|
Kashmiri Language
Kashmiri () or Koshur (, /kəːʃur/) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by around 7 million Kashmiris of the Kashmir region, primarily in the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. In 2020, the Parliament of India passed a bill to make Kashmiri an official language of Jammu and Kashmir along with Dogri, Hindi, Urdu and English. Kashmiri is also among the 22 scheduled languages of India. Kashmiri has split ergativity and the unusual verb-second word order. Geographic distribution and status There are about 6.8 million speakers of Kashmiri and related dialects in Jammu and Kashmir and amongst the Kashmiri diaspora in other states of India. The precise figures from the 2011 census are 6,554,36 for Kashmiri as a "mother tongue" and 6,797,587 for Kashmiri as a "language" (which includes closely related smaller dialects/languages). Most Kashmiri speakers are located in the Kashmir Valley and other areas of Jammu and Kashmir. In the Kashmir valley, they form a majority. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perso-Arabic Script
The Persian alphabet ( fa, الفبای فارسی, Alefbâye Fârsi) is a writing system that is a version of the Arabic script used for the Persian language spoken in Iran ( Western Persian) and Afghanistan (Dari Persian) since the 7th century after the Muslim conquest of Persia. The Persian dialect spoken in Tajikistan (Tajiki Persian) is written in the Tajik alphabet, a modified version of the Cyrillic alphabet which has been in use since the Soviet era. The Persian alphabet is directly derived and developed from the Arabic alphabet. After the Muslim conquest of Persia and the fall of the Sasanian Empire in the 7th century, Arabic became the language of government and especially religion in Persia for two centuries. The replacement of the Pahlavi scripts with the Persian alphabet to write the Persian language was done by the Saffarid dynasty and Samanid dynasty in 9th-century Greater Khorasan. The script is mostly but not exclusively right-to-left; mathematical expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir Region
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompasses a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hattian Bala District
The Hattian Bala District ( ur, ) is one of the ten districts of Azad Kashmir, Pakistan. The district's headquarters is the town of Hattian Bala. Prior to 2009, the Hattian Bala District was a tehsil within Muzaffarabad District. History Before the establishment of Azad Kashmir in 1947, what is now the Hattian Bala District was the part of the Uri Tehsil of the Baramulla District in Jammu and Kashmir. Following the ceasefire of the first war between India and Pakistan, Hattian Bala became part of the Muzaffarabad District and remained so until 2009. During Pakistan's coalition government of Sardar Muhammad Yaqoob Khan, Hattian Bala was made a district in July 2009. Geography The Hattian Bala District is bounded on the north and east by the Kupwara District and the Baramulla District of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir, on the south by the Bagh District, and on the west by the Muzaffarabad District. The Hattian Bala District has a population of 230,529. Economy The ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neelum District
The district of Neelum (spelt also ''Neelam''; ur, ) is the northernmost of 10 districts located within the Pakistani-administered territory of Azad Kashmir. Taking up the larger part of the Neelam Valley, the district has a population of around people (as of 2017). It was among the worst-hit areas of Pakistan during the 2005 Kashmir earthquake. Location The district is bordered on the north and north-east by the Diamer District, the Astore District, and the Skardu District of Gilgit-Baltistan, on the south by the Kupwara District and the Bandipora District of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir, on the south-west by the Muzaffarabad District, and by the west by the Mansehra District of Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province. The Neelum Valley was known before the partition as ''Kishanganga'' and was subsequently renamed for the village of Neelam. It flows from the Gurez Valley in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir and roughly follows first a western and then a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muzaffarabad District
The Muzaffarabad District ( ur, ) is one of the 10 districts of Pakistan's dependent territory of Azad Kashmir. The district is located on the banks of the Jhelum River, Jhelum and Neelum River, Neelum rivers and is very hilly. The total area of the Muzaffarabad District is . The district is part of the Muzaffarabad Division, and the city of Muzaffarabad serves as the capital of Azad Kashmir. The district is bounded on the north-east by the Neelum District and the Kupwara District of Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir, on the south-east by the Hattian Bala District, on the south by the Bagh District, and on the west by the Mansehra District and the Abbottabad District of Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province. Population and languages The total population of the district according to the 2017 census is 650,370. The main language of the district, spoken by about half of its inhabitants, is generally considered to be a variety of Pahari (Pothwari), Pahari. Though occasionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1998 Pakistan Census
The 1998 Census of Pakistan was the fifth Pakistani national census. It provided a detailed enumeration of the population of Pakistan at the time it was conducted under the authority of the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, an agency of the Government of Pakistan. According to the 1998 census, the population of Pakistan proper (excluding disputed territories) stood at 130,857,717 people. With the inclusion of the population of Azad Jammu & Kashmir and Gilgit−Baltistan, the population stood at 134,714,017 people. Despite being mandated by the Constitution of Pakistan to be held every 10 years, this was the first census to take place in Pakistan after the 1981 census that took place 17 years earlier, and the next census would not be held for another 19 years, until 2017. The inconsistencies in Pakistan's national elections are due in part to political turmoil and instability within the country. City Results This is the list of population of cities of Pakistan in 1998 census ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir Valley
The Kashmir Valley, also known as the ''Vale of Kashmir'', is an intermontane valley concentrated in the Kashmir Division of the Indian- union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. The valley is bounded on the southwest by the Pir Panjal Range and on the northeast by the main Himalayas range. It is approximately long and wide, and drained by the Jhelum River. Geography The Kashmir Valley lies between latitude 33° and 35°N, and longitude 73° and 76°E. The valley is wide and covers in area. It is bounded by sub-ranges of the Western Himalayas: the Great Himalayas bound it in the northeast and separate it from the Tibetan plateau, whereas the Pir Panjal Range in the Lesser Himalayas bounds it on the west and the south, and separates it from the Punjab Plain. The valley has an average elevation of above sea-level, but the surrounding Pir Panjal range has an average elevation of . The Jhelum River is the main river of the Valley. It originates at Verinag; its most importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmiri Diaspora
The Kashmiri diaspora refers to Kashmiris who have migrated out of the Kashmir into other areas and countries, and their descendants. India Punjab Estimated, 1,000-1,200 Kashmiri Hindus live in Pathankot, Gurdaspur and Cities of Doaba region and of Punjab. Gujarat 10,000 Kashmiri Hindus live in Gujarat. They settled here after 1990 exodus. Himachal Pradesh The state of Himachal Pradesh in India has the second-largest Kashmiri language speakers after Kashmir Valley and adjoining areas. Kashmiri Pandits migrated to this region over centuries and a including from 1947–48 to 1989–91. Large number of Kashmiri Pandits also came here after the eruption of militancy in the valley . Pakistan Punjab Heavy taxes under the Sikh rule, coupled with famine and starvation, caused many Kashmiri villagers to migrate to the plains of Punjab. These claims, made in Kashmiri histories, were corroborated by European travelers. When one such European traveler, Moorcroft, left the Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
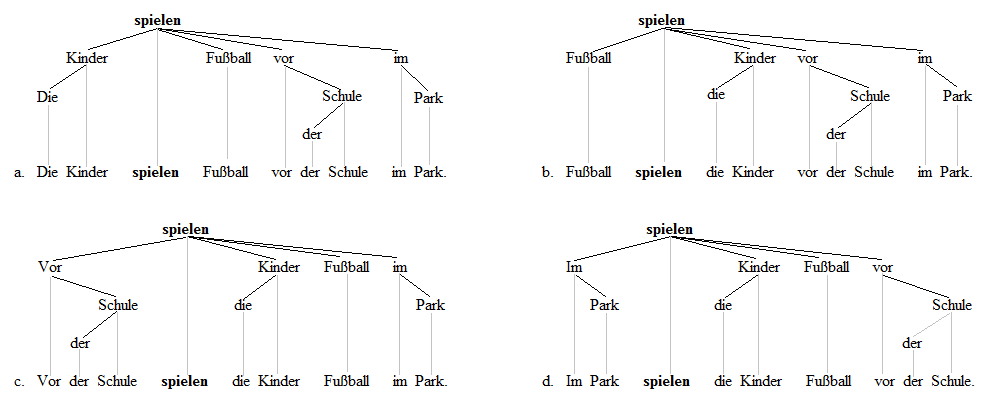
V2 Word Order
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words (a single constituent). Examples of V2 in English include (brackets indicating a single constituent): * "Neither do I", " ever in my lifehave I seen such things" If English used V2 in all situations, the following would be correct: * " * n schoollearned I about animals", " * hen she comes home from worktakes she a nap" V2 word order is common in the Germanic languages and is also found in Northeast Caucasian Ingush, Uto-Aztecan O'odham, and fragmentarily in Romance Sursilvan (a Rhaeto-Romansh variety) and Finno-Ugric Estonian. Of the Germanic family, English is exceptional in having predominantly SVO order instead of V2, although there are vestiges of the V2 phenomenon. Most Germanic languages do not normally use V2 order in embedded clauses, with a few ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split Ergativity
In linguistic typology, split ergativity is a feature of certain languages where some constructions use ergative syntax and morphology, but other constructions show another pattern, usually nominative–accusative. The conditions in which ergative constructions are used varies among different languages. Nominative–accusative vs. ergative–absolutive Nominative–accusative languages (including European languages, with the notable exception of Basque) treat both the actor in a clause with a transitive verb and the experiencer in a clause with an intransitive verb in the same way grammatically. If the language uses case markers, they take the same case. If it uses word order, it is parallel. For example, consider these two English sentences: * Jane was chasing John. * Jane was sweating. The grammatical role of "Jane" is identical. In both cases, "Jane" is the subject. In ergative–absolutive languages (such as Basque and Georgian, or the Eskimo–Aleut and Mayan langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages With Official Status In India
There is no national language in India. However, article 343(1) of the Indian constitution specifically mentions that, "The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script. The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals," while the clause 3 of Official Languages Act, 1963 mentions the, "Continuation of English Language for official purposes of the Union and for use in Parliament", thus denoting Hindi and English as the official languages of the Union. Business in the Indian parliament can only be conducted in Hindi or in English. English is allowed to be used in official purposes such as parliamentary proceedings, judiciary, communications between the Central Government and a State Government. There are various official languages in India at the state/territory level. States within India have the liberty and powers to specify their own official language(s) through legislation. In additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |