers in Indian history. He ruled the largest empire in India after the decline of the Delhi Sultanate.Keay, John, India: A History, New York: Harper Collins, 2000, p.302 Presiding over the empire at its zenith, he is regarded as an icon by many Indians. Krishnadevaraya earned the titles ''Karnatakaratna Simhasanadeeshwara'' (lit. "Lord of the Jewelled Throne of Karnataka"), ''Yavana Rajya Pratistapanacharya'' (lit. "Establishment of the King to Bahmani Throne"), ''Kannada Rajya Rama Ramana'' (lit. "Lord of the Kannada Empire), ''Andhra Bhoja'' (lit. "Scholar of Andhra"), ''Gaubrahmana Pratipalaka'' (lit. "Protector of Brahmins and Cows") and ''Mooru Rayara Ganda'' (lit. "Lord of Three Kings"). He became the dominant ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amuktamalyada
Āmuktamālyada ( te, ఆముక్తమాల్యద) is a Telugu epic poem composed by Krishnadevaraya, the Vijayanagara Emperor in the early 16th century. Amuktamalyada translates to "One who offered the garland after wearing it himself". Considered as a masterpiece, Amuktamalyada describes the story of wedding of the Hindu Lord Ranganayaka, an avatar, of Vishnu and Goda Devi aka Andal the Tamil Alvar poet and daughter of Periyalvar, at Srirangam. Krishnadevaraya Krishnadevaraya was the king of the Vijayanagara Empire reigning between 1509–1530. He was the third ruler of the Tuluva Dynasty, and presided over the Vijayanagara empire at its zenith. Krishna Deva Raya earned the titles of ''Kannada Rajya Rama Ramana'' (''lit'', "Lord of the Kannada empire"), ''Andhra Bhoja'' and ''Mooru Rayara Ganda'' (''lit'', "King of three Kings"). He became the dominant ruler of the peninsula of India by defeating the Sultans of Bijapur, Golconda, the Bahmani Sultanate and the Gajapa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Circars
The Northern Circars (also spelt Sarkars) was a division of British India's Madras Presidency. It consisted of a narrow slip of territory lying along the western side of the Bay of Bengal from 15° 40′ to 20° 17′ north latitude, in the present-day Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. The Subah of Deccan (Hyderabab/Golconda) consisted of 22 circars. These northern circars were five in number and the most prominent ones in the Subah. They became British in a protracted piecemeal process lasting from 1758 to 1823, involving diplomacy and financial settlements rather than military conquest. The annexation by the British of the Northern Circars deprived Hyderabad State, the Nizam's dominion, of the considerable coastline it formerly had, assuming the shape it is now remembered for: that of a landlocked princely state with territories in Central Deccan, bounded on all sides by British India. Etymology ''Circar'' was an English spelling of ''sarkar'', a Mughal term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |